|
Seafloor Depth Versus Age
The depth of the seafloor on the flanks of a mid-ocean ridge is determined mainly by the ''age'' of the oceanic lithosphere; older seafloor is deeper. During seafloor spreading, lithosphere and mantle cooling, contraction, and isostatic adjustment with age cause seafloor deepening. This relationship has come to be better understood since around 1969 with significant updates in 1974 and 1977. Two main theories have been put forward to explain this observation: one where the mantle including the lithosphere is cooling; the cooling mantle model, and a second where a lithosphere plate cools above a mantle at a constant temperature; the cooling plate model. The cooling mantle model explains the age-depth observations for seafloor younger than 80 million years. The cooling plate model explains the age-depth observations best for seafloor older that 20 million years. In addition, the cooling plate model explains the almost constant depth and heat flow observed in very old seafloor and lith ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mid-ocean Ridge
A mid-ocean ridge (MOR) is a seafloor mountain system formed by plate tectonics. It typically has a depth of about and rises about above the deepest portion of an ocean basin. This feature is where seafloor spreading takes place along a divergent plate boundary. The rate of seafloor spreading determines the morphology of the crest of the mid-ocean ridge and its width in an ocean basin. The production of new seafloor and oceanic lithosphere results from mantle upwelling in response to plate separation. The melt rises as magma at the linear weakness between the separating plates, and emerges as lava, creating new oceanic crust and lithosphere upon cooling. The first discovered mid-ocean ridge was the Mid-Atlantic Ridge, which is a spreading center that bisects the North and South Atlantic basins; hence the origin of the name 'mid-ocean ridge'. Most oceanic spreading centers are not in the middle of their hosting ocean basis but regardless, are traditionally called mid-ocean ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Error Function
In mathematics, the error function (also called the Gauss error function), often denoted by , is a complex function of a complex variable defined as: :\operatorname z = \frac\int_0^z e^\,\mathrm dt. This integral is a special (non- elementary) sigmoid function that occurs often in probability, statistics, and partial differential equations. In many of these applications, the function argument is a real number. If the function argument is real, then the function value is also real. In statistics, for non-negative values of , the error function has the following interpretation: for a random variable that is normally distributed with mean 0 and standard deviation , is the probability that falls in the range . Two closely related functions are the complementary error function () defined as :\operatorname z = 1 - \operatorname z, and the imaginary error function () defined as :\operatorname z = -i\operatorname iz, where is the imaginary unit Name The name "error functi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Coastal And Oceanic Landforms
The coast, also known as the coastline or seashore, is defined as the area where land meets the ocean, or as a line that forms the boundary between the land and the coastline. The Earth has around of coastline. Coasts are important zones in natural ecosystems, often home to a wide range of biodiversity. On land, they harbor important ecosystems such as freshwater or estuarine wetlands, which are important for bird populations and other terrestrial animals. In wave-protected areas they harbor saltmarshes, mangroves or seagrasses, all of which can provide nursery habitat for finfish, shellfish, and other aquatic species. Rocky shores are usually found along exposed coasts and provide habitat for a wide range of sessile animals (e.g. mussels, starfish, barnacles) and various kinds of seaweeds. Along tropical coasts with clear, nutrient-poor water, coral reefs can often be found between depths of . According to a United Nations atlas, 44% of all people live within 5 km (3.3m ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Oceanic Ridges
A mid-ocean ridge (MOR) is a seafloor mountain system formed by plate tectonics. It typically has a depth of about and rises about above the deepest portion of an ocean basin. This feature is where seafloor spreading takes place along a Divergent boundary, divergent plate boundary. The rate of seafloor spreading determines the morphology of the crest of the mid-ocean ridge and its width in an ocean basin. The production of new seafloor and oceanic lithosphere results from Mantle (geology), mantle upwelling in response to plate separation. The melt rises as magma at the linear weakness between the separating plates, and emerges as lava, creating new oceanic crust and lithosphere upon cooling. The first discovered mid-ocean ridge was the Mid-Atlantic Ridge, which is a spreading center that bisects the North and South Atlantic basins; hence the origin of the name 'mid-ocean ridge'. Most oceanic spreading centers are not in the middle of their hosting ocean basis but regardless, a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
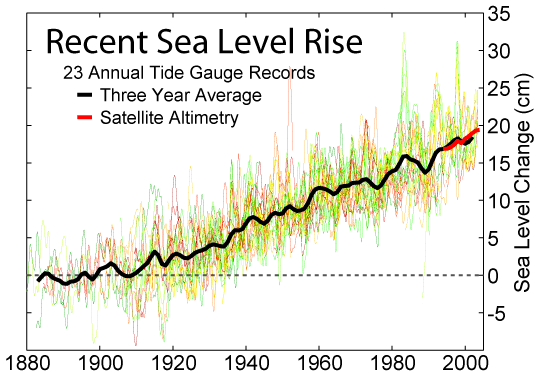
Sea Level Rise
Globally, sea levels are rising due to human-caused climate change. Between 1901 and 2018, the globally averaged sea level rose by , or 1–2 mm per year on average.IPCC, 2019Summary for Policymakers InIPCC Special Report on the Ocean and Cryosphere in a Changing Climate .-O. Pörtner, D.C. Roberts, V. Masson-Delmotte, P. Zhai, M. Tignor, E. Poloczanska, K. Mintenbeck, A. Alegría, M. Nicolai, A. Okem, J. Petzold, B. Rama, N.M. Weyer (eds.) Cambridge University Press, Cambridge, UK and New York, NY, USA. https://doi.org/10.1017/9781009157964.001. This rate is accelerating, with sea levels now rising by 3.7 mm per year. Climate scientists expect further acceleration during the 21st century. Climate change heats (and therefore expands) the ocean and melts land-based ice sheets and glaciers. Between 1993 and 2018, the thermal expansion of water contributed 42% to sea level rise; melting of temperate glaciers, 21%; Greenland, 15%; and Antarctica, 8%. Over the next 2 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sea Level Equation
Post-glacial rebound (also called isostatic rebound or crustal rebound) is the rise of land masses after the removal of the huge weight of ice sheets during the last glacial period, which had caused isostatic depression. Post-glacial rebound and isostatic depression are phases of glacial isostasy (glacial isostatic adjustment, glacioisostasy), the deformation of the Earth's crust in response to changes in ice mass distribution. The direct raising effects of post-glacial rebound are readily apparent in parts of Northern Eurasia, Northern America, Patagonia, and Antarctica. However, through the processes of ''ocean siphoning'' and ''continental levering'', the effects of post-glacial rebound on sea level are felt globally far from the locations of current and former ice sheets.Milne, G.A., and J.X. Mitrovica (2008) ''Searching for eustasy in deglacial sea-level histories.'' Quaternary Science Reviews. 27:2292–2302. Overview During the last glacial period, much of northern Eu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sea-level Curve
The sea-level curve is the representation of the changes of the sea level throughout the geological history. The first such curve is the Vail curve or Exxon curve. The names of the curve refer to the fact that in 1977 a team of Exxon geologists from Esso Production Research headed by Peter Vail published a monograph on global eustatic sea-level changes. Their sea-level curve was based on seismic and biostratigraphic data accumulated during petroleum exploration. The Vail curve (and the monograph itself) was the subject of debate among geologists, because it was based on undisclosed commercially confidential stratigraphic data, and hence not independently verifiable. Because of this, there were later efforts to establish a sea-level curve based on non-commercial data. In 1987–1988 a revised eustatic sea-level curve for the Mesozoic and Cenozoic eras was published, now known as the Haq sea-level curve, in reference to the oceanographer Bilal Haq. Haq and Stephen Schutter ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sea Level
Mean sea level (MSL, often shortened to sea level) is an average surface level of one or more among Earth's coastal bodies of water from which heights such as elevation may be measured. The global MSL is a type of vertical datuma standardised geodetic datumthat is used, for example, as a chart datum in cartography and marine navigation, or, in aviation, as the standard sea level at which atmospheric pressure is measured to calibrate altitude and, consequently, aircraft flight levels. A common and relatively straightforward mean sea-level standard is instead the midpoint between a mean low and mean high tide at a particular location. Sea levels can be affected by many factors and are known to have varied greatly over geological time scales. Current sea level rise is mainly caused by human-induced climate change. When temperatures rise, mountain glaciers and the polar ice caps melt, increasing the amount of water in water bodies. Because most of human settlement and in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sea Level Rise
Globally, sea levels are rising due to human-caused climate change. Between 1901 and 2018, the globally averaged sea level rose by , or 1–2 mm per year on average.IPCC, 2019Summary for Policymakers InIPCC Special Report on the Ocean and Cryosphere in a Changing Climate .-O. Pörtner, D.C. Roberts, V. Masson-Delmotte, P. Zhai, M. Tignor, E. Poloczanska, K. Mintenbeck, A. Alegría, M. Nicolai, A. Okem, J. Petzold, B. Rama, N.M. Weyer (eds.) Cambridge University Press, Cambridge, UK and New York, NY, USA. https://doi.org/10.1017/9781009157964.001. This rate is accelerating, with sea levels now rising by 3.7 mm per year. Climate scientists expect further acceleration during the 21st century. Climate change heats (and therefore expands) the ocean and melts land-based ice sheets and glaciers. Between 1993 and 2018, the thermal expansion of water contributed 42% to sea level rise; melting of temperate glaciers, 21%; Greenland, 15%; and Antarctica, 8%. Over the next 2 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Eustatic
Mean sea level (MSL, often shortened to sea level) is an average surface level of one or more among Earth's coastal bodies of water from which heights such as elevation may be measured. The global MSL is a type of vertical datuma standardised geodetic datumthat is used, for example, as a chart datum in cartography and marine navigation, or, in aviation, as the standard sea level at which atmospheric pressure is measured to calibrate altitude and, consequently, aircraft flight levels. A common and relatively straightforward mean sea-level standard is instead the midpoint between a mean low and mean high tide at a particular location. Sea levels can be affected by many factors and are known to have varied greatly over geological time scales. Current sea level rise is mainly caused by human-induced climate change. When temperatures rise, mountain glaciers and the polar ice caps melt, increasing the amount of water in water bodies. Because most of human settlement and infrastruct ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
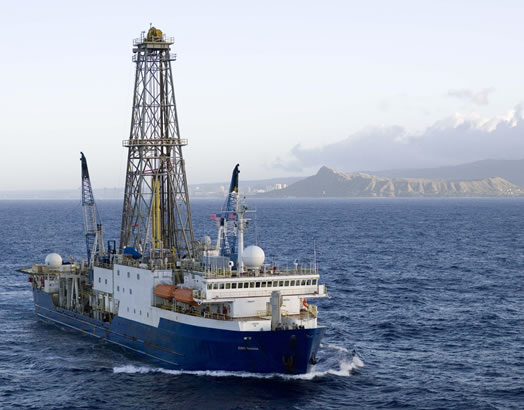
Ocean Drilling Program
The Ocean Drilling Program (ODP) was a multinational effort to explore and study the composition and structure of the Earth's oceanic basins. ODP, which began in 1985, was the successor to the Deep Sea Drilling Project initiated in 1968 by the United States. ODP was an international effort with contributions of Australia, Germany, France, Japan, the United Kingdom and the ESF Consortium for Ocean Drilling (ECOD) including 12 further countries. The program used the drillship ''JOIDES Resolution'' on 110 expeditions (legs) to collect about 2,000 deep sea cores from major geological features located in the ocean basins of the world. Drilling discoveries led to further questions and hypotheses, as well as to new disciplines in earth sciences such as the field of paleoceanography. In 2004 ODP transformed into the Integrated Ocean Drilling Program (IODP). See also * Project Mohole * Deep Sea Drilling Program The Deep Sea Drilling Project (DSDP) was an ocean drilling project ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
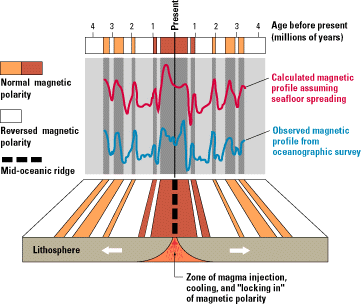
Vine–Matthews–Morley Hypothesis
The Vine–Matthews–Morley hypothesis, also known as the Morley–Vine–Matthews hypothesis, was the first key scientific test of the seafloor spreading theory of continental drift and plate tectonics. Its key impact was that it allowed the rates of plate motions at mid-ocean ridges to be computed. It states that the Earth's oceanic crust acts as a recorder of reversals in the geomagnetic field direction as seafloor spreading takes place. History Harry Hess proposed the seafloor spreading hypothesis in 1960 (published in 1962); the term "spreading of the seafloor" was introduced by geophysicist Robert S. Dietz in 1961. According to Hess, seafloor was created at mid-oceanic ridges by the convection of the earth's mantle, pushing and spreading the older crust away from the ridge. Geophysicist Frederick John Vine and the Canadian geologist Lawrence W. Morley independently realized that if Hess's seafloor spreading theory was correct, then the rocks surrounding the mid-oceanic ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |