|
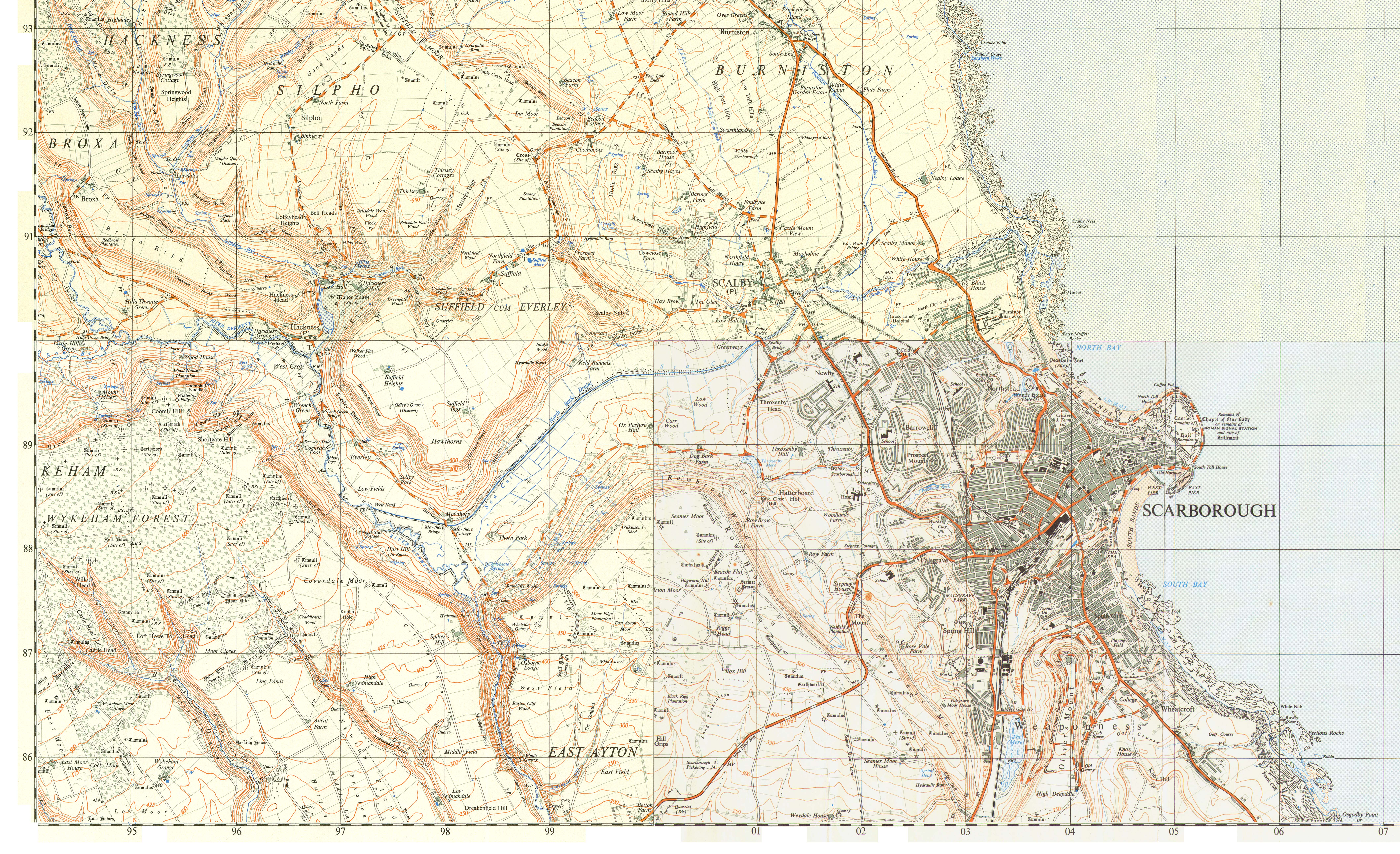
Sea Cut (Scalby Beck)
The Sea Cut (Scalby Beck)Also known as New Cut and Scalby Brook is a small river that enters the North Sea at Scalby Mills, Scarborough, North Yorkshire, England. The beck is fed from local streams in Scalby, Newby and Burniston and other watercourses draining off the nearby hills. It is also a bypass channel for the upper reaches of the River Derwent when it is under flood conditions. History The Sea Cut is fed by small streams and becks mainly draining water away from the hills on the western side of Scalby and Newby. In response to major flooding on the River Derwent in 1799, a canalised beck was cut between Everley and Newby Bridge (the present day A171 road bridge that spans the beck between Newby and Scalby). The Sea Cut was primarily to stop flooding in West and East Ayton further downstream. This means that water flowing in the River Derwent takes before reaching the sea via the Humber Estuary as opposed to the relatively short distance via the Sea Cut. This scheme, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
England
England is a country that is part of the United Kingdom. It shares land borders with Wales to its west and Scotland to its north. The Irish Sea lies northwest and the Celtic Sea to the southwest. It is separated from continental Europe by the North Sea to the east and the English Channel to the south. The country covers five-eighths of the island of Great Britain, which lies in the North Atlantic, and includes over 100 smaller islands, such as the Isles of Scilly and the Isle of Wight. The area now called England was first inhabited by modern humans during the Upper Paleolithic period, but takes its name from the Angles, a Germanic tribe deriving its name from the Anglia peninsula, who settled during the 5th and 6th centuries. England became a unified state in the 10th century and has had a significant cultural and legal impact on the wider world since the Age of Discovery, which began during the 15th century. The English language, the Anglican Church, and Engli ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
William Chapman (engineer)
William Chapman (1749–1832) was an English engineer. Born in Whitby, he worked on the construction of the Old and Humber Docks in Hull, as well as many drainage and canal projects. He is credited with the invention of the bogie and articulation (see Articulated vehicle) for rail vehicles. Personal life William Chapman was born on 7 March 1749 in Whitby. His father, Captain William Chapman, already had three daughters from his first marriage, but William was the first of ten children born to his second wife, Hannah Baynes. He left home in 1765, moving to Barnes, Sunderland, and then to Newcastle. Two years later, he joined the Merchant Navy, and was able to enrol in the Guild of Master Mariners in 1769. Next he set up as a merchant and coal fitter, and with his brother, took out a lease on collieries at St. Anthony's and Wallsend in 1778. Despite initial success, the project ran into financial difficulties, and both men were declared bankrupt in 1782. The failure did not dete ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tabular Hills
The Tabular Hills form an east–west line along the southern bounds of the North York Moors, between Scarborough in the east and Black Hambleton in the west. The name refers to their flat summits composed of hard Corallian limestone, known locally as "nabs". They form the northern boundary of the Vale of Pickering. Description Steep-sided river valleys break through the Tabular Hills to form a broken series of tablet-shaped hills. The most distinctive feature is their northern escarpment, which rises to about 200 ft (60 m) above the moorland to the north. At their western end, beyond the River Rye, they join with the north-south Hambleton Hills, which have a similar geological basis. Striking among the river valleys are Newton Dale and Forge Valley – deep channels formed when an exit to the North Sea for glacial meltwater was denied by the North Sea ice-sheet, pouring over the lowest points in the local landscape during the last ice age and cutting steeply sided channels ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Site Of Importance For Nature Conservation
Site of Nature Conservation Interest (SNCI), Site of Importance for Nature Conservation (SINC) and regionally important geological site (RIGS) are designations used by local authorities in the United Kingdom for sites of substantive local nature conservation and geological value. The Department for Environment, Food and Rural Affairs has recommended the generic term 'local site', which is divided into 'local wildlife site' and 'local geological site'. There are approximately 35,000 local sites, and according to the former Minister for Biodiversity, Jim Knight, they make a vital contribution to delivering the United Kingdom Biodiversity Action Plan, UK and Local Biodiversity Action Plans and the Geodiversity Action Plan, as well as maintaining local natural character and distinctiveness. Sites of Special Scientific Interest (SSSIs) and local nature reserves (LNRs) have statutory protection, but they are only intended to cover a representative selection of sites, and Local sites are ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Second World War
World War II or the Second World War, often abbreviated as WWII or WW2, was a world war that lasted from 1939 to 1945. It involved the vast majority of the world's countries—including all of the great powers—forming two opposing military alliances: the Allies and the Axis powers. World War II was a total war that directly involved more than 100 million personnel from more than 30 countries. The major participants in the war threw their entire economic, industrial, and scientific capabilities behind the war effort, blurring the distinction between civilian and military resources. Aircraft played a major role in the conflict, enabling the strategic bombing of population centres and deploying the only two nuclear weapons ever used in war. World War II was by far the deadliest conflict in human history; it resulted in 70 to 85 million fatalities, mostly among civilians. Tens of millions died due to genocides (including the Holocaust), starvation, ma ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
First World War
World War I (28 July 1914 11 November 1918), often abbreviated as WWI, was one of the deadliest global conflicts in history. Belligerents included much of Europe, the Russian Empire, the United States, and the Ottoman Empire, with fighting occurring throughout Europe, the Middle East, Africa, the Pacific, and parts of Asia. An estimated 9 million soldiers were killed in combat, plus another 23 million wounded, while 5 million civilians died as a result of military action, hunger, and disease. Millions more died in genocides within the Ottoman Empire and in the 1918 influenza pandemic, which was exacerbated by the movement of combatants during the war. Prior to 1914, the European great powers were divided between the Triple Entente (comprising France, Russia, and Britain) and the Triple Alliance (containing Germany, Austria-Hungary, and Italy). Tensions in the Balkans came to a head on 28 June 1914, following the assassination of Archduke Franz Ferdina ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Smallpox
Smallpox was an infectious disease caused by variola virus (often called smallpox virus) which belongs to the genus Orthopoxvirus. The last naturally occurring case was diagnosed in October 1977, and the World Health Organization (WHO) certified the global eradication of the disease in 1980, making it the only human disease to be eradicated. The initial symptoms of the disease included fever and vomiting. This was followed by formation of ulcers in the mouth and a skin rash. Over a number of days, the skin rash turned into the characteristic fluid-filled blisters with a dent in the center. The bumps then scabbed over and fell off, leaving scars. The disease was spread between people or via contaminated objects. Prevention was achieved mainly through the smallpox vaccine. Once the disease had developed, certain antiviral medication may have helped. The risk of death was about 30%, with higher rates among babies. Often, those who survived had extensive scarring of their ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Scalby Railway Station
Scalby railway station was a railway station on the Scarborough & Whitby Railway. History The station opened on 16 July 1885, and served the village of Scalby. It was situated immediately north of Scalby Viaduct and had a single platform, a goods bay, and another siding. The station closed to regular traffic on 2 March 1953, the station building was then converted into a camping cottage. Two camping coaches were positioned here by the North Eastern Region from 1954 to 1956 and four coaches were here from 1957 until 1964. Occasional trains stopped for users of these facilities until final closure in 1964, Quick (2022) notes that two or three trains each way had definite calls in the working timetable of June 1961. In 1974 the station was completely demolished, and a road called Chichester Close has been built on the site since. Some of the stonework has been reused as corner stones, embedded in the brickwork, of houses in this street. Scalby Viaduct still stands, and has fou ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mill Race
A mill race, millrace or millrun, mill lade (Scotland) or mill leat (Southwest England) is the current of water that turns a water wheel, or the channel ( sluice) conducting water to or from a water wheel. Compared with the broad waters of a mill pond, the narrow current is swift and powerful. The race leading to the water wheel on a wide stream or mill pond is called the head race (or headraceDictionary.com, word definition), and the race leading away from the wheel is called the tail raceChamber's Twentieth Century Dictionary, 1968, p=674 (or tailrace). A mill race has many geographically specific names, such as ''leat, lade, flume, goit, penstock''. These words all have more precise definitions and meanings will differ elsewhere. The original undershot waterwheel, described by Vitruvius, was a 'run of the river wheel' placed so a fast flowing stream would press against and turn the bottom of a bucketed wheel. In the first meaning of the term, the millrace was the stream; in t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Youth Hostel
A hostel is a form of low-cost, short-term shared sociable lodging where guests can rent a bed, usually a bunk bed in a dormitory, with shared use of a lounge and sometimes a kitchen. Rooms can be mixed or single-sex and have private or shared bathrooms. Private rooms may also be available, but the property must offer dormitories to be considered a hostel. Hostels are popular forms of lodging for backpackers. They are part of the sharing economy. Benefits of hostels include lower costs and opportunities to meet people from different places, find travel partners, and share travel ideas. Some hostels, such as Zostel in India or Hostelling International, cater to a niche market of travelers. For example, one hostel might feature in-house social gatherings such as movie nights or communal dinners, another might feature local tours, one might be known for its parties, and another might have a quieter place to relax in serenity, or be located on the beach. Newer hostels focus on a more ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Coastal Erosion
Coastal erosion is the loss or displacement of land, or the long-term removal of sediment and rocks along the coastline due to the action of waves, currents, tides, wind-driven water, waterborne ice, or other impacts of storms. The landward retreat of the shoreline can be measured and described over a temporal scale of tides, seasons, and other short-term cyclic processes. Coastal erosion may be caused by hydraulic action, abrasion, impact and corrosion by wind and water, and other forces, natural or unnatural. On non-rocky coasts, coastal erosion results in rock formations in areas where the coastline contains rock layers or fracture zones with varying resistance to erosion. Softer areas become eroded much faster than harder ones, which typically result in landforms such as tunnels, bridges, columns, and pillars. Over time the coast generally evens out. The softer areas fill up with sediment eroded from hard areas, and rock formations are eroded away. Also erosion commonly ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |