|
Seacourt Stream
Hinksey Stream is a branch of the River Thames to the west of the city of Oxford, England. It starts as Seacourt Stream (also known as Wytham Stream), which leaves the Thames at a bifurcation north of the village of Wytham, and rejoins the river south of the city near Kennington. Course Seacourt Stream From the bifurcation Seacourt Stream flows south past Wytham and under the A34 Oxford Ring Road. Near the site of the lost village of Seacourt Botley Stream branches off Seacourt Stream on its left bank, and flows 0.8 km to enter Bulstake Stream.Oxford Area Flood Information Guidance Booklet , pages 37–38. Seacourt Stream then flows under |
Hinksey Stream, North Hinksey Village - Geograph
Hinksey is a place name associated with Oxford and Oxfordshire. In 1974, many of the places associated with the name were transferred from the county of Berkshire in the county boundary changes. History The place-name is of Old English origin. It is first mentioned in the 10th century in the form Hengestesige, and probably means "stallion island". It may also mean "island of a man named Hengest", but there is no evidence to link the place to the historical Hengest. Place names ending in “-ey” (“island”, commonly used of higher ground in a marshy area) are of early formation, probably names bestowed by the first English farmers who tackled the area. The Hinksey villages were not mentioned as separate villages until 1316. Hinxey Hall was located in Oxford during the 14th to 16th centuries. The Carfax Conduit from Hinksey Hill to Carfax in the centre of Oxford was completed in 1617. Hinksey Halt railway station served New Hinksey in south Oxford during 1908−15. In 1934, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
A4144 Road
The A4144 road is an A road in Oxford, England. It links Upper Wolvercote in the north and Redbridge in the south via central Oxford. The A4144 consists largely of Woodstock Road in the north and Abingdon Road in the south. It also includes Beaumont Street, St Giles' and part of Worcester Street. Much of the A4144 is the former route of the A34 road The A34 is a major road in England. It runs from the A33 and M3 at Winchester in Hampshire, to the A6 and A6042 in Salford, close to Manchester City Centre. It forms a large part of the major trunk route from Southampton, via Oxford, to B ..., which used to pass through central Oxford until 1962 when the Western Bypass Road was completed. References Roads in Oxfordshire Transport in Oxford {{UK-road-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
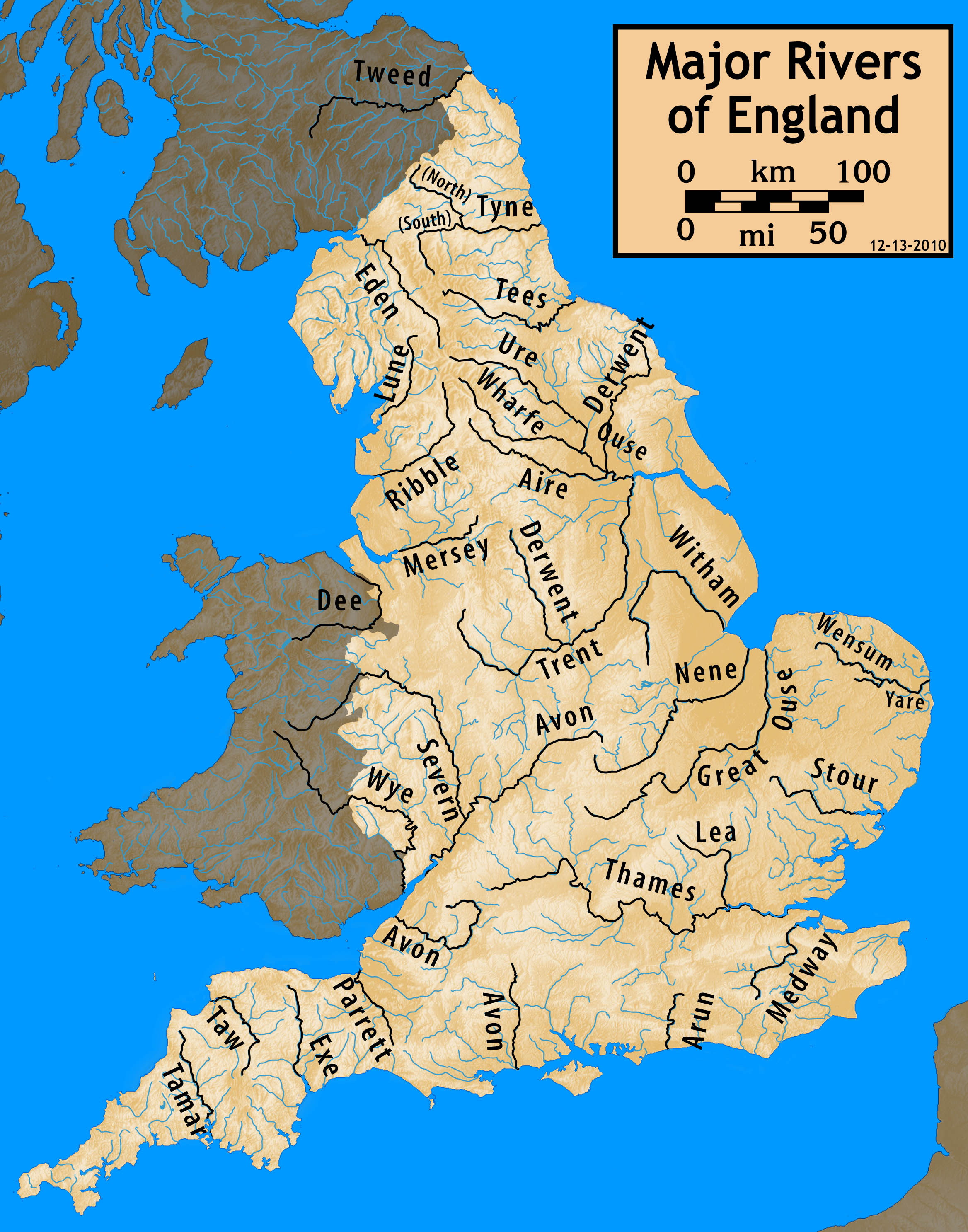
List Of Rivers Of England
This is a list of rivers of England, organised geographically and taken anti-clockwise around the English coast where the various rivers discharge into the surrounding seas, from the Solway Firth on the Scottish border to the Welsh Dee on the Welsh border, and again from the Wye on the Welsh border anti-clockwise to the Tweed on the Scottish border. Tributaries are listed down the page in an upstream direction, i.e. the first tributary listed is closest to the sea, and tributaries of tributaries are treated similarly. Thus, in the first catchment below, the River Sark is the lowermost tributary of the Border Esk and the Hether Burn is the lowermost tributary of the River Lyne. The main stem (or principal) river of a catchment is labelled as (MS), left-bank tributaries are indicated by (L), right-bank tributaries by (R). Note that in general usage, the 'left (or right) bank of a river' refers to the left (or right) hand bank, as seen when looking downstream. Where a named river ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Grandpont
Grandpont is a mainly residential area in south Oxford. It is west of Abingdon Road, and consists mainly of narrow streets that run at right angles to the main road, with terraced late- Victorian and Edwardian houses. It also contains the Grandpont Nature Park—a riverside park managed by Oxford City Council (). The park covers and was created in 1985 on the site of a gas works that was demolished in 1960. The former railway bridge, used to carry coal from the main railway line across the River Thames to the older gas works in St Ebbes on the north bank, still stands, and is in use as a footbridge. A later bridge, Grandpont Bridge, provides a more direct pedestrian and cycle route across the river to St Ebbes. History The name of the area derives from the Grandpont, a medieval stone causeway now known to survive within the core of the modern Abingdon Road for a distance of at least 700 metres south of the city centre. The causeway may have been first built in the Anglo-Saxon ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Oxfordshire
Oxfordshire is a ceremonial and non-metropolitan county in the north west of South East England. It is a mainly rural county, with its largest settlement being the city of Oxford. The county is a centre of research and development, primarily due to the work of the University of Oxford and several notable science parks. These include the Harwell Science and Innovation Campus and Milton Park, both situated around the towns of Didcot and Abingdon-on-Thames. It is a landlocked county, bordered by six counties: Berkshire to the south, Buckinghamshire to the east, Wiltshire to the south west, Gloucestershire to the west, Warwickshire to the north west, and Northamptonshire to the north east. Oxfordshire is locally governed by Oxfordshire County Council, together with local councils of its five non-metropolitan districts: City of Oxford, Cherwell, South Oxfordshire, Vale of White Horse, and West Oxfordshire. Present-day Oxfordshire spanning the area south of the Thames was h ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Berkshire
Berkshire ( ; in the 17th century sometimes spelt phonetically as Barkeshire; abbreviated Berks.) is a historic county in South East England. One of the home counties, Berkshire was recognised by Queen Elizabeth II as the Royal County of Berkshire in 1957 because of the presence of Windsor Castle, and letters patent were issued in 1974. Berkshire is a county of historic origin, a ceremonial county and a non-metropolitan county without a county council. The county town is Reading. The River Thames formed the historic northern boundary, from Buscot in the west to Old Windsor in the east. The historic county, therefore, includes territory that is now administered by the Vale of White Horse and parts of South Oxfordshire in Oxfordshire, but excludes Caversham, Slough and five less populous settlements in the east of the Royal Borough of Windsor and Maidenhead. All the changes mentioned, apart from the change to Caversham, took place in 1974. The towns of Abingdon, Didcot, Far ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Wessex
la, Regnum Occidentalium Saxonum , conventional_long_name = Kingdom of the West Saxons , common_name = Wessex , image_map = Southern British Isles 9th century.svg , map_caption = Southern Britain in the ninth century , event_start = Established , year_start = 519 , event_end = English unification , year_end = 12 July 927 , event1 = , date_event1 = , event_pre = Settlement , date_pre = 5th–6th century , event_post = Norman conquest , date_post = 14 October 1066 , border_s2 = no , common_languages = Old English *West Saxon dialect British Latin , religion = PaganismChristianity , leader1 = Cerdic (first) , leader2 = Ine , leader3 = Ecgberht , leader4 = Alfred the Great , leader5 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mercia
la, Merciorum regnum , conventional_long_name=Kingdom of Mercia , common_name=Mercia , status=Kingdom , status_text=Independent kingdom (527–879)Client state of Wessex () , life_span=527–918 , era=Heptarchy , event_start= , date_start= , year_start=527 , event_end= , date_end= , year_end=918 , event1= , date_event1= , event2= , date_event2= , event3= , date_event3= , event4= , date_event4= , p1=Sub-Roman Britain , flag_p1=Vexilloid of the Roman Empire.svg , border_p1=no , p2=Hwicce , flag_p2= , p3=Kingdom of Lindsey , flag_p3= , p4=Kingdom of Northumbria , flag_p4= , s1=Kingdom of England , flag_s1=Flag of Wessex.svg , border_s1=no , s2= , flag_s2= , image_flag= , image_map=Mercian Supremacy x 4 alt.png , image_map_caption=The Kingdom of Mercia (thick line) and the kingdom's extent during the Mercian Supremacy (green shading) , national_motto= , national_anthem= , common_languages=Old English *Mercian dialect British Latin , currency=Sceat Penny , religion=PaganismChristia ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Anglo-Saxon England
Anglo-Saxon England or Early Medieval England, existing from the 5th to the 11th centuries from the end of Roman Britain until the Norman conquest in 1066, consisted of various Anglo-Saxon kingdoms until 927, when it was united as the Kingdom of England by King Æthelstan (r. 927–939). It became part of the short-lived North Sea Empire of Cnut the Great, a personal union between England, Denmark and Norway in the 11th century. The Anglo-Saxons migrated to England from mainland northwestern Europe after the Roman Empire abandoned Britain at the beginning of the fifth century. Anglo-Saxon history thus begins during the period of sub-Roman Britain following the end of Roman control, and traces the establishment of Anglo-Saxon kingdoms in the 5th and 6th centuries (conventionally identified as seven main kingdoms: Northumbria, Mercia, East Anglia, Essex, Kent, Sussex, and Wessex); their Christianisation during the 7th century; the threat of Viking invasions and Danish settle ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ferry Hinksey
North Hinksey is a village and civil parish in Oxfordshire, England, immediately west of Oxford. The civil parish includes the large settlement of Botley, effectively a suburb of Oxford. North Hinksey was part of Berkshire until the 1974 boundary changes transferred it to Oxfordshire. The village of North Hinksey has a manor house, The Fishes public house, a Church of England primary school and a Church of England parish church, St. Lawrence's, which dates back to at least the 12th century. Four of the older houses have thatched roofs. There was also the administrative offices of the Church of England Diocese of Oxford (Diocesan Church House) in the enlarged former vicarage. This, as of September 2016 is to be converted to housing. Harcourt Hill and Raleigh Park lie to the southwest of the village. All the shopping and other facilities in the parish are now found in Botley. The centre of the old village is now effectively cut off from much of the newer part of Botley b ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ferry Hinksey Road
Ferry Hinksey Road is a road in west Oxford, England, leading south from the Botley Road. The road leads to the Osney Mead Industrial Estate to the east, started in 1961. To the east is Osney Ditch. History The road is named after the village of Ferry Hinksey, now known as North Hinksey, on the other side of Hinksey Stream, one of the branches of the River Thames in Oxford. There was once a punt ferry that operated over Bulstake Stream. The most notable path between Oxford and North Hinksey, a continuation of Ferry Hinksey Road, is a metalled bridleway and cycle track, variously known as Willow Walk and Ruskin's Ride. The latter is named after John Ruskin (1819–1900) who used to pass this way between Ferry Hinksey and Oxford, where he was the first Slade Professor of Fine Art from 1869. The path was originally built in 1876–77 by Aubrey Harcourt (1852–1904), a major local landowner, but was not made open to the public until 1922. There is also a smaller unmade path wh ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Thames Path
The Thames Path is a National Trail following the River Thames from its source near Kemble, Gloucestershire, Kemble in Gloucestershire to the Woolwich foot tunnel, south east London. It is about long. A path was first proposed in 1948 but it only opened in 1996. The Thames Path's entire length can be walked, and a few parts can be cycled. Some parts of the Thames Path, particularly west of Oxford, are subject to flooding during the winter. The river is also Tide, tidal downstream from Teddington Lock and the lower parts of these paths may be underwater if there is a particularly high tide, although the Thames Barrier protects London from catastrophic flooding. The Thames Path uses the river towpath between Inglesham and Putney and available paths elsewhere. Historically, towpath traffic crossed the river using many ferry, ferries, but few of these crossings exist now and some diversion from the towpath is necessary. Description and access to the river The general aim of the pa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |