|
Scott River (California)
The Scott River is a U.S. Geological Survey. National Hydrography Dataset high-resolution flowline dataThe National Map accessed March 9, 2011 river in Siskiyou County, California, United States. It is a tributary of the Klamath River, one of the largest rivers in California. History Historically, fur trappers called the river the Beaver River, before the Hudson's Bay Company nearly extirpated beaver from the area in the early 19th century. Scott Valley was first entered ( first Europeans) Stephen Meek, Thomas McKay, George Adolphus Duzel and 16 other Hudson's Bay trappers in 1836. In 1850 alone, Meek reportedly trapped 1,800 beaver in Scott Valley, which was then known as Beaver Valley. Meek, who had hunted all over the West, declared the Beaver Valley one of the best places he had ever seen to trap beaver and hunt game, and returned to retire there at the Josiah Doll ranch from 1871 until his death in 1889 at the age of 90. The 1850 discovery of gold during the California Gold Ru ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
United States
The United States of America (U.S.A. or USA), commonly known as the United States (U.S. or US) or America, is a country primarily located in North America. It consists of 50 states, a federal district, five major unincorporated territories, nine Minor Outlying Islands, and 326 Indian reservations. The United States is also in free association with three Pacific Island sovereign states: the Federated States of Micronesia, the Marshall Islands, and the Republic of Palau. It is the world's third-largest country by both land and total area. It shares land borders with Canada to its north and with Mexico to its south and has maritime borders with the Bahamas, Cuba, Russia, and other nations. With a population of over 333 million, it is the most populous country in the Americas and the third most populous in the world. The national capital of the United States is Washington, D.C. and its most populous city and principal financial center is New York City. Paleo-Americ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Forestry
Forestry is the science and craft of creating, managing, planting, using, conserving and repairing forests, woodlands, and associated resources for human and environmental benefits. Forestry is practiced in plantations and natural stands. The science of forestry has elements that belong to the biological, physical, social, political and managerial sciences. Forest management play essential role of creation and modification of habitats and affect ecosystem services provisioning. Modern forestry generally embraces a broad range of concerns, in what is known as multiple-use management, including: the provision of timber, fuel wood, wildlife habitat, natural water quality management, recreation, landscape and community protection, employment, aesthetically appealing landscapes, biodiversity management, watershed management, erosion control, and preserving forests as " sinks" for atmospheric carbon dioxide. Forest ecosystems have come to be seen as the most important componen ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rivers Of Siskiyou County, California
A river is a natural flowing watercourse, usually freshwater, flowing towards an ocean, sea, lake or another river. In some cases, a river flows into the ground and becomes dry at the end of its course without reaching another body of water. Small rivers can be referred to using names such as creek, brook, rivulet, and rill. There are no official definitions for the generic term river as applied to geographic features, although in some countries or communities a stream is defined by its size. Many names for small rivers are specific to geographic location; examples are "run" in some parts of the United States, "burn" in Scotland and northeast England, and "beck" in northern England. Sometimes a river is defined as being larger than a creek, but not always: the language is vague. Rivers are part of the water cycle. Water generally collects in a river from precipitation through a drainage basin from surface runoff and other sources such as groundwater recharge, sprin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
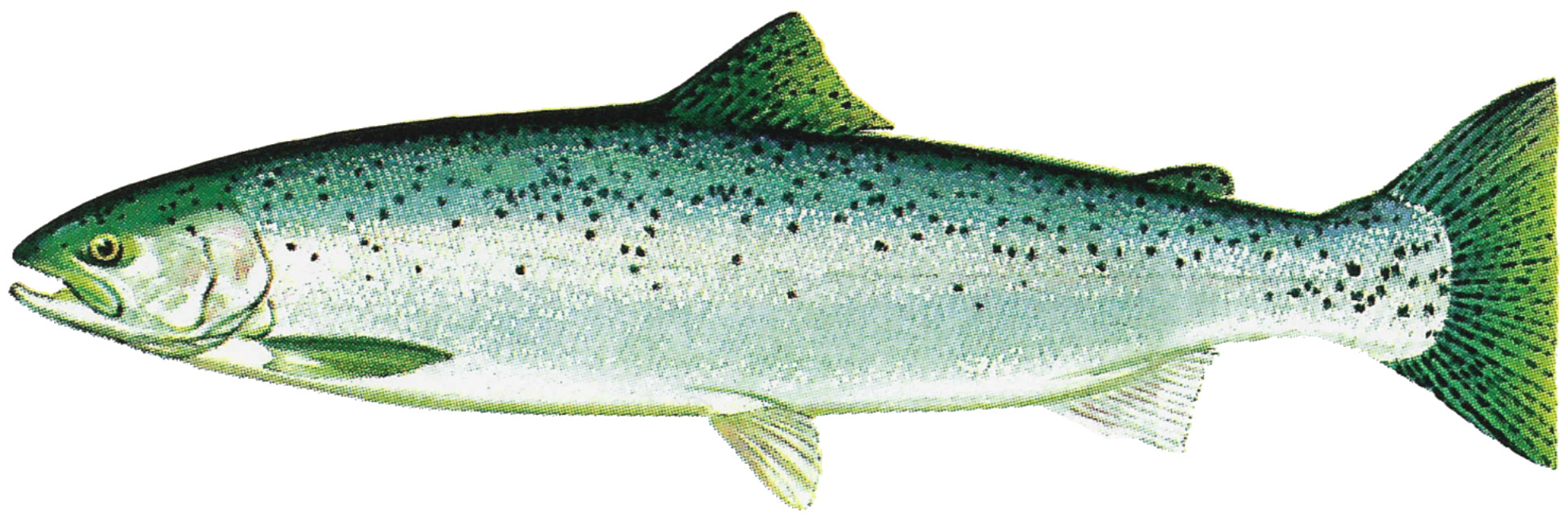
Rainbow Trout
The rainbow trout (''Oncorhynchus mykiss'') is a species of trout native to cold-water tributaries of the Pacific Ocean in Asia and North America. The steelhead (sometimes called "steelhead trout") is an anadromous (sea-run) form of the coastal rainbow trout or Columbia River redband trout that usually returns to freshwater to spawn after living two to three years in the ocean. Freshwater forms that have been introduced into the Great Lakes and migrate into tributaries to spawn are also called steelhead. Adult freshwater stream rainbow trout average between , while lake-dwelling and anadromous forms may reach . Coloration varies widely based on subspecies, forms, and habitat. Adult fish are distinguished by a broad reddish stripe along the lateral line, from gills to the tail, which is most vivid in breeding males. Wild-caught and hatchery-reared forms of the species have been transplanted and introduced for food or sport in at least 45 countries and every continent except ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bridge Creek (John Day River)
Bridge Creek is a tributary of the John Day River in the U.S. state of Oregon. Part of the drainage basin of the Columbia River, its watershed covers in Wheeler County. From its headwaters in the Ochoco Mountains in central Oregon, the creek flows generally northeast for about from Mount Pisgah in the Bridge Creek Wilderness to the small city of Mitchell on U.S. Route 26. From Mitchell, it flows generally northwest for about , passing through the Painted Hills unit of the John Day Fossil Beds National Monument before meeting the John Day River. Bridge Creek is subject to occasional flash floods, which have affected Mitchell as well as rural areas nearby. Surging water along the creek, which flows parallel to Main Street in Mitchell, caused great damage in 1884 and 1904. A third flood occurred on July 13, 1956, shortly after an intense thunderstorm in the Ochoco Mountains. The creek is usually less than deep in Mitchell during July. Minutes after the thunderstorm, a s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
NOAA
The National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration (abbreviated as NOAA ) is an United States scientific and regulatory agency within the United States Department of Commerce that forecasts weather, monitors oceanic and atmospheric conditions, charts the seas, conducts deep sea exploration, and manages fishing and protection of marine mammals and endangered species in the U.S. exclusive economic zone. Purpose and function NOAA's specific roles include: * ''Supplying Environmental Information Products''. NOAA supplies to its customers and partners information pertaining to the state of the oceans and the atmosphere, such as weather warnings and forecasts via the National Weather Service. NOAA's information services extend as well to climate, ecosystems, and commerce. * ''Providing Environmental Stewardship Services''. NOAA is a steward of U.S. coastal and marine environments. In coordination with federal, state, local, tribal and international authorities, NOAA manages the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tailings
In mining, tailings are the materials left over after the process of separating the valuable fraction from the uneconomic fraction (gangue) of an ore. Tailings are different to overburden, which is the waste rock or other material that overlies an ore or mineral body and is displaced during mining without being processed. The extraction of minerals from ore can be done two ways: placer mining, which uses water and gravity to concentrate the valuable minerals, or hard rock mining, which pulverizes the rock containing the ore and then relies on chemical reactions to concentrate the sought-after material. In the latter, the extraction of minerals from ore requires comminution, i.e., grinding the ore into fine particles to facilitate extraction of the target element(s). Because of this comminution, tailings consist of a slurry of fine particles, ranging from the size of a grain of sand to a few micrometres. Mine tailings are usually produced from the mill in slurry form, which i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mercury (element)
Mercury is a chemical element with the symbol Hg and atomic number 80. It is also known as quicksilver and was formerly named hydrargyrum ( ) from the Greek words, ''hydor'' (water) and ''argyros'' (silver). A heavy, silvery d-block A block of the periodic table is a set of elements unified by the atomic orbitals their valence electrons or vacancies lie in. The term appears to have been first used by Charles Janet. Each block is named after its characteristic orbital: s-blo ... element, mercury is the only metallic element that is known to be liquid at standard temperature and pressure; the only other element that is liquid under these conditions is the halogen bromine, though metals such as caesium, gallium, and rubidium melt just above room temperature. Mercury occurs in deposits throughout the world mostly as cinnabar (mercuric sulfide). The red pigment vermilion is obtained by Mill (grinding), grinding natural cinnabar or synthetic mercuric sulfide. Mercury is used in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dredging
Dredging is the excavation of material from a water environment. Possible reasons for dredging include improving existing water features; reshaping land and water features to alter drainage, navigability, and commercial use; constructing dams, dikes, and other controls for streams and shorelines; and recovering valuable mineral deposits or marine life having commercial value. In all but a few situations the excavation is undertaken by a specialist floating plant, known as a dredger. Dredging is carried out in many different locations and for many different purposes, but the main objectives are usually to recover material of value or use, or to create a greater depth of water. Dredges have been classified as suction or mechanical. Dredging has significant environmental impacts: it can disturb marine sediments, leading to both short- and long-term water pollution, destroy important seabed ecosystems, and can release human-sourced toxins captured in the sediment. Description ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Farm
A farm (also called an agricultural holding) is an area of land that is devoted primarily to agricultural processes with the primary objective of producing food and other crops; it is the basic facility in food production. The name is used for specialized units such as arable farms, vegetable farms, fruit farms, dairy, pig and poultry farms, and land used for the production of natural fiber, biofuel and other commodities. It includes ranches, feedlots, orchards, plantations and estates, smallholdings and hobby farms, and includes the farmhouse and agricultural buildings as well as the land. In modern times the term has been extended so as to include such industrial operations as wind farms and fish farms, both of which can operate on land or sea. There are about 570 million farms in the world, most of which are small and family-operated. Small farms with a land area of fewer than 2 hectares operate about 1% of the world's agricultural land, and family farms comprise about ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Grazing
In agriculture, grazing is a method of animal husbandry whereby domestic livestock are allowed outdoors to roam around and consume wild vegetations in order to convert the otherwise indigestible (by human gut) cellulose within grass and other forages into meat, milk, wool and other animal products, often on land unsuitable for arable farming. Farmers may employ many different strategies of grazing for optimum production: grazing may be continuous, seasonal, or rotational within a grazing period. Longer rotations are found in ley farming, alternating arable and fodder crops; in rest rotation, deferred rotation, and mob grazing, giving grasses a longer time to recover or leaving land fallow. Patch-burn sets up a rotation of fresh grass after burning with two years of rest. Conservation grazing proposes to use grazing animals to improve the biodiversity of a site, but studies show that the greatest benefit to biodiversity comes from removing grazing animals from the landscape. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Drainage Basin
A drainage basin is an area of land where all flowing surface water converges to a single point, such as a river mouth, or flows into another body of water, such as a lake or ocean. A basin is separated from adjacent basins by a perimeter, the '' drainage divide'', made up of a succession of elevated features, such as ridges and hills. A basin may consist of smaller basins that merge at river confluences, forming a hierarchical pattern. Other terms for a drainage basin are catchment area, catchment basin, drainage area, river basin, water basin, and impluvium. In North America, they are commonly called a watershed, though in other English-speaking places, "watershed" is used only in its original sense, that of a drainage divide. In a closed drainage basin, or endorheic basin, the water converges to a single point inside the basin, known as a sink, which may be a permanent lake, a dry lake, or a point where surface water is lost underground. Drainage basins are similar ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |




.png)
