|
Scholte Wave
A Scholte wave is a surface wave (interface wave) propagating at an interface between a fluid and an elastic solid medium (such as an interface between water and sand). The wave is of maximum intensity at the interface and decreases exponentially away from the interface into both the fluid and the solid medium. It is named after J. G. Scholte, who discovered it in 1947. This wave is similar to a Stoneley wave, which propagates at a solid-solid interface, and a Rayleigh wave Rayleigh waves are a type of surface acoustic wave that travel along the surface of solids. They can be produced in materials in many ways, such as by a localized impact or by piezo-electric transduction, and are frequently used in non-destructi ..., which propagates at a vacuum-solid interface. References {{Reflist Surface waves ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Surface Wave
In physics, a surface wave is a mechanical wave that propagates along the interface between differing media. A common example is gravity waves along the surface of liquids, such as ocean waves. Gravity waves can also occur within liquids, at the interface between two fluids with different densities. Elastic surface waves can travel along the surface of solids, such as '' Rayleigh'' or ''Love'' waves. Electromagnetic waves can also propagate as "surface waves" in that they can be guided along with a refractive index gradient or along an interface between two media having different dielectric constants. In radio transmission, a '' ground wave'' is a guided wave that propagates close to the surface of the Earth. Mechanical waves In seismology, several types of surface waves are encountered. Surface waves, in this mechanical sense, are commonly known as either '' Love waves'' (L waves) or '' Rayleigh waves''. A seismic wave is a wave that ''travels through the Earth, often ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Geophysical Journal International
''Geophysical Journal International'' is a monthly peer-reviewed scientific journal published by Oxford University Press on behalf of the Royal Astronomical Society and the Deutsche Geophysikalische Gesellschaft (German Geophysical Society). The journal publishes original research papers, research notes, letters, and book reviews. It was established in 1922. The editor-in-chief is Joerg Renner (Ruhr University Bochum). The journal covers research on all aspects of theoretical, computational, applied and observational geophysics. History The journal was formerly entitled ''Geophysical Journal'' (Oxford) from January 1988 to June 1989. The ''Geophysical Journal'' was itself formed by the merger of three other publications: ''Geophysical Journal of the Royal Astronomical Society'', ''Journal of Geophysics'', and ''Annales Geophysicae, Series B: Terrestrial and Planetary Physics''. ''Geophysical Journal of the Royal Astronomical Society'' was in existence from March 1958 to Decembe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Stoneley Wave
A Stoneley wave is a boundary wave (or interface wave) that typically propagates along a solid-solid interface. When found at a liquid-solid interface, this wave is also referred to as a Scholte wave. The wave is of maximum intensity at the interface and decreases exponentially away from it. It is named after the British seismologist Dr. Robert Stoneley (1894–1976), a lecturer in the University of Leeds, who discovered it on October 1, 1924. Occurrence and use Stoneley waves are most commonly generated during borehole sonic logging and vertical seismic profiling. They propagate along the walls of a fluid-filled borehole. They make up a large part of the low-frequency component of the signal from the seismic source and their attenuation is sensitive to fractures and formation permeability. Recent studies have found that Stoneley wave processing in borehole help to distinguish between fractured versus non-fractured coal seam. Therefore, analysis of Stoneley waves can make it ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
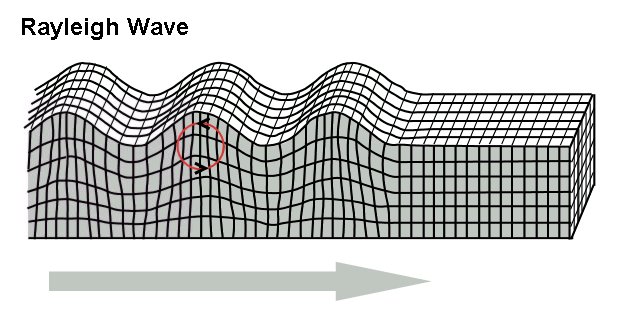
Rayleigh Wave
Rayleigh waves are a type of surface acoustic wave that travel along the surface of solids. They can be produced in materials in many ways, such as by a localized impact or by piezo-electric transduction, and are frequently used in non-destructive testing for detecting defects. Rayleigh waves are part of the seismic waves that are produced on the Earth by earthquakes. When guided in layers they are referred to as Lamb waves, Rayleigh–Lamb waves, or generalized Rayleigh waves. Characteristics Rayleigh waves are a type of surface wave that travel near the surface of solids. Rayleigh waves include both longitudinal and transverse motions that decrease exponentially in amplitude as distance from the surface increases. There is a phase difference between these component motions. The existence of Rayleigh waves was predicted in 1885 by Lord Rayleigh, after whom they were named. In isotropic solids these waves cause the surface particles to move in ellipses in planes normal ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |