|
Segna Di Buonaventure
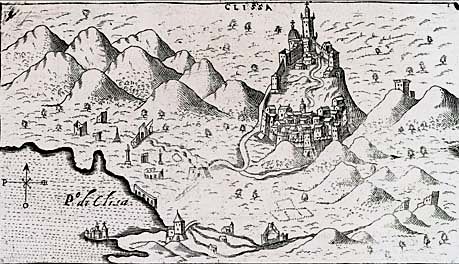
Senj (; it, Segna, la, Senia, Hungarian and german: Zengg) is a town on the upper Adriatic coast in Croatia, in the foothills of the Mala Kapela and Velebit mountains. The symbol of the town is the Nehaj Fortress ( hr, Tvrđava Nehaj) which was completed in 1558. For a time this was the seat of the Uskoks ( it, Uscocchi), who were Christian refugees from Ottoman Bosnia resettled here to protect the Habsburg borderlands. The Republic of Venice accused the Uskoks of piracy and declared war on them which led to their expulsion following a truce in 1617. Senj is to be found in the Lika-Senj County of Croatia, the Roman Catholic Diocese of Gospić-Senj and the Roman Catholic Archdiocese of Rijeka. History Senj has apparently been inhabited since prehistoric times. A settlement called ''Athyinites'' in today's Senj was mentioned in Greek documents dated to 4th century BC. The Illyrian tribe Iapydes inhabited the area as it was located in Illyria. ''Senia'' was a thriving t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
List Of Cities And Towns In Croatia
An urbanized area in Croatia can gain the status of ''grad'' (which can be translated as town or city as there is no distinction between the two terms in Croatian language, Croatian) if it meets one of the following requirements: # is the center of a Counties of Croatia, county (''županija''), or # has more than 10,000 residents, or # is defined by an exception (where the necessary historical, economic or geographic reasons exist) A city (town) represents an urban, historical, natural, economic and social whole. The suburbs comprising an economic and social whole with the city, connected with it by daily migration movements and daily needs of the population of local significance, may also be included into the composition of a city as unit of local self-government. ''Grad'' (city/town) is the local administrative equivalent of ''Municipalities of Croatia, općina'' (translated as "Municipalities of Croatia, municipality"), with the only distinction being that the former usually co ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Uskoks
The Uskoks ( hr, Uskoci, , singular: ; notes on naming) were irregular soldiers in Habsburg Croatia that inhabited areas on the eastern Adriatic coast and surrounding territories during the Ottoman wars in Europe. Bands of Uskoks fought a guerrilla war against the Ottomans, and they formed small units and rowed swift boats. Since the uskoks were checked on land and were rarely paid their annual subsidy, they resorted to acts of piracy. The exploits of the Uskoks contributed to a renewal of war between Venice and the Ottoman Empire (1571–1573). An extremely curious picture of contemporary manners is presented by the Venetian agents, whose reports on this war resemble a knightly chronicle of the Middle Ages. These chronicles contain information pertaining to single combats, tournaments and other chivalrous adventures. Many of these troops served abroad. After a series of incidents that escalated into the Uskok War (1615–1618), the Uskok activity in their stronghold of Sen ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ancient Rome
In modern historiography, ancient Rome refers to Roman civilisation from the founding of the city of Rome in the 8th century BC to the collapse of the Western Roman Empire in the 5th century AD. It encompasses the Roman Kingdom (753–509 BC), Roman Republic (509–27 BC) and Roman Empire (27 BC–476 AD) until the fall of the western empire. Ancient Rome began as an Italic settlement, traditionally dated to 753 BC, beside the River Tiber in the Italian Peninsula. The settlement grew into the city and polity of Rome, and came to control its neighbours through a combination of treaties and military strength. It eventually dominated the Italian Peninsula, assimilated the Greek culture of southern Italy ( Magna Grecia) and the Etruscan culture and acquired an Empire that took in much of Europe and the lands and peoples surrounding the Mediterranean Sea. It was among the largest empires in the ancient world, with an estimated 50 to 90 million inhabitants, roughly 20% of t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Iapydes
The Iapydes (or Iapodes, Japodes; el, Ἰάποδες) were an ancient people who dwelt north of and inland from the Liburnians, off the Adriatic coast and eastwards of the Istrian peninsula. They occupied the interior of the country between the ''Colapis'' (Kupa) and ''Oeneus'' (Una) rivers, and the Velebit mountain range (''Mons Baebius'') which separated them from the coastal Liburnians. Their territory covered the central inlands of modern Croatia and Una River Valley in today's Bosnia and Herzegovina. Archaeological documentation confirms their presence in these countries at least from 9th century BC, and they persisted in their area longer than a millennium. The ancient written documentation on inland Iapydes is scarcer than on the adjacent coastal peoples (Liburni, Delmatae, etc.) that had more frequent maritime contacts with ancient Greeks and Romans. The Iapydes had their maximal development and territorial expansion from the 8th to 4th centuries BC. They settled mostly i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Illyrians
The Illyrians ( grc, Ἰλλυριοί, ''Illyrioi''; la, Illyrii) were a group of Indo-European languages, Indo-European-speaking peoples who inhabited the western Balkan Peninsula in ancient times. They constituted one of the three main Paleo-Balkan languages, Paleo-Balkan populations, along with the Thracians and Ancient Greece, Greeks. The territory the Illyrians inhabited came to be known as Illyria to later Greek and Roman Republic, Roman authors, who identified a territory that corresponds to most of Albania, Montenegro, Kosovo, much of Croatia and Bosnia and Herzegovina, western and central Serbia and some parts of Slovenia between the Adriatic Sea in the west, the Drava river in the north, the Great Morava, Morava river in the east and in the south the Aous (modern Vjosa) river or possibly the Ceraunian Mountains. The first account of Illyrian peoples dates back to the 6th century BC, in the works of the ancient Greek writer Hecataeus of Miletus. The name "Illyrians", ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ancient Greece
Ancient Greece ( el, Ἑλλάς, Hellás) was a northeastern Mediterranean civilization, existing from the Greek Dark Ages of the 12th–9th centuries BC to the end of classical antiquity ( AD 600), that comprised a loose collection of culturally and linguistically related city-states and other territories. Most of these regions were officially unified only once, for 13 years, under Alexander the Great's empire from 336 to 323 BC (though this excludes a number of Greek city-states free from Alexander's jurisdiction in the western Mediterranean, around the Black Sea, Cyprus, and Cyrenaica). In Western history, the era of classical antiquity was immediately followed by the Early Middle Ages and the Byzantine period. Roughly three centuries after the Late Bronze Age collapse of Mycenaean Greece, Greek urban poleis began to form in the 8th century BC, ushering in the Archaic period and the colonization of the Mediterranean Basin. This was followed by the age of Classical G ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
1888 Zengg 12kr Mg
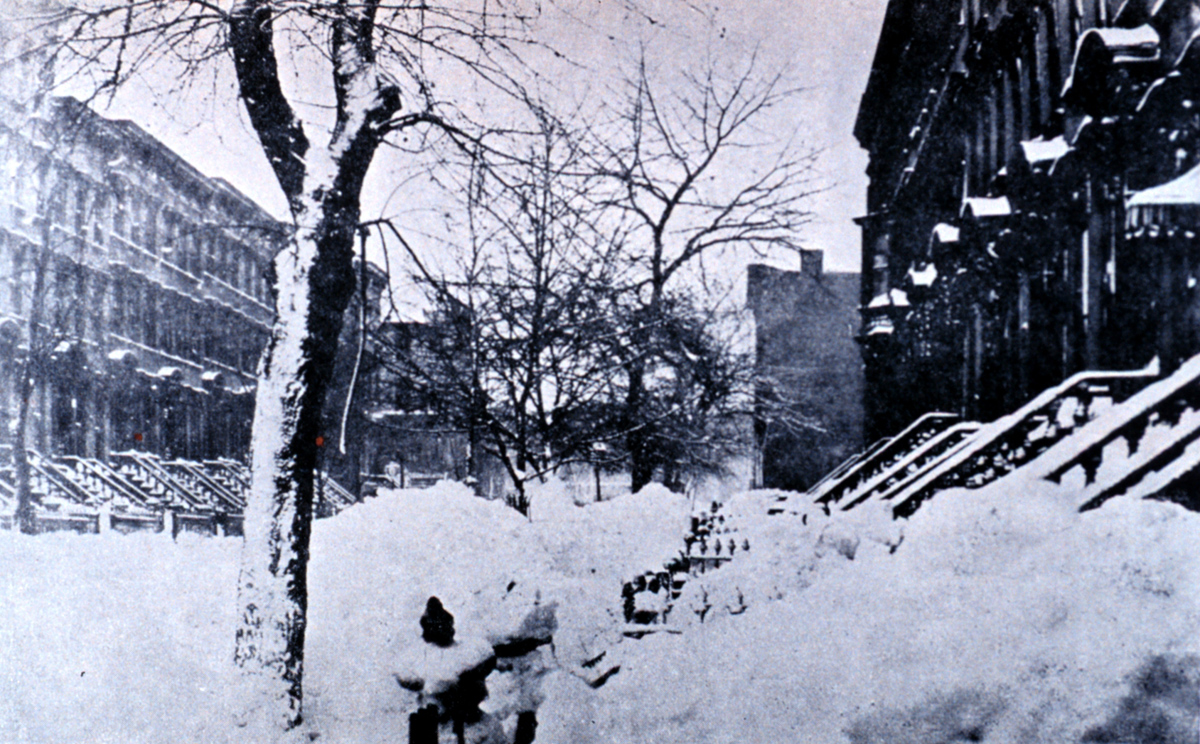
In Germany, 1888 is known as the Year of the Three Emperors. Currently, it is the year that, when written in Roman numerals, has the most digits (13). The next year that also has 13 digits is the year 2388. The record will be surpassed as late as 2888, which has 14 digits. Events January–March * January 3 – The 91-centimeter telescope at Lick Observatory in California is first used. * January 12 – The Schoolhouse Blizzard hits Dakota Territory, the states of Montana, Minnesota, Nebraska, Kansas, and Texas, leaving 235 dead, many of them children on their way home from school. * January 13 – The National Geographic Society is founded in Washington, D.C. * January 21 – The Amateur Athletic Union is founded by William Buckingham Curtis in the United States. * January 26 – The Lawn Tennis Association is founded in England. * February 6 – Gillis Bildt becomes Prime Minister of Sweden (1888–1889). * February 27 – In West Orange ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |

.jpg)


.jpg)
