|
Sea-to-Sky Corridor
The Sea-to-Sky Corridor, often referred to as the Corridor or the Sea to Sky Country, is a region in British Columbia spreading from Horseshoe Bay through Whistler to the Pemberton Valley and sometimes beyond to include Birken and D'Arcy. From Whistler on up, the region overlaps with the older and more historic Lillooet Country, of which Squamish, at the region's centre, was once the southward extension in the days when it was the rail-port terminus from the Interior, via Lillooet, and accessible from the Lower Mainland only by sea. Most of the region is in the Squamish-Lillooet Regional District, although south of Britannia Beach a small part of the region is in the Greater Vancouver Regional District. The term "Corridor" refers to the alignment of the region's towns along Highway 99, also known as the Sea to Sky Highway, which links together the regions' three main centres - Squamish, Whistler and Pemberton. There is little development other than resource extraction ou ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
List Of Regions Of Canada
The list of regions of Canada is a summary of geographical areas on a hierarchy that ranges from national (groups of provinces and territories) at the top to local regions and sub-regions of provinces at the bottom. Administrative regions that rank below a province and above a municipality are also included if they have a comprehensive range of functions compared to the limited functions of specialized government agencies. Some provinces and groups of provinces are also quasi-administrative regions at the federal level for purposes such as representation in the Senate of Canada. However regional municipalities (or regional districts in British Columbia) are included with local municipalities in the article List of municipalities in Canada. National regions The provinces and territories are sometimes grouped into regions, listed here from west to east by province, followed by the three territories. Seats in the Senate are equally divided among four regions: the West, Ontario, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Squamish, British Columbia
Squamish (; Sḵwx̱wú7mesh sníchim: Sḵwx̱wú7mesh, ; 2016 census population 19,512) is a community and a district municipality in the Canadian province of British Columbia, located at the north end of Howe Sound on the Sea to Sky Highway. The population of the Squamish census agglomeration, which includes First Nation reserves of the Squamish Nation although they are not governed by the municipality, is 19,893. Indigenous Squamish people have lived in the area for thousands of years. The town of Squamish had its beginning during the construction of the Pacific Great Eastern Railway in the 1910s. It was the first southern terminus of that railway (now a part of CN). The town remains important in the operations of the line and also the port. Forestry has traditionally been the main industry in the area, and the town's largest employer was the pulp mill operated by Western Forest Products. However, Western's operations in Squamish permanently ceased on January 26, 2006. Bef ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Stawamus (village)
Stawamus (St'a7mes or , in the original Squamish language )) is a village at the head of Howe Sound, located on Stawamus Indian Reserve No. 24, at the mouth of the Stawamus River and Mamquam Blind Channel, 1km south of Squamish, British Columbia. The village is home to the indigenous Squamish people and houses satellite offices of the Squamish Nation. The village is also the centre for administrative, educational and health services in the Upper Squamish region of the Squamish Nation. Population The 2011 National Household Survey of the Census of Canada gives the population of the Indian reserve encompassing this village as 95, 10 of whom are non-aboriginal in origin and are of British Isles ethnic origin). The Community Profile for the same year, however, says 97 and 100. See also * History of the Squamish people *Squamish Nation The Squamish Nation, Sḵwx̱wú7mesh Úxwumixw () in Sḵwx̱wú7mesh Sníchim (Squamish language), is an Indian Act government originally imp ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Shannon Falls
Shannon Falls Provincial Park is a provincial park in British Columbia, Canada. It is located from Vancouver and south of Squamish along the Sea to Sky Highway. The park covers an area of . The main point of interest is Shannon Falls, the third highest waterfall in BC, where water falls from a height of . The falls are named after a William Shannon who first settled the property in 1889 and made bricks in the area. The park also protects the surrounding area on the north-east shore of the Howe Sound. Just to the north are Murrin Provincial Park and Stawamus Chief Provincial Park. Located immediately across the highway from Shannon Falls is a privately operated campground and restaurant, plus the entrance to the Darrell Bay ferry terminal for Woodfibre (Darrell Bay was formerly named Shannon Bay). The Sea to Sky Gondola adjoins the park. The gondola line was deliberately cut in 2019 and again in 2020 after repairs. The falls and adjoining woods are commonly used in television ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Darrell Bay, British Columbia
Darrell Bay, formerly Shannon Bay, is a bay and associated ferry terminal and unincorporated settlement on the northeast coast of Howe Sound to the south of Squamish, British Columbia, Canada Canada is a country in North America. Its ten provinces and three territories extend from the Atlantic Ocean to the Pacific Ocean and northward into the Arctic Ocean, covering over , making it the world's second-largest country by tot .... It is adjacent to Shannon Falls Provincial Park, which lies immediately across BC Highway 99 (the Sea to Sky Highway). Known locally as Shannon Bay until 1949, after William Shannon, one of the original landholders in the vicinity and the namesake of Shannon Falls, it was renamed by the Hydrographic Service as the result of a petition from Darrell Burgess, who owned a fishing camp at this spot (the locality was already known as Burgess Camp, though the bay was Shannon Bay). No reason was indicated why the established local name was not s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Furry Creek, British Columbia
Furry Creek is a community in the Canadian province of British Columbia, located on Howe Sound in the Squamish-Lillooet Regional District, north of Vancouver and south of Squamish. History The creek was named in the 1870s after early prospector and settler Oliver Furry. Loggers worked the slopes, and a two adits from the Britannia Creek mine opened into Furry Creek where logging camp A logging camp (or lumber camp) is a transitory work site used in the logging industry. Before the second half of the 20th century, these camps were the primary place where lumberjacks would live and work to fell trees in a particular area. Many ... supplied timbers for mine shoring in the early 1900s. Dams on Phyllis and Marion Lake and Furry Creek redirected water from Furry Creek to the Britannia mine for power generation. Later in the century a gravel pit operated in the area. Cabins and borstal at nearby Porteau Cove made the area sparsely populated for many years, with some camping an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lions Bay, British Columbia
Lions Bay ( Sḵwx̱wú7mesh: Ch'ích'iyúy Elx̱wíḵn, ) is a small residential community in British Columbia, Canada, located between Vancouver and Squamish on the steep eastern shore of Howe Sound. In the 2021 census the community had a population of 1,390, BC's 36th smallest municipality by population. At , it is BC's 10th smallest municipality by land area. Originally a boat-access summer camping destination for Vancouverites, Lions Bay began to be permanently settled in the 1960s. The community incorporated as a village municipality in January 1971. History In 1889, distinctive twin peaks in the North Shore mountains were dubbed the Lions by a Judge Gray, for their supposed resemblance from Vancouver to the lion statues around Nelson's Column on London's Trafalgar Square. They are the Transformed Sisters, Ch'ich'iyúy Elxwíkn, of Coast Salish legend. The small bay on Howe Sound where pre-road climbers were dropped off to climb them was the "Lions Bay." The exte ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sunshine Coast (British Columbia)
The Sunshine Coast is a geographic subregion of the British Columbia Coast that generally comprises the regional districts of qathet and Sunshine Coast. While populous and frequently visited by tourists, the Sunshine Coast can be reached only by ferry (commonly BC Ferries) or by floatplane, as no access roads have been built around or across the fjords separating it from the rest of the province. Geography The Sunshine Coast is a subregion of the mainland coast of British Columbia. It is bound by Howe Sound to the southeast, Desolation Sound to the northwest, the Pacific Ranges to the northeast, and the Strait of Georgia to the southwest. The region is bisected by Jervis Inlet. The region features a coastal lowland that gradually transitions to steep-sided mountains as you move toward the northeast. The major islands of the Sunshine Coast include Anvil Island, Gambier Island, Goat Island, Hernando Island, Keats Island, Savary Island, and most of the Northern Gulf Islands. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
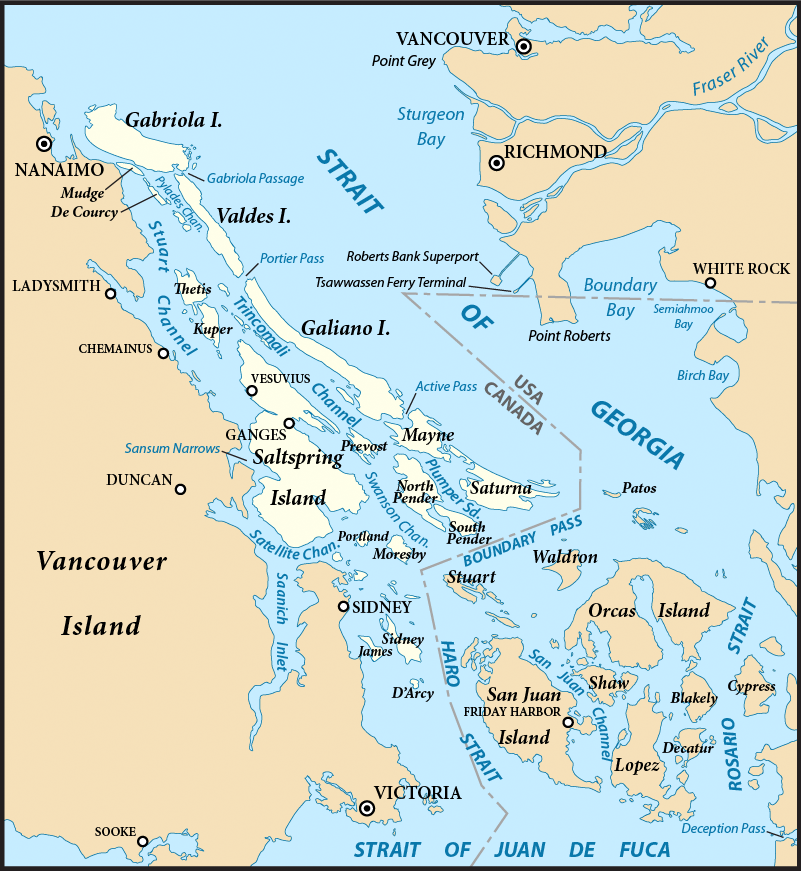
Gulf Islands
The Gulf Islands are a group of islands in the Salish Sea between Vancouver Island and the mainland coast of British Columbia. Etymology The name "Gulf Islands" comes from "Gulf of Georgia," the original term used by George Vancouver in his mapping of the southern part of the archipelago and which before the San Juan Island dispute also was taken to include what have since been called the San Juan Islands. Strictly speaking, the Strait of Georgia is only the wide, open waters of the main strait between the mainland and Vancouver Island, and does not officially refer to the adjoining waters between the islands and Vancouver Island but has become a common misnomer for the entire Gulf, which includes waters such as Active Pass (between Galiano Island and Mayne Island), Trincomali Channel (between Galiano Island and Saltspring Island), Sansum Narrows (between Saltspring Island and Vancouver Island), and Malaspina Strait (between Texada Island and the mainland around Powe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cheakamus Canyon
{{disambiguation, geo ...
Cheakamus is an anglicization of Chiyakmesh, the Skwxw7mesh language name for one of their villages, now located on Cheakamus Indian Reserve No. 11. Cheakamus may also refer to: *Cheakamus River *Cheakamus Lake *Cheakamus Powerhouse, on the Squamish River * ''Cheakamus'' (ship), see Union Steamship Company of British Columbia The Union Steamship Company of British Columbia was a pioneer firm on coastal British Columbia. It was founded in November 1889 by John Darling, a director of the Union Steamship Company of New Zealand, and nine local businessmen. The company be ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
British Columbia Highway 99
Highway 99 is a provincial highway in British Columbia that serves Greater Vancouver and the Squamish–Lillooet corridor over a length of . It is a major north–south artery within Vancouver and connects the city to several suburbs as well as the U.S. border, where it continues south as Interstate 5. The central section of the route, also known as the Sea to Sky Highway, serves the communities of Squamish, Whistler, and Pemberton. Highway 99 continues through Lillooet and ends at a junction with Highway 97 near Cache Creek. The highway's number, assigned in 1940, was derived from former U.S. Route 99, the predecessor to Interstate 5 and a major route for the U.S. West Coast. Highway 99 originally comprised the King George Highway in Surrey, portions of Kingsway from New Westminster to Vancouver, and local streets. It was extended across the Lions Gate Bridge and to Horseshoe Bay in the 1950s along a new highway that would later be incorporated into Highway 1 (the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |