|
Secret Britain
''Secret Britain'' is a BBC documentary series which has aired on BBC One since 15 August 2010. The series explores some of the United Kingdom's hidden corners such as deserted beaches and tumbling waterfalls, showcasing the very best of what the British countryside has to offer. The show focuses on a variety of areas of the British countryside, with a few minutes dedicated to each particular area of interest. As of the third series, the programme is presented by Ellie Harrison, Chris Hollins and Denise Lewis Denise Lewis (born 27 August 1972) is a British sports presenter and former track and field athlete, who specialised in the heptathlon. She won the gold medal in the heptathlon at the 2000 Sydney Olympics, was twice Commonwealth Games champion, .... Episodes Transmissions Series 1 Series 2 Series 3 References External links * BBC television documentaries BBC high definition shows Nature educational television series 2010 British television series de ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nature Documentary
A nature documentary or wildlife documentary is a genre of documentary film or series about animals, plants, or other non-human living creatures, usually concentrating on video taken in their natural habitat but also often including footage of trained and captive animals. Sometimes they are about wildlife or ecosystems in relationship to human beings. Such programmes are most frequently made for television, particularly for public broadcasting channels, but some are also made for the cinema medium. The proliferation of this genre occurred almost simultaneously alongside the production of similar television series. History In cinema Robert J. Flaherty's 1922 film ''Nanook of the North'' is typically cited as the first feature-length documentary. Decades later, Walt Disney Productions pioneered the serial theatrical release of nature-documentaries with its production of the True-Life Adventures series, a collection of fourteen full length and short subject nature films from 1948 to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rocky Valley
Rocky Valley ( kw, Glynn Duwy, meaning ''deep valley of the river Duwy'') is a small valley in the parish of Tintagel, north Cornwall, England, United Kingdom. The valley has been carved by the Trevillet River ( kw, Duwy, meaning ''dark river'') in Trethevy around one mile east of Tintagel. At their highest point the slate canyon walls tower over seventy feet above the river below. Rocky Valley was mentioned in travel books as a place of exceptional beauty as early as 1897. The valley is owned by the National Trust for Places of Historic Interest or Natural Beauty, National Trust and is home to 161 different species of moss. St Nectan's Glen, Saint Nectan's Glen is an area of woodland stretching for around one mile along both banks of the Trevillet River; its most prominent feature is St Nectan's Kieve. The South West Coast Path descends into and out of the valley a little way inland due to the sheer cliffs on the coast; the rocks at the seaward end of the valley are dangero ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
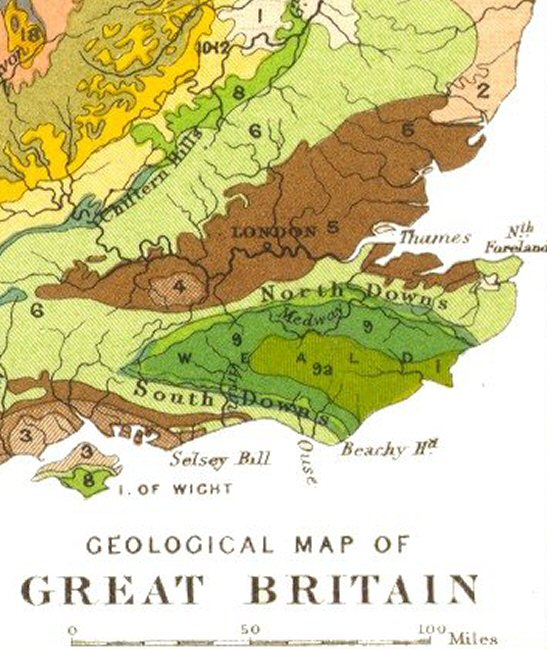
The Chilterns
The Chiltern Hills is a chalk escarpment in England. The area, northwest of London, covers stretching from Goring-on-Thames in the southwest to Hitchin in the northeast - across Oxfordshire, Buckinghamshire, Hertfordshire, and Bedfordshire. The hills are at their widest. In 1965 almost half of the Chiltern Hills was designated as an Area of Outstanding Natural Beauty (AONB). The northwest boundary is clearly defined by the escarpment. The dip slope is by definition more gradual, and merges with the landscape to the southeast. The southwest endpoint is the River Thames. The hills decline slowly in prominence in northeast Bedfordshire.The Changing Landscape of the Chilterns Chilterns AoNB, Accessed 19 February 2012 |
Lincolnshire Wolds
The Lincolnshire Wolds are a range of low hills in the county of Lincolnshire, England which run roughly parallel with the North Sea coast, from the Humber Estuary in the north-west to the edge of the Lincolnshire Fens in the south-east. They are a designated Area of Outstanding Natural Beauty (AONB), and the highest area of land in eastern England between Yorkshire and Kent.Ordnance Survey maps: Geology The Wolds are formed largely from a series of pure marine limestones formed during the Cretaceous period, known collectively as the Chalk Group. The chalk overlies a series of other sedimentary strata of late Jurassic/early Cretaceous age. The strata dip gently to the east and form a scarp which runs southeast from Barton upon Humber via Caistor before it loses its identity north of Spilsby. To the north of the Humber Gap, the same formations continue as the Yorkshire Wolds. The rock succession in stratigraphic order i.e. youngest/uppermost first, is this: *White Chalk Subgro ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Heigham Holmes
Heigham Holmes is a national nature reserve located within the Norfolk Broads in the English county of Norfolk. The reserve is, in effect, an island, being surrounded by the river channels, drainage ditches and wetland areas of the Broads. It is only accessible by an unusual floating swing bridge across the River Thurne from the village of Martham. The reserve is owned by the National Trust and is within the Broads National Park and the civil parish of Potter Heigham. It is only opened to the public for one day a year. It has been suggested that Heigham Holmes was used by the Special Operations Executive as a secret airfield between 1940 and 1944, with Lysander aircraft operating from the airfield to ferry agents to occupied Europe. However, no evidence of an airfield has been found in any records (military or local), maps or on aerial photographs, and any military-type structures that may have existed would appear to have been removed by the end of the Second World War, there ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Norfolk Broads
Norfolk () is a ceremonial and non-metropolitan county in East Anglia in England. It borders Lincolnshire to the north-west, Cambridgeshire to the west and south-west, and Suffolk to the south. Its northern and eastern boundaries are the North Sea, with The Wash to the north-west. The county town is the city of Norwich. With an area of and a population of 859,400, Norfolk is a largely rural county with a population density of 401 per square mile (155 per km2). Of the county's population, 40% live in four major built up areas: Norwich (213,000), Great Yarmouth (63,000), King's Lynn (46,000) and Thetford (25,000). The Broads is a network of rivers and lakes in the east of the county, extending south into Suffolk. The area is protected by the Broads Authority and has similar status to a national park. History The area that was to become Norfolk was settled in pre-Roman times, (there were Palaeolithic settlers as early as 950,000 years ago) with camps along the higher land in th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
East Anglia
East Anglia is an area in the East of England, often defined as including the counties of Norfolk, Suffolk and Cambridgeshire. The name derives from the Anglo-Saxon kingdom of the East Angles, a people whose name originated in Anglia, in what is now Northern Germany. Area Definitions of what constitutes East Anglia vary. The Anglo-Saxon Kingdom of East Anglia, established in the 6th century, originally consisted of the modern counties of Norfolk and Suffolk and expanded west into at least part of Cambridgeshire, typically the northernmost parts known as The Fens. The modern NUTS 3 statistical unit of East Anglia comprises Norfolk, Suffolk and Cambridgeshire (including the City of Peterborough unitary authority). Those three counties have formed the Roman Catholic Diocese of East Anglia since 1976, and were the subject of a possible government devolution package in 2016. Essex has sometimes been included in definitions of East Anglia, including by the London Society o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
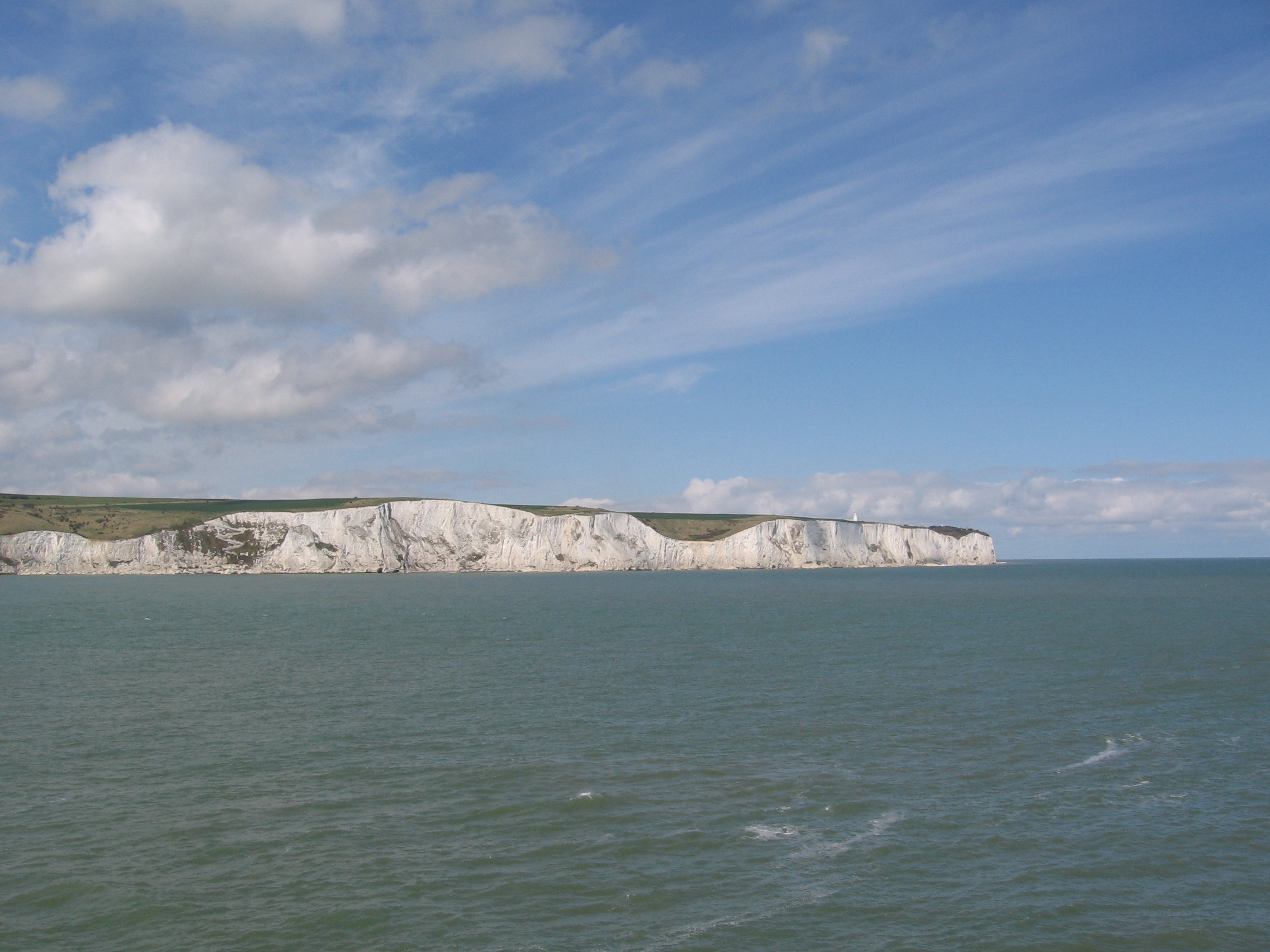
Langdon Bay, Kent
Langdon Bay is a bay in east Kent, England. It is two miles east of the town of Dover, and is named after the nearby villages of Langdon, East Langdon and West Langdon. The cliffs around it are known as the Langdon Cliffs. A prominent zig-zag path down the cliff-face is visible from the sea and connects with the National Trust path by means of a step ladder. An additional means of exit from the beach being a return on foot to St Margaret's Bay. At the far western end is a restricted area of the Port of Dover, and occasionally walkers will be escorted out by the Dover Port Police. History The bay is known for the Langdon Bay Hoard – a collection of Bronze Age metal objects found nearby in 1974. This includes bronze axes of a French type and is thought to represent the cargo of a boat that was caught in a storm just after leaving the English coast, either jettisoned to lighten and save the boat or sunk with it (if there was a wreck, it is now lost). This demonstrates that ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dungeness (headland)
Dungeness () is a headland on the coast of Kent, England, formed largely of a shingle beach in the form of a cuspate foreland. It shelters a large area of low-lying land, Romney Marsh. Dungeness spans Dungeness Nuclear Power Station, the hamlet of Dungeness, and an ecological site at the same location. It lies within the civil parish of Lydd. Etymology Dungeness's name means "the headland at Denge", referring to nearby Denge Marsh. The marsh is first mentioned in 774 as ''Dengemersc''. Its name may mean "marsh of the pasture district", from Old English ''denn *gē mersc'', or else "marsh with manured land", from Old English ''dyncge mersc''. Nature Ecology Dungeness is one of the largest expanses of shingle in Europe. It is of international conservation importance for its geomorphology, plant and invertebrate communities and bird life. This is recognised and protected mostly through its conservation designations as a national nature reserve (NNR), a Special Protection Area ( ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
South Downs
The South Downs are a range of chalk hills that extends for about across the south-eastern coastal counties of England from the Itchen valley of Hampshire in the west to Beachy Head, in the Eastbourne Downland Estate, East Sussex, in the east. The Downs are bounded on the northern side by a steep escarpment, from whose crest there are extensive views northwards across the Weald. The South Downs National Park forms a much larger area than the chalk range of the South Downs and includes large parts of the Weald. The South Downs are characterised by rolling chalk downland with close-cropped turf and dry valleys, and are recognised as one of the most important chalk landscapes in England. The range is one of the four main areas of chalk downland in southern England. The South Downs are relatively less populated compared to South East England as a whole, although there has been large-scale urban encroachment onto the chalk downland by major seaside resorts, including most notably ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Salisbury Plain
Salisbury Plain is a chalk plateau in the south western part of central southern England covering . It is part of a system of chalk downlands throughout eastern and southern England formed by the rocks of the Chalk Group and largely lies within the county of Wiltshire, but stretches into Hampshire. The plain is famous for its rich archaeology, including Stonehenge, one of England's best known landmarks. Large areas are given over to military training and thus the sparsely populated plain is the biggest remaining area of calcareous grassland in northwest Europe. Additionally the plain has arable land, and a few small areas of beech trees and coniferous woodland. Its highest point is Easton Hill. Physical geography The boundaries of Salisbury Plain have never been truly defined, and there is some difference of opinion as to its exact area. The river valleys surrounding it, and other downs and plains beyond them loosely define its boundaries. To the north the scarp of the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Stover Canal
The Stover Canal is a canal located in Devon, England. It was opened in 1792 and served the ball clay industry until it closed in the early 1940s. Today it is derelict, but the Stover Canal Society is aiming to restore it and reopen it to navigation. History The canal was built at a time when the ball clay industry was expanding, but transport of the bulky product was difficult. James Templer (1748–1813) of Stover House, Teigngrace, saw this as an opportunity, and began to construct the canal at his own expense in January 1790. He planned to reach Bovey Tracey, passing through Jewsbridge, near Heathfield en route, and to construct a branch to Chudleigh. Having invested over £1,000 in the project, he sought an Act of Parliament which would allow him to raise more capital, but although the Act was passed on 11 June 1792, he did not invoke its powers, as the canal had already reached Ventiford, Teigngrace and he did not extend it further. As built, the canal was long and inc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |




_-_geograph.org.uk_-_261112.jpg)