|
Scorpion Sting
A scorpion sting is an injury caused by the stinger of a scorpion resulting in the medical condition known as scorpionism, which may vary in severity. The anatomical part of the scorpion that delivers the sting is called a "telson". In typical cases, scorpion stings usually result in pain, paresthesia, and variable swelling. In serious cases, scorpion stings may involve the envenomation of humans by toxic scorpions, which may result in extreme pain, serious illness, or even death depending on the toxicity of the venom. Most scorpion stings range in severity from minor swelling to medically significant lesions, with only a few able to cause severe allergic, neurotic or necrotic reactions. However, scorpion stings account for approximately 3,000 deaths a year worldwide. The Brazilian yellow scorpion ('' Tityus serrulatus'') is one species known for being especially dangerous, being responsible for most scorpion sting fatalities in South America. Scorpion stings are seen all over the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Stinger
A stinger (or sting) is a sharp organ found in various animals (typically insects and other arthropods) capable of injecting venom, usually by piercing the epidermis of another animal. An insect sting is complicated by its introduction of venom, although not all stings are venomous. Bites, which can introduce saliva as well as additional pathogens and diseases, are often confused with stings, and vice versa. Specific components of venom are believed to give rise to an allergic reaction, which in turn produces skin lesions that may vary from a small itching weal, or slightly elevated area of the skin, to large areas of inflamed skin covered by vesicles and crusted lesions. Stinging insects produce a painful swelling of the skin, the severity of the lesion varying according to the location of the sting, the identity of the insect and the sensitivity of the subject. Many species of bees and wasps have two poison glands, one gland secreting a toxin in which formic acid is one ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sub-Saharan Africa
Sub-Saharan Africa is, geographically, the area and regions of the continent of Africa that lies south of the Sahara. These include West Africa, East Africa, Central Africa, and Southern Africa. Geopolitically, in addition to the List of sovereign states and dependent territories in Africa, African countries and territories that are situated fully in that specified region, the term may also include polities that only have part of their territory located in that region, per the definition of the United Nations (UN). This is considered a non-standardized geographical region with the number of countries included varying from 46 to 48 depending on the organization describing the region (e.g. UN, WHO, World Bank, etc.). The Regions of the African Union, African Union uses a different regional breakdown, recognizing all 55 member states on the continent - grouping them into 5 distinct and standard regions. The term serves as a grouping counterpart to North Africa, which is instead ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Buthidae
The Buthidae are the largest family of scorpions, containing about 100 genera and 1339 species as of 2022. A few very large genera (''Ananteris'', ''Centruroides'', '' Compsobuthus'', or '' Tityus'') are known, but a high number of species-poor or monotypic ones also exist. New taxa are being described at a rate of several new species per year. They have a osmopolitandistribution throughout tropical and subtropical environments worldwide. Together with four other families, the Buthidae make up the superfamily Buthoidea. The family was established by Carl Ludwig Koch in 1837. Around 20 species of medically important (meaning potentially lethal to humans) scorpions are known, and all but one of these ('' Hemiscorpius lepturus'') are members of the Buthidae. In dead specimens, the spine beneath the stinger, characteristic for this family, can be observed. List of genera and number of species The following genera are recognised in the family Buthidae: * '' Aegaeobuthus'' Kovarik, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vasoactive Intestinal Polypeptide
Vasoactive intestinal peptide, also known as vasoactive intestinal polypeptide or VIP, is a peptide hormone that is vasoactive in the intestine. VIP is a peptide of 28 amino acid residues that belongs to a glucagon/secretin superfamily, the ligand of class II G protein–coupled receptors. VIP is produced in many tissues of vertebrates including the gut, pancreas, and suprachiasmatic nuclei of the hypothalamus in the brain. VIP stimulates contractility in the heart, causes vasodilation, increases glycogenolysis, lowers arterial blood pressure and relaxes the smooth muscle of trachea, stomach and gallbladder. In humans, the vasoactive intestinal peptide is encoded by the ''VIP'' gene. VIP has a half-life (t½) in the blood of about two minutes. Function In the body VIP has an effect on several tissues: In the digestive system, VIP seems to induce smooth muscle relaxation (lower esophageal sphincter, stomach, gallbladder), stimulate secretion of water into pancreatic juice an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Agitoxin
Agitoxin is a toxin found in the venom of the scorpion '' Leiurus quinquestriatus hebraeus'' (yellow scorpion). Other toxins found in this species include charybdotoxin (CTX). CTX is a close homologue of Agitoxin. Structure Agitoxin can be purified using HPLC techniques. Primary structure: Three types of agitoxin can be distinguished, each identified as comprising 38 amino acids. They are highly homologous, differing only in the identity of the residues at positions 7, 15, 29 and 31. *Agitoxin-1 Gly-Val-Pro-Ile-Asn-Val-Lys-Cys-Thr-Gly-Ser-Pro-Gln-Cys-Leu-Lys-Pro-Cys-Lys-Asp-Ala-Gly-Met-Arg-Phe-Gly-Lys-Cys-Ile-Asn-Gly-Lys-Cys-His-Cys-Thr-Pro-Lys (GVPINVKCTGSPQCLKPCKDAGMRFGKCINGKCHCTPK, molecular weight = 4014.87 Da, molecular formula = C169H278N52O47S7) *Agitoxin-2 Gly-Val-Pro-Ile-Asn-Val-Ser-Cys-Thr-Gly-Ser-Pro-Gln-Cys-Ile-Lys-Pro-Cys-Lys-Asp-Ala-Gly-Met-Arg-Phe-Gly-Lys-Cys-Met-Asn-Arg-Lys-Cys-His-Cys-Thr-Pro-Lys (GVPINVSCTGSPQCIKPCKDAGMRFGKCMNRKCHCTPK, molecular weight ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
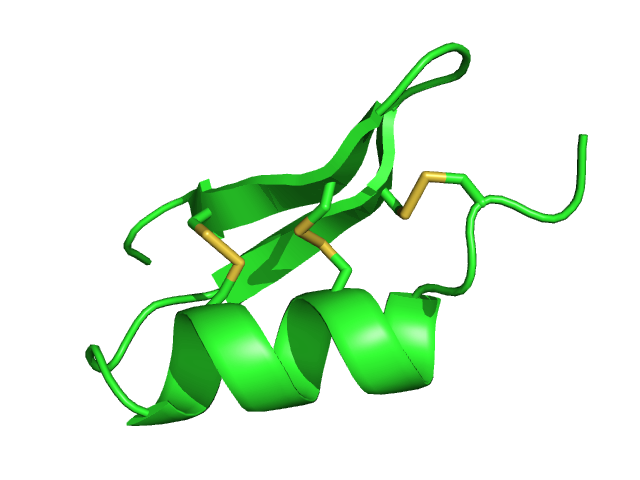
Scyllatoxin
Scyllatoxin (also leiurotoxin I) is a toxin, from the scorpion '' Leiurus quinquestriatus hebraeus'', which blocks small-conductance Ca2+-activated K+ channels. It is named after Scylla, a sea monster from Greek mythology. Charybdotoxin is also found in the venom from the same species of scorpion, and is named after the sea monster Charybdis. In Greek mythology, Scylla and Charybdis lived on rocks on opposing sides of a narrow strait of water. Sources Scyllatoxin is one of the components of the venom of the Israeli scorpion ''‘Leiurus quinquestriatus hebraeus’''. It consists of only 0.02% of the total protein in crude venom. Chemistry Leiurotoxin I is a 31-residue peptide (sequence AFCNLRMCQLSCRSLGLLGKCIGDKCECVKH-NH2), with a helix and a short antiparallel β-sheet. This toxin is stabilized by disulfide bonds: Cys8-Cys26 and Cys12-Cys28 is bound to the β-sheet, while Cys3-Cys21 is bound to an N-terminal segment preceding the helix. Leiurotoxin adopts the ά/β motif. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Charybdotoxin
Charybdotoxin (CTX) is a 37 amino acid neurotoxin from the venom of the scorpion '' Leiurus quinquestriatus hebraeus'' (''deathstalker'') that blocks calcium-activated potassium channels. This blockade causes hyperexcitability of the nervous system. It is a close homologue of agitoxin and both toxins come from ''Leiurus quinquestriatus hebraeus''. It is named after Charybdis, a sea monster from Greek myth. Chemical properties Family The Charybdotoxin family of scorpion toxins is a group of small peptides that has many family members, such as the pandinotoxin, derived from the venom of scorpion Pandinus imperator. Structure Scorpions such as the deathstalker paralyze their prey by injecting a potent mix of peptide toxins. Charybdotoxin, a 37 amino acid, 4 kDa neurotoxin with the molecular formula C176H277N57O55S7, is one of the peptide toxins that can be extracted from the venom of the scorpion. Its structure is very similar to that of margatoxin. Charybdotoxin contains three d ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chlorotoxin
Chlorotoxin is a 36-amino acid peptide found in the venom of the deathstalker scorpion (''Leiurus quinquestriatus'') which blocks small-conductance chloride channels. The fact that chlorotoxin binds preferentially to glioma cells has allowed the development of methods for the treatment and diagnosis of several types of cancer. Sources Chlorotoxin can be purified from crude leiurus, which belongs to the scorpion toxin protein superfamily. Chemistry Chlorotoxin is a small toxin and at pH 7 is highly positively charged. It is a peptide consisting of 36 amino acids, with 8 cysteines forming 4 disulfide bonds. Chlorotoxin has a considerable sequence homology to the class of small insectotoxins. Target Chlorotoxin is the first reported high-affinity peptide ligand for Cl− channels and it blocks small conductance chloride channels. Each chloride channel can be closed by only one ligand molecule. Using a recombinant chlorotoxin it was demonstrated that chlorotoxin specifical ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Neurotoxin
Neurotoxins are toxins that are destructive to nerve tissue (causing neurotoxicity). Neurotoxins are an extensive class of exogenous chemical neurological insultsSpencer 2000 that can adversely affect function in both developing and mature nervous tissue.Olney 2002 The term can also be used to classify endogenous compounds, which, when abnormally contacted, can prove neurologically toxic. Though neurotoxins are often neurologically destructive, their ability to specifically target neural components is important in the study of nervous systems. Common examples of neurotoxins include lead, ethanol (drinking alcohol), glutamate,Choi 1987 nitric oxide, botulinum toxin (e.g. Botox), tetanus toxin,Simpson 1986 and tetrodotoxin. Some substances such as nitric oxide and glutamate are in fact essential for proper function of the body and only exert neurotoxic effects at excessive concentrations. Neurotoxins inhibit neuron control over ion concentrations across the cell membrane, or com ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Serotonin
Serotonin () or 5-hydroxytryptamine (5-HT) is a monoamine neurotransmitter. Its biological function is complex and multifaceted, modulating mood, cognition, reward, learning, memory, and numerous physiological processes such as vomiting and vasoconstriction. Approximately 90% of the serotonin that the body produces is in the intestinal tract. Biochemically, the indoleamine molecule derives from the amino acid tryptophan, via the (rate-limiting) hydroxylation of the 5 position on the ring (forming the intermediate 5-hydroxytryptophan), and then decarboxylation to produce serotonin. Serotonin is primarily found in the enteric nervous system located in the gastrointestinal tract (GI tract). However, it is also produced in the central nervous system (CNS), specifically in the raphe nuclei located in the brainstem, Merkel cells located in the skin, pulmonary neuroendocrine cells and taste receptor cells in the tongue. Additionally, serotonin is stored in blood platelets and is ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Antivenom
Antivenom, also known as antivenin, venom antiserum, and antivenom immunoglobulin, is a specific treatment for envenomation. It is composed of antibodies and used to treat certain venomous bites and stings. Antivenoms are recommended only if there is significant toxicity or a high risk of toxicity. The specific antivenom needed depends on the species involved. It is given by injection. Side effects may be severe. They include serum sickness, shortness of breath, and allergic reactions including anaphylaxis. Antivenom is traditionally made by collecting venom from the relevant animal and injecting small amounts of it into a domestic animal. The antibodies that form are then collected from the domestic animal's blood and purified. Versions are available for spider bites, snake bites, fish stings, and scorpion stings. Due to the high cost of producing antibody-based antivenoms and their short shelf lives when not refrigerated, alternative methods of production of antivenoms ar ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Arizona Bark Scorpion
:''The striped bark scorpion and the closely related Baja California bark scorpion are also called bark scorpions.'' The Arizona bark scorpion (''Centruroides sculpturatus'', once included in ''Centruroides exilicauda'') is a small light brown scorpion common to the Sonoran Desert in the southwestern United States and northwestern Mexico. An adult male can reach 8 cm in length (3.14 inches), while a female is slightly smaller, with a maximum length of 7 cm (2.75 inches). Predators Arizona bark scorpions are eaten by a wide variety of animals such as pallid bats, birds (especially owls), reptiles, and other vertebrates. Some examples include spiders, snakes, peccaries, rodents, and other scorpions. Development, pesticides and collecting scorpions for research or the pet trade also reduces the bark scorpion population. The painful and potentially deadly venom of Arizona bark scorpions has little effect on grasshopper mice. Scientists have found the scorpi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |