|
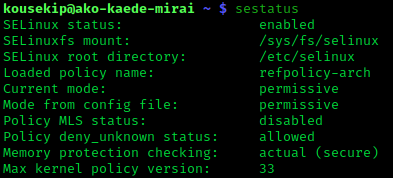
Security-Enhanced Linux
Security-Enhanced Linux (SELinux) is a Linux kernel security module that provides a mechanism for supporting access control security policies, including mandatory access controls (MAC). SELinux is a set of kernel modifications and user-space tools that have been added to various Linux distributions. Its architecture strives to separate enforcement of security decisions from the security policy, and streamlines the amount of software involved with security policy enforcement. The key concepts underlying SELinux can be traced to several earlier projects by the United States National Security Agency (NSA). Overview The NSA Security-enhanced Linux Team describes NSA SELinux as a set of patches to the Linux kernel and utilities to provide a strong, flexible, mandatory access control (MAC) architecture into the major subsystems of the kernel. It provides an enhanced mechanism to enforce the separation of information based on confidentiality and integrity requirements, which allows ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Arch Linux
Arch Linux () is an independently developed, x86-64 general-purpose Linux distribution that strives to provide the latest stable versions of most software by following a Rolling release, rolling-release model. The default installation is a minimal base system, configured by the user to only add what is purposely required. #Pacman, Pacman, a package manager written specifically for Arch Linux, is used to install, remove and update Package (package management system), software packages. Arch Linux uses a Rolling release, rolling release model, meaning there are no "major releases" of completely new versions of the system; a regular system update is all that is needed to obtain the latest Arch software; the installation images released every month by the Arch team are simply up-to-date snapshots of the main system components. Arch Linux has comprehensive documentation, consisting of a community-run wiki known as the ArchWiki. History Inspired by CRUX, another minimalist distrib ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Superuser
In computing, the superuser is a special user account used for system administration. Depending on the operating system (OS), the actual name of this account might be root, administrator, admin or supervisor. In some cases, the actual name of the account is not the determining factor; on Unix-like systems, for example, the user with a user identifier (UID) of zero is the superuser, regardless of the name of that account; and in systems which implement a role based security model, any user with the role of superuser (or its synonyms) can carry out all actions of the superuser account. The principle of least privilege recommends that most users and applications run under an ordinary account to perform their work, as a superuser account is capable of making unrestricted, potentially adverse, system-wide changes. Unix and Unix-like In Unix-like computer OSes (such as Linux), ''root'' is the conventional name of the user who has all rights or permissions (to all files and programs) i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
FreeBSD
FreeBSD is a free and open-source Unix-like operating system descended from the Berkeley Software Distribution (BSD), which was based on Research Unix. The first version of FreeBSD was released in 1993. In 2005, FreeBSD was the most popular open-source BSD operating system, accounting for more than three-quarters of all installed and permissively licensed BSD systems. FreeBSD has similarities with Linux, with two major differences in scope and licensing: FreeBSD maintains a complete system, i.e. the project delivers a kernel, device drivers, userland utilities, and documentation, as opposed to Linux only delivering a kernel and drivers, and relying on third-parties for system software; FreeBSD source code is generally released under a permissive BSD license, as opposed to the copyleft GPL used by Linux. The FreeBSD project includes a security team overseeing all software shipped in the base distribution. A wide range of additional third-party applications may be installe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
TrustedBSD
FreeBSD is a free and open-source Unix-like operating system descended from the Berkeley Software Distribution (BSD), which was based on Research Unix. The first version of FreeBSD was released in 1993. In 2005, FreeBSD was the most popular open-source BSD operating system, accounting for more than three-quarters of all installed and permissively licensed BSD systems. FreeBSD has similarities with Linux, with two major differences in scope and licensing: FreeBSD maintains a complete system, i.e. the project delivers a kernel, device drivers, userland utilities, and documentation, as opposed to Linux only delivering a kernel and drivers, and relying on third-parties for system software; FreeBSD source code is generally released under a permissive BSD license, as opposed to the copyleft GPL used by Linux. The FreeBSD project includes a security team overseeing all software shipped in the base distribution. A wide range of additional third-party applications may be installed fro ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
FLASK
Flask may refer to: Container * Hip flask, a small container used to carry a small amount of liquid * Laboratory flask, laboratory glassware for holding larger volumes than simple test tubes ** Erlenmeyer flask, a common laboratory flask with a flat bottom, a conical body, and a cylindrical neck * Vacuum flask, a container designed to keep warm drinks warm and refrigerated drinks cold Other * Flask (metal casting), a containing frame without a top or bottom, with sides only, used to hold molding sand * Flask (web framework), a web framework for the Python programming language * Powder flask, a small container for gunpowder * FLASK, the Flux Advanced Security Kernel, an operating system security architecture * Flask (unit), a unit used in UK avoirdupois weight to measure the element mercury * The Flask, Hampstead, a Grade II listed public house at 14 Flask Walk, Hampstead, London * The Flask, Highgate The Flask is a Grade II listed public house at 74–76 Highgate West Hill, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Secure Computing Corporation
Secure Computing Corporation (SCC) was a public company that developed and sold computer security appliances and hosted services to protect users and data. McAfee acquired the company in 2008. The company also developed filtering systems used by governments such as Iran and Saudi Arabia that blocks their citizens from accessing information on the Internet.Snuffing out Net's benefit to democracy Jim Landers, '' Dallas Morning News'', December 20, 2005; accessed September 20, 2008.Iran targets dissent ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Network Associates
McAfee Corp. ( ), formerly known as McAfee Associates, Inc. from 1987 to 1997 and 2004 to 2014, Network Associates Inc. from 1997 to 2004, and Intel Security Group from 2014 to 2017, is an American global computer security software company headquartered in San Jose, California. The company was purchased by Intel in February 2011, and became part of the Intel Security division. In 2017, Intel had a strategic deal with TPG Capital and converted Intel Security into a joint venture between both companies called McAfee. Thoma Bravo took a minority stake in the new company, and Intel retained a 49% stake. The owners took McAfee public on the NASDAQ in 2020, and in 2022 an investor group led by Advent International Corporation took it private again. History 1987–1999 The company was founded in 1987 as McAfee Associates, named for its founder John McAfee, who resigned from the company in 1994. McAfee was incorporated in the state of Delaware in 1992. In 1993, McAfee stepped ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Open-source Software
Open-source software (OSS) is computer software that is released under a license in which the copyright holder grants users the rights to use, study, change, and distribute the software and its source code to anyone and for any purpose. Open-source software may be developed in a collaborative public manner. Open-source software is a prominent example of open collaboration, meaning any capable user is able to participate online in development, making the number of possible contributors indefinite. The ability to examine the code facilitates public trust in the software. Open-source software development can bring in diverse perspectives beyond those of a single company. A 2008 report by the Standish Group stated that adoption of open-source software models has resulted in savings of about $60 billion per year for consumers. Open source code can be used for studying and allows capable end users to adapt software to their personal needs in a similar way user scripts an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Linux Kernel Mainline
The Linux kernel is a free and open-source, monolithic, modular, multitasking, Unix-like operating system kernel. It was originally authored in 1991 by Linus Torvalds for his i386-based PC, and it was soon adopted as the kernel for the GNU operating system, which was written to be a free (libre) replacement for Unix. Linux is provided under the GNU General Public License version 2 only, but it contains files under other compatible licenses. Since the late 1990s, it has been included as part of a large number of operating system distributions, many of which are commonly also called Linux. Linux is deployed on a wide variety of computing systems, such as embedded devices, mobile devices (including its use in the Android operating system), personal computers, servers, mainframes, and supercomputers. It can be tailored for specific architectures and for several usage scenarios using a family of simple commands (that is, without the need of manually editing its source code be ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rainbow Series
The Rainbow Series (sometimes known as the Rainbow Books) is a series of computer security standards and guidelines published by the United States government in the 1980s and 1990s. They were originally published by the U.S. Department of Defense Computer Security Center, and then by the National Computer Security Center. Objective These standards describe a process of evaluation for trusted systems. In some cases, U.S. government entities (as well as private firms) would require formal validation of computer technology using this process as part of their procurement criteria. Many of these standards have influenced, and have been superseded by, the Common Criteria. The books have nicknames based on the color of its cover. For example, the Trusted Computer System Evaluation Criteria was referred to as "The Orange Book." In the book entitled ''Applied Cryptography'', security expert Bruce Schneier states of NCSC-TG-021 that he "can't even begin to describe the color of hecove ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Type Enforcement Architecture
The concept of type enforcement (TE), in the field of information technology, is an access control mechanism for regulating access in computer systems. Implementing TE gives priority to mandatory access control (MAC) over discretionary access control (DAC). Access clearance is first given to a subject (e.g. process) accessing objects (e.g. files, records, messages) based on rules defined in an attached security context. A security context in a domain is defined by a domain security policy. In the Linux security module (LSM) in SELinux, the security context is an extended attribute. Type enforcement implementation is a prerequisite for MAC, and a first step before multilevel security (MLS) or its replacement multi categories security (MCS). It is a complement of role-based access control (RBAC). Control Type enforcement implies fine-grained control over the operating system, not only to have control over process execution, but also over domain transition or authorization scheme. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Role-based Access Control
In computer systems security, role-based access control (RBAC) or role-based security is an approach to restricting system access to authorized users. It is an approach to implement mandatory access control (MAC) or discretionary access control (DAC). Role-based access control is a policy-neutral access-control mechanism defined around roles and privileges. The components of RBAC such as role-permissions, user-role and role-role relationships make it simple to perform user assignments. A study by NIST has demonstrated that RBAC addresses many needs of commercial and government organizations. RBAC can be used to facilitate administration of security in large organizations with hundreds of users and thousands of permissions. Although RBAC is different from MAC and DAC access control frameworks, it can enforce these policies without any complication. Design Within an organization, roles are created for various job functions. The permissions to perform certain operations are assign ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |