|
Second-order Intercept Point
The Second-order intercept point, also known as the SOI, IP2, or IIP2 (Input intercept point), is a measure of linearity that quantifies the second-order distortion generated by nonlinear systems and devices. Examples of frequently used devices that are concerned with this measure are amplifier An amplifier, electronic amplifier or (informally) amp is an electronic device that can increase the magnitude of a signal (a time-varying voltage or current). It may increase the power significantly, or its main effect may be to boost t ...s and mixers. It is related to the third-order intercept point, which is generally used for quantifying degree of nonlinearity of a nonlinear system or it can also be used to estimate the nonlinear products present at the output of such a system. Definition At low power levels, the fundamental output power rises in a one-to-one ratio (in terms of dB) of the input power, while the second-order output power rises in a two-to-one ratio. If th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nonlinear System
In mathematics and science, a nonlinear system is a system in which the change of the output is not proportional to the change of the input. Nonlinear problems are of interest to engineers, biologists, physicists, mathematicians, and many other scientists because most systems are inherently nonlinear in nature. Nonlinear dynamical systems, describing changes in variables over time, may appear chaotic, unpredictable, or counterintuitive, contrasting with much simpler linear systems. Typically, the behavior of a nonlinear system is described in mathematics by a nonlinear system of equations, which is a set of simultaneous equations in which the unknowns (or the unknown functions in the case of differential equations) appear as variables of a polynomial of degree higher than one or in the argument of a function which is not a polynomial of degree one. In other words, in a nonlinear system of equations, the equation(s) to be solved cannot be written as a linear combination of the un ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Amplifier
An amplifier, electronic amplifier or (informally) amp is an electronic device that can increase the magnitude of a signal (a time-varying voltage or current). It may increase the power significantly, or its main effect may be to boost the voltage or current (power, voltage or current amplifier). It is a two-port electronic circuit that uses electric power from a power supply to increase the amplitude of a signal applied to its input terminals, producing a greater amplitude signal at its output. The ratio of output to input voltage, current, or power is termed gain (voltage, current, or power gain). An amplifier, by definition has gain greater than unity (if the gain is less than unity, the device is an attenuator). An amplifier can either be a separate piece of equipment or an electrical circuit contained within another device. Amplification is fundamental to modern electronics, and amplifiers are widely used in almost all electronic equipment. Amplifiers can be categorize ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
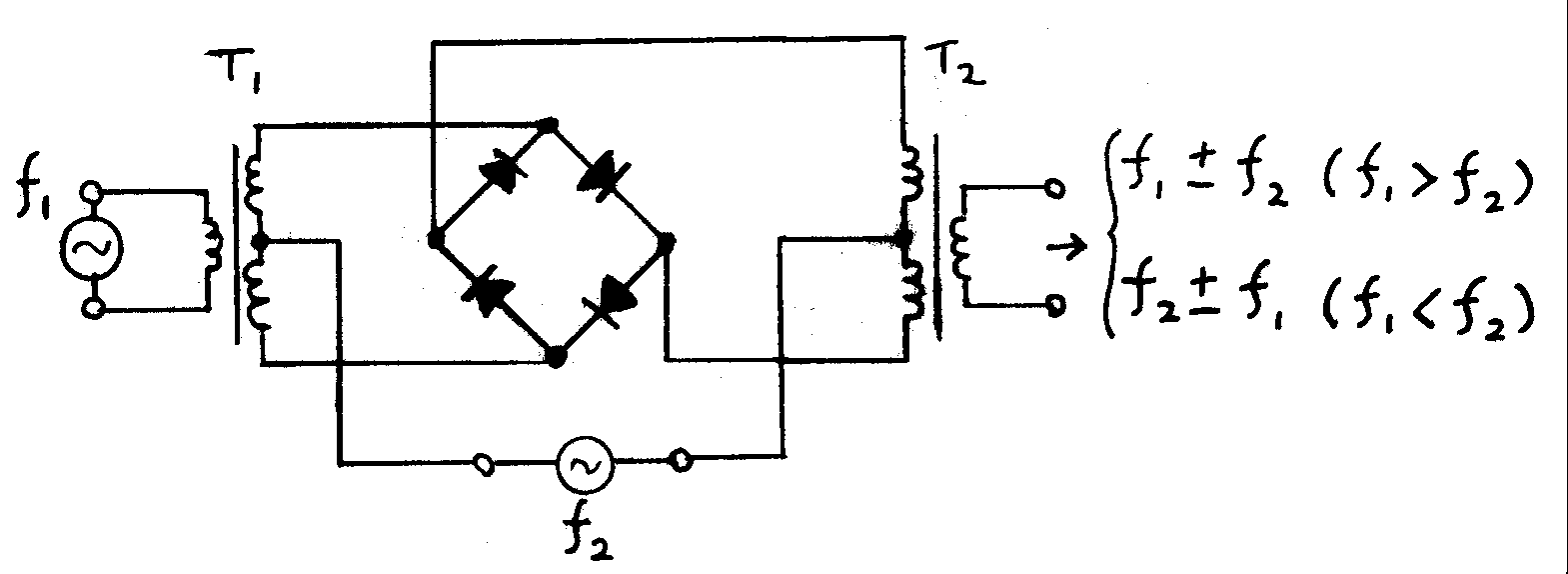
Frequency Mixer
In electronics, a mixer, or frequency mixer, is an electrical circuit that creates new frequencies from two signals applied to it. In its most common application, two signals are applied to a mixer, and it produces new signals at the sum and difference of the original frequencies. Other frequency components may also be produced in a practical frequency mixer. Mixers are widely used to shift signals from one frequency range to another, a process known as heterodyning, for convenience in transmission or further signal processing. For example, a key component of a superheterodyne receiver is a mixer used to move received signals to a common intermediate frequency. Frequency mixers are also used to modulate a carrier signal in radio transmitters. Types The essential characteristic of a mixer is that it produces a component in its output which is the product of the two input signals. Both active and passive circuits can realize mixers. Passive mixers use one or more diodes and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Third-order Intercept Point
In telecommunications, a third-order intercept point (IP3 or TOI) is a specific figure of merit associated with the more general third-order intermodulation distortion (IMD3), which is a measure for weakly nonlinear systems and devices, for example receiver (radio), receivers, linear electronic amplifier, amplifiers and frequency mixer, mixers. It is based on the idea that the device nonlinearity can be modeled using a low-order polynomial, derived by means of Taylor series expansion. The third-order intercept point relates nonlinear products caused by the third-order nonlinear term to the linearly amplified signal, in contrast to the second-order intercept point that uses second-order terms. The intercept point is a purely mathematical concept and does not correspond to a practically occurring physical power level. In many cases, it lies far beyond the damage threshold of the device. Definitions Two different definitions for intercept points are in use: * ''Based on harmonics'': ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Decibel
The decibel (symbol: dB) is a relative unit of measurement equal to one tenth of a bel (B). It expresses the ratio of two values of a power or root-power quantity on a logarithmic scale. Two signals whose levels differ by one decibel have a power ratio of 101/10 (approximately ) or root-power ratio of 10 (approximately ). The unit expresses a relative change or an absolute value. In the latter case, the numeric value expresses the ratio of a value to a fixed reference value; when used in this way, the unit symbol is often suffixed with letter codes that indicate the reference value. For example, for the reference value of 1 volt, a common suffix is " V" (e.g., "20 dBV"). Two principal types of scaling of the decibel are in common use. When expressing a power ratio, it is defined as ten times the logarithm in base 10. That is, a change in ''power'' by a factor of 10 corresponds to a 10 dB change in level. When expressing root-power quantities, a change in ''ampl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Intermodulation Intercept Point
The intermodulation intercept point in electronics is a measure of an electrical device's linearity. When driven by two sinusoidal waveforms, it is the theoretical power level at which the power of the desired tone and the nth-order (where n is odd) intermodulation product intersect. See also * Second-order intercept point The Second-order intercept point, also known as the SOI, IP2, or IIP2 (Input intercept point), is a measure of linearity that quantifies the second-order distortion generated by nonlinear systems and devices. Examples of frequently used devices t ... (IP2/SOI) * Third-order intercept point (IP3/TOI) * Fifth-order intercept point (IP5) References Amplifiers {{Sound-tech-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Third-order Intercept Point
In telecommunications, a third-order intercept point (IP3 or TOI) is a specific figure of merit associated with the more general third-order intermodulation distortion (IMD3), which is a measure for weakly nonlinear systems and devices, for example receiver (radio), receivers, linear electronic amplifier, amplifiers and frequency mixer, mixers. It is based on the idea that the device nonlinearity can be modeled using a low-order polynomial, derived by means of Taylor series expansion. The third-order intercept point relates nonlinear products caused by the third-order nonlinear term to the linearly amplified signal, in contrast to the second-order intercept point that uses second-order terms. The intercept point is a purely mathematical concept and does not correspond to a practically occurring physical power level. In many cases, it lies far beyond the damage threshold of the device. Definitions Two different definitions for intercept points are in use: * ''Based on harmonics'': ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |

.png)
.jpg)