|
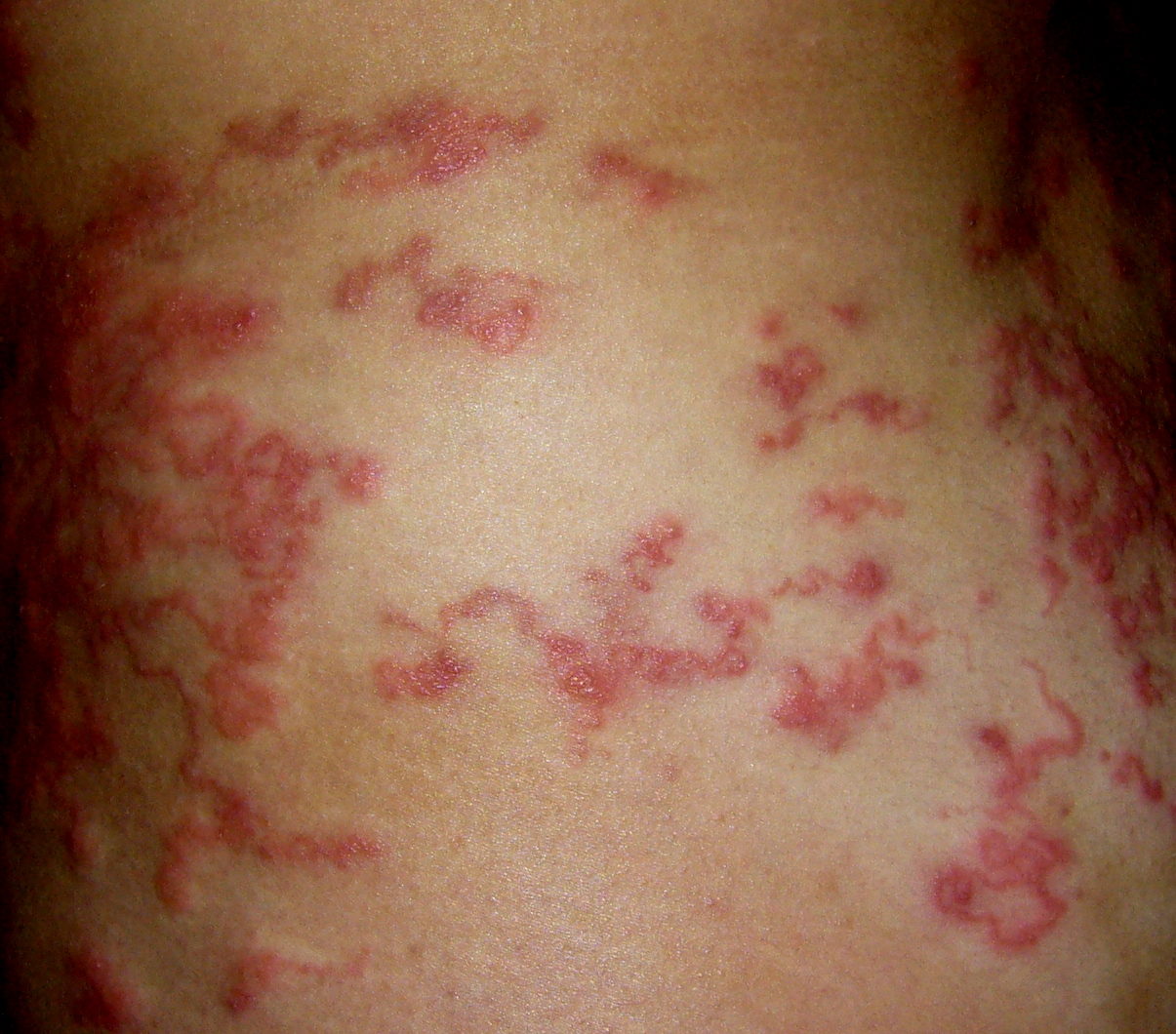
Serpiginous
Serpiginous, first known to be used in the 15th century, is a term from Latin serpere to creep, usually referring to a creeping, snakelike or slowly progressive skin disease. It is used to describe the rash in cutaneous larvae migrans, erythema annulare centrifugum, purpura annularis telangiectoides, ringworm. and sometimes occurs in bullous pemphigoid. It is also used to describe serpiginous choroiditis, a rare eye condition in which irregularly shaped (serpiginous) lesions are seen in two layers of the eye surface (the choriocapillaris The capillary lamina of choroid or choriocapillaris is a layer of capillaries that is immediately adjacent to Bruch's membrane in the choroid. The choriocapillaris was first described in man by Hovius in 1702, although it was not so named until 1 ... and the retinal pigment epithelium). References Dermatologic terminology {{Dermatology-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Larva Migrans Cutanea
A larva (; plural larvae ) is a distinct juvenile form many animals undergo before metamorphosis into adults. Animals with indirect development such as insects, amphibians, or cnidarians typically have a larval phase of their life cycle. The larva's appearance is generally very different from the adult form (''e.g.'' caterpillars and butterflies) including different unique structures and organs that do not occur in the adult form. Their diet may also be considerably different. Larvae are frequently adapted to different environments than adults. For example, some larvae such as tadpoles live almost exclusively in aquatic environments, but can live outside water as adult frogs. By living in a distinct environment, larvae may be given shelter from predators and reduce competition for resources with the adult population. Animals in the larval stage will consume food to fuel their transition into the adult form. In some organisms like polychaetes and barnacles, adults are immo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cutaneous Larvae Migrans
Cutaneous larva migrans (abbreviated CLM) is a skin disease in humans, caused by the larvae of various nematode parasites of the hookworm family ( Ancylostomatidae). These parasites live in the intestines of dogs, cats, and wild animals and should not be confused with other members of the hookworm family for which humans are definitive hosts, namely '' Ancylostoma duodenale'' and ''Necator americanus''. Colloquially called creeping eruption due to its presentation, the disease is also somewhat ambiguously known as " ground itch" or (in some parts of the southern United States) "sandworms", as the larvae like to live in sandy soil. Another vernacular name is plumber's itch. The medical term CLM literally means "wandering larvae in the skin". Symptoms and signs The infection causes a red, intensely pruritic (itchy) eruption, and may look like twirling lesions. The itching can become very painful and if scratched may allow a secondary bacterial infection to develop. Cutaneous larva ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Erythema Annulare Centrifugum
Erythema annulare centrifugum (EAC), is a descriptive term for a class of skin lesion presenting redness (erythema) in a ring form (''anulare'') that spreads from a center (''centrifugum''). It was first described by Darier in 1916.J. Darier. De l’érythème annulaire centrifuge (érythème papulo-circineé migrateuse et chronique) et de quelques éruptions analogues. Annales de dermatologie et de syphilographie, Paris, 1916-1917, 5: 57-58. Many different terms have been used to classify these types of lesions and it is still controversial on what exactly defines EAC. Some of the types include annular erythema (deep and superficial), erythema perstans, erythema gyratum perstans, erythema gyratum repens, darier erythema (deep gyrate erythema) and erythema figuratum perstans. Symptoms Occurring at any age these lesions appear as raised pink-red ring or bulls-eye marks. They range in size from . The lesions sometimes increase size and spread over time and may not be complete rings ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Purpura Annularis Telangiectoides
Majocchi's disease, also known as Purpura annularis telangiectodes of Majocchi is a not-well-recognized and uncommon skin condition characterized by purple/bluish-red 1- to 3-cm annular patches composed of dark red telangiectases with petechiae. It is one of a group of disorders referred to as pigmented purpuric dermatosis that all occur as a result of vascular inflammation and pigment deposition. Treatment Majocchi's disease is a chronic condition for which there is no cure. It often follows a recurrent course of alternating improvement and flares. There are treatments available to help improve the symptoms for some individuals, but responses vary. Some of these treatments include the application of topical steroids and ultraviolet therapy. The use of narrowband UVB and psoralen Psoralen (also called psoralene) is the parent compound in a family of naturally occurring organic compounds known as the linear furanocoumarins. It is structurally related to coumarin by the a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tinea Corporis
Tinea corporis is a fungal infection of the body, similar to other forms of tinea. Specifically, it is a type of dermatophytosis (or ringworm) that appears on the arms and legs, especially on glabrous skin; however, it may occur on any superficial part of the body. Signs and symptoms It may have a variety of appearances; most easily identifiable are the enlarging raised red rings with a central area of clearing (ringworm). The same appearances of ringworm may also occur on the scalp (tinea capitis), beard area (tinea barbae) or the groin (tinea cruris, known as jock itch or dhobi itch). Other classic features of tinea corporis include: * Itching occurs on infected area. * The edge of the rash appears elevated and is scaly to touch. * Sometimes the skin surrounding the rash may be dry and flaky. * Almost invariably, there will be hair loss in areas of the infection. Causes Tinea corporis is caused by a tiny fungus known as dermatophyte. These tiny organisms normally live on the su ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bullous Pemphigoid
Bullous pemphigoid (type of pemphigoid) is an autoimmune pruritic skin disease which typically occurs in people aged over 60, that may involve the formation of blisters ( bullae) in the space between the epidermal and dermal skin layers. It is classified as a type II hypersensitivity reaction, which involves formation of anti- hemidesmosome antibodies, causing a loss of keratinocytes to basement membrane adhesion. Signs and symptoms Clinically, the earliest lesions may appear as a hives-like red raised rash, but could also appear dermatitic, targetoid, lichenoid, nodular, or even without a rash ( essential pruritus). Tense bullae eventually erupt, most commonly at the inner thighs and upper arms, but the trunk and extremities are frequently both involved. Any part of the skin surface can be involved. Oral lesions are present in a minority of cases. The disease may be acute, but can last from months to years with periods of exacerbation and remission. Several other skin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Serpiginous Choroiditis
Serpiginous choroiditis, also known as geographic or helicoid choroidopathy, is an uncommon chronic progressive inflammatory disease affecting adult men and women equally in the second to seventh decades of life. Presentation In this condition the posterior uveitis shows a geographic pattern. The inflammation begins in the juxtapapillary choroid and intermittently spreads centrifugally. The overlying retinal pigment epithelium and the outer retina are involved in the inflammatory process. A closely related condition is multifocal serpiginoid choroiditis. This is caused by tuberculosis Tuberculosis (TB) is an infectious disease usually caused by '' Mycobacterium tuberculosis'' (MTB) bacteria. Tuberculosis generally affects the lungs, but it can also affect other parts of the body. Most infections show no symptoms, i .... The distinction between these two conditions is important as the latter responds to anti tuberculosis treatment while the former does not. Dia ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Choriocapillaris
The capillary lamina of choroid or choriocapillaris is a layer of capillaries that is immediately adjacent to Bruch's membrane in the choroid. The choriocapillaris was first described in man by Hovius in 1702, although it was not so named until 1838, by Eschricht. Passera (1896) described its form as star-shaped, radiating capillaries beneath the pigment epithelium of the retina, and Duke-Elder and Wybar (1961) have emphasized its nature as a network of capillaries in one plane. The choriocapillaris serves multiple functions that include sustaining the photoreceptors, filtering waste produced in the outer retina and regulating the temperature of macula. The capillary wall is permeable to plasma proteins which is probably of great importance for the supply of vitamin A to the pigment epithelium . The choroidal blood vessels can be divided into two categories: the choriocapillaris, and the larger caliber arteries and veins that lie just posterior to the choriocapillaris (these can ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |