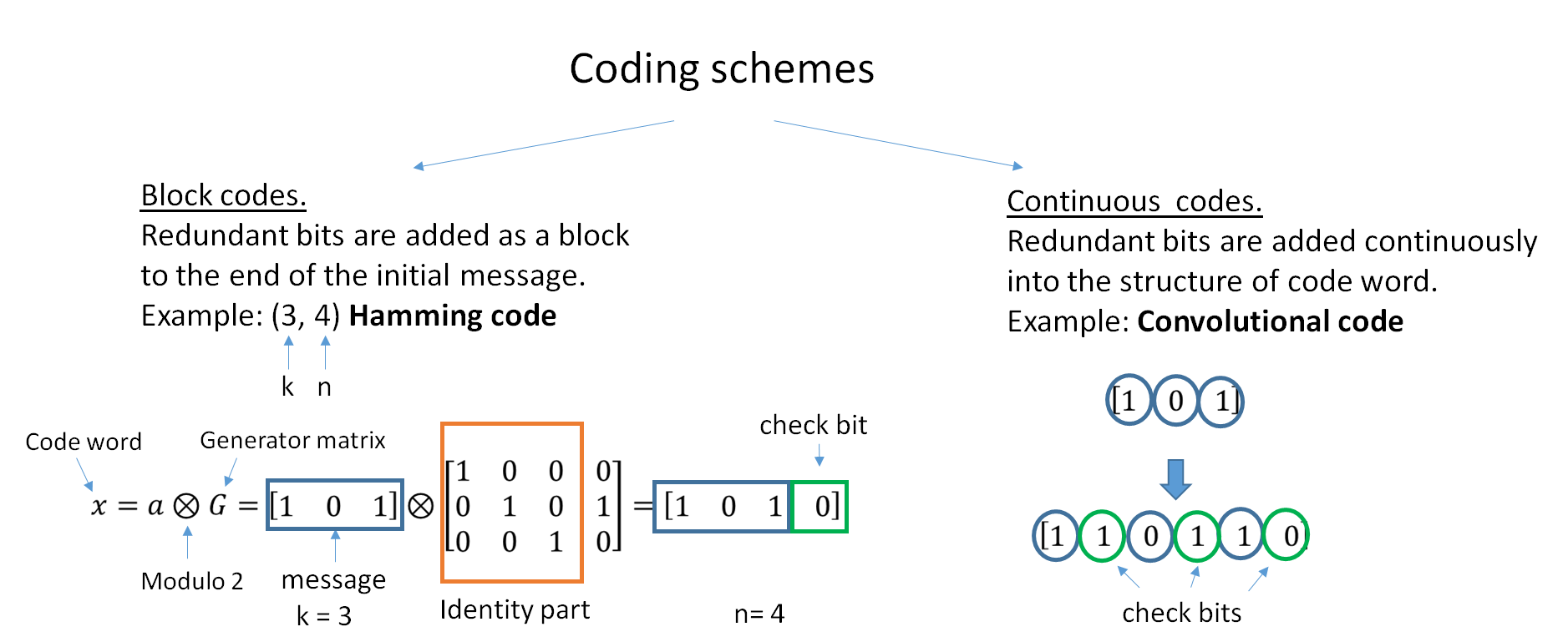
|
SerDes Framer Interface
SerDes Framer Interface is a standard for telecommunications abbreviated as SFI. Variants include: * SFI-4 or SerDes Framer Interface Level 4, a standardized Electrical Interface by the Optical Internetworking Forum (OIF) for connecting a synchronous optical networking (SONET) framer component to an optical serializer/deserializer (SerDes) for Optical Carrier transmission rate OC-192 interfaces at about 10 Gigabits per second. * SFI-5 or SerDes Framer Interface Level 5, a standardized Electrical Interface by the OIF for connecting a SONET Framer component to an optical SerDes for OC-768, about 40 Gbit/s. Electrically, it consists of 16 pairs of SerDes channels each running at 3.125 Gbit/s which gives an aggregate bandwidth of 50 Gbit/s accommodating up to 25% of Forward Error Correction See also * XFP transceiver The XFP (10 gigabit small form-factor pluggable) is a standard for transceivers for high-speed computer network and telecommunication links that use optic ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Telecommunications
Telecommunication is the transmission of information by various types of technologies over wire, radio, optical, or other electromagnetic systems. It has its origin in the desire of humans for communication over a distance greater than that feasible with the human voice, but with a similar scale of expediency; thus, slow systems (such as postal mail) are excluded from the field. The transmission media in telecommunication have evolved through numerous stages of technology, from beacons and other visual signals (such as smoke signals, semaphore telegraphs, signal flags, and optical heliographs), to electrical cable and electromagnetic radiation, including light. Such transmission paths are often divided into communication channels, which afford the advantages of multiplexing multiple concurrent communication sessions. ''Telecommunication'' is often used in its plural form. Other examples of pre-modern long-distance communication included audio messages, such as coded d ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Optical Internetworking Forum
The Optical Internetworking Forum (OIF) is a prominent non-profit consortium that was founded in 1998. It promotes the development and deployment of interoperable computer networking products and services through implementation agreements (IAs) for optical networking products and component technologies including SerDes devices. OIF also creates benchmarks, performs worldwide interoperability testing, builds market awareness and promotes education for optical technologies. The Network Processing Forum merged into OIF in June 2006. The OIF has around a hundred member companies and has four face-to-face meetings per year. It is managed by Association Management Solutions and operates using parliamentary debate rules and transparent decision making. The technical content is member-driven. The OIF operates under a RAND licensing framework. It maintains liaison relationships with many other standards-developing organizations including the ITU, IEEE 802.3, the ONF, the InfiniBand T ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Synchronous Optical Networking
Synchronous optical networking (SONET) and synchronous digital hierarchy (SDH) are standardized protocols that transfer multiple digital bit streams synchronously over optical fiber using lasers or highly coherent light from light-emitting diodes (LEDs). At low transmission rates data can also be transferred via an electrical interface. The method was developed to replace the plesiochronous digital hierarchy (PDH) system for transporting large amounts of telephone calls and data traffic over the same fiber without the problems of synchronization. SONET and SDH, which are essentially the same, were originally designed to transport circuit mode communications (e.g., DS1, DS3) from a variety of different sources, but they were primarily designed to support real-time, uncompressed, circuit-switched voice encoded in PCM format. The primary difficulty in doing this prior to SONET/SDH was that the synchronization sources of these various circuits were different. This meant that eac ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Serializer/deserializer
{{Use American English, date = March 2019 A Serializer/Deserializer (SerDes) is a pair of functional blocks commonly used in high speed communications to compensate for limited input/output. These blocks convert data between serial data and parallel interfaces in each direction. The term "SerDes" generically refers to interfaces used in various technologies and applications. The primary use of a SerDes is to provide data transmission over a single line or a differential pair in order to minimize the number of I/O pins and interconnects. Generic function The basic SerDes function is made up of two functional blocks: the Parallel In Serial Out (PISO) block (aka Parallel-to-Serial converter) and the Serial In Parallel Out (SIPO) block (aka Serial-to-Parallel converter). There are 4 different SerDes architectures: (1) Parallel clock SerDes, (2) Embedded clock SerDes, (3) 8b/10b SerDes, (4) Bit interleaved SerDes. The PISO (Parallel Input, Serial Output) block typically has a paral ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Optical Carrier Transmission Rates
Optical Carrier transmission rates are a standardized set of specifications of transmission bandwidth for digital signals that can be carried on Synchronous Optical Networking (SONET) fiber optic networks. Transmission rates are defined by rate of the bitstream of the digital signal and are designated by hyphenation of the acronym OC and an integer value of the multiple of the basic unit of rate, e.g., OC-48. The base unit is 51.84 Mbit/s. Thus, the speed of optical-carrier-classified lines labeled as OC-n is ''n'' × 51.84 Mbit/s. Optical Carrier specifications Optical Carrier classifications are based on the abbreviation ''OC'' followed by a number specifying a multiple of 51.84 Mbit/s: ''n'' × 51.84 Mbit/s => OC-''n''. For example, an OC-3 transmission medium has 3 times the transmission capacity of OC-1. OC-1 OC-1 is a SONET line with transmission speeds of up to 51.84 Mbit/s (payload: 50.112 Mbit/s; overhead: 1.728 Mbit/s) using optical fib ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
SerDes
{{Use American English, date = March 2019 A Serializer/Deserializer (SerDes) is a pair of functional blocks commonly used in high speed communications to compensate for limited input/output. These blocks convert data between serial data and parallel interfaces in each direction. The term "SerDes" generically refers to interfaces used in various technologies and applications. The primary use of a SerDes is to provide data transmission over a single line or a differential pair in order to minimize the number of I/O pins and interconnects. Generic function The basic SerDes function is made up of two functional blocks: the Parallel In Serial Out (PISO) block (aka Parallel-to-Serial converter) and the Serial In Parallel Out (SIPO) block (aka Serial-to-Parallel converter). There are 4 different SerDes architectures: (1) Parallel clock SerDes, (2) Embedded clock SerDes, (3) 8b/10b SerDes, (4) Bit interleaved SerDes. The PISO (Parallel Input, Serial Output) block typically has a paral ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Forward Error Correction
In computing, telecommunication, information theory, and coding theory, an error correction code, sometimes error correcting code, (ECC) is used for controlling errors in data over unreliable or noisy communication channels. The central idea is the sender encodes the message with redundant information in the form of an ECC. The redundancy allows the receiver to detect a limited number of errors that may occur anywhere in the message, and often to correct these errors without retransmission. The American mathematician Richard Hamming pioneered this field in the 1940s and invented the first error-correcting code in 1950: the Hamming (7,4) code. ECC contrasts with error detection in that errors that are encountered can be corrected, not simply detected. The advantage is that a system using ECC does not require a reverse channel to request retransmission of data when an error occurs. The downside is that there is a fixed overhead that is added to the message, thereby requiring a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
XFP Transceiver
The XFP (10 gigabit small form-factor pluggable) is a standard for transceivers for high-speed computer network and telecommunication links that use optical fiber. It was defined by an industry group in 2002, along with its interface to other electrical components, which is called XFI. XFP is a slightly larger form factor than the popular small form-factor pluggable transceiver, SFP and SFP+. Description XFP modules are hot swappable and support multiple physical layer variants. They typically operate at near-infrared wavelengths (colors) of 850 nm, 1310 nm or 1550 nm. XFP modules use an LC fiber connector type to achieve higher density. Principal applications include 10 Gigabit Ethernet, 10 Gbit/s Fibre Channel, synchronous optical networking (SONET) at OC-192 rates, synchronous optical networking STM-64, 10 Gbit/s Optical Transport Network (OTN) OTU-2, and parallel optics links. They can operate over a single wavelength or use dense wavelength- ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
System Packet Interface
The System Packet Interface (SPI) family of Interoperability Agreements from the Optical Internetworking Forum specify chip-to-chip, channelized, packet interfaces commonly used in synchronous optical networking and Ethernet applications. A typical application of such a packet level interface is between a framer (for optical network) or a MAC (for IP network) and a network processor. Another application of this interface might be between a packet processor ASIC and a traffic manager device. Context There are two broad categories of chip-to-chip interfaces. The first, exemplified by PCI-Express and HyperTransport, supports reads and writes of memory addresses. The second broad category carries user packets over 1 or more channels and is exemplified by the IEEE 802.3 family of Media Independent Interfaces and the Optical Internetworking Forum family of System Packet Interfaces. Of these last two, the family of System Packet Interfaces is optimized to carry user packets from ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Common Electrical I/O
The Common Electrical I/O (CEI) refers to a series of influential Interoperability Agreements (IAs) that have been published by the Optical Internetworking Forum (OIF). CEI defines the electrical and jitter requirements for 3.125, 6, 11, 25-28, and 56 Gbit/s electrical interfaces. CEI, the Common Electrical I/O The Common Electrical I/O (CEI) Interoperability Agreement published by the OIF defines the electrical and jitter requirements for 3.125, 6, 11, 25-28, and 56 Gbit/s SerDes interfaces. This CEI specification has defined SerDes interfaces for the industry since 2004, and it has been highly influential. The development of electrical interfaces at the OIF began with SPI-3 in 2000, and the first differential interface was published in 2003. The seventh generation electrical interface, CEI-56G, defines five reaches of 56 Gbit/s interfaces. The OIF began work on its eighth generation with its CEI-112G project. CEI has influenced or has been adopted or adapted in many other seri ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fiber-optic Communications
Fiber-optic communication is a method of transmitting information from one place to another by sending pulses of infrared light through an optical fiber. The light is a form of carrier wave that is modulated to carry information. Fiber is preferred over electrical cabling when high bandwidth, long distance, or immunity to electromagnetic interference is required. This type of communication can transmit voice, video, and telemetry through local area networks or across long distances. Optical fiber is used by many telecommunications companies to transmit telephone signals, internet communication, and cable television signals. Researchers at Bell Labs have reached a record bandwidth–distance product of over kilometers per second using fiber-optic communication. Background First developed in the 1970s, fiber-optics have revolutionized the telecommunications industry and have played a major role in the advent of the Information Age. Because of its advantages over electrical ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |