|
Schoening Peak
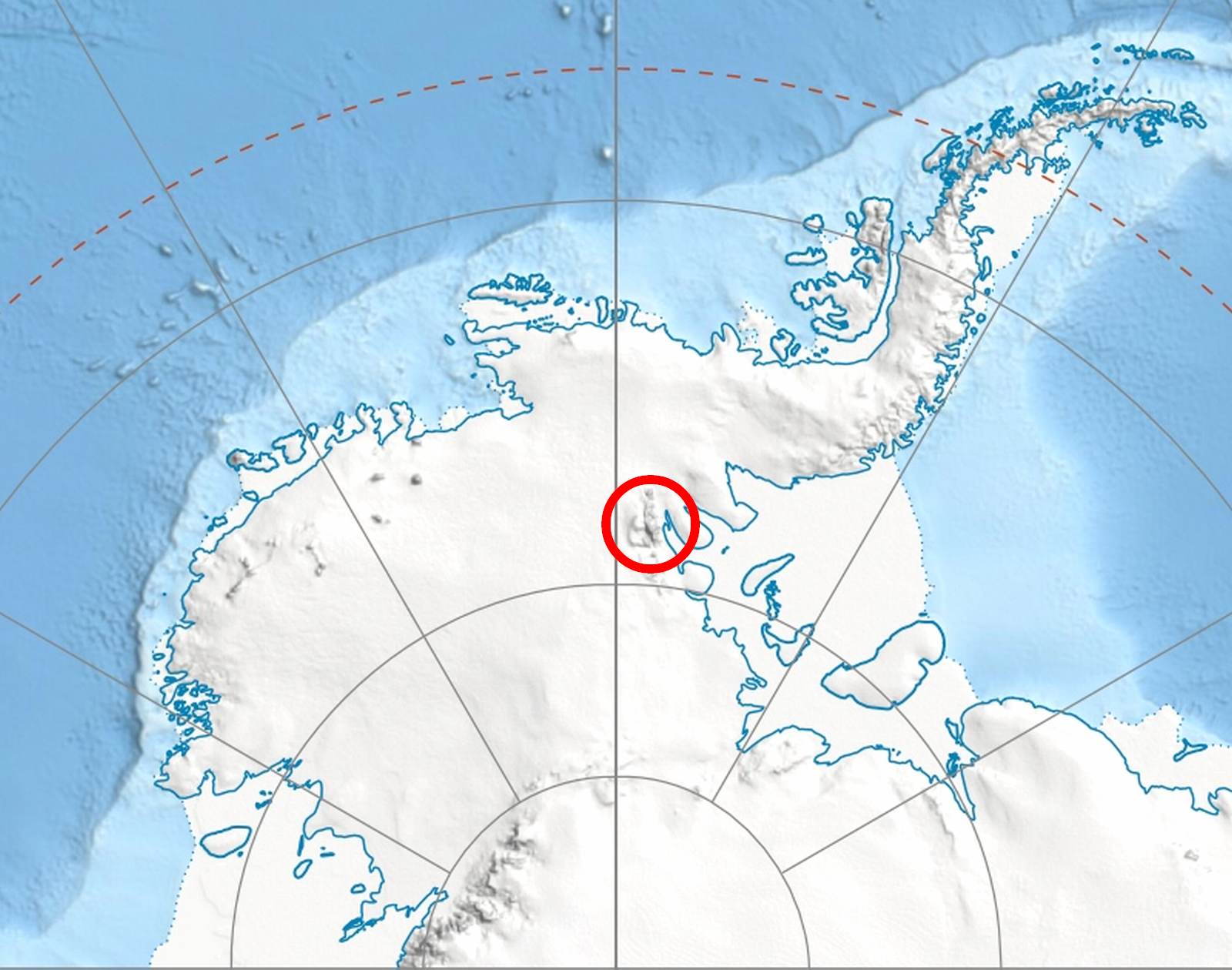
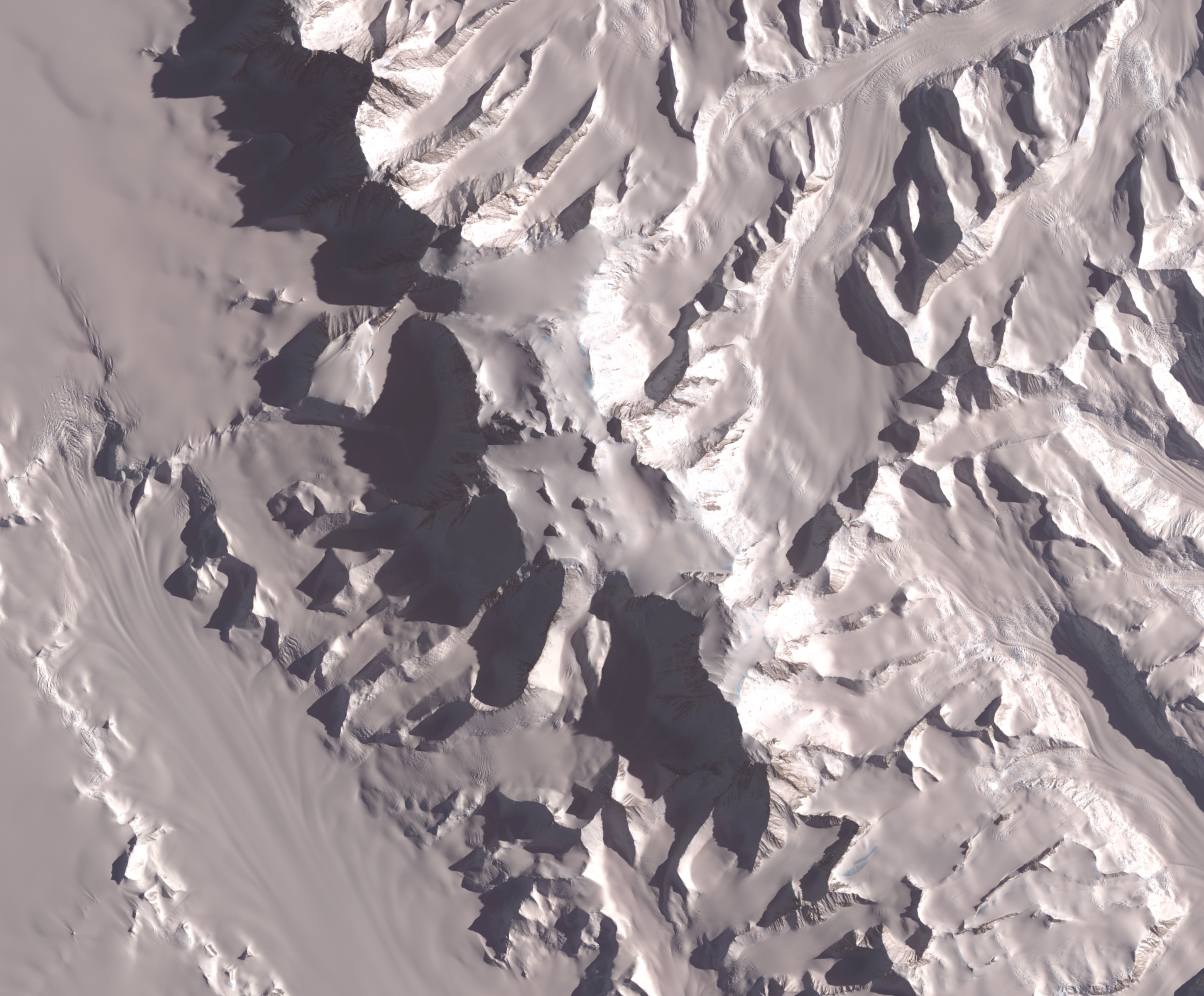
Schoening Peak is a high, steep and rocky peak, at the northeast edge of the ice-covered Vinson Plateau in the Sentinel Range of the Ellsworth Mountains, Antarctica. It surmounts Hinkley Glacier to the north and Dater Glacier to the northeast. The peak was named by US-ACAN in 2006 after Peter K. Schoening (1927-2004), member of the 1966–67 American Antarctic Mountaineering Expedition that made the first ascent of Mount Vinson, the summit of Antarctica, and other high mountains in the Sentinel Range. Location Schoening Peak is located at , which is east of Mount Vinson, northwest of Marts Peak, northeast of Opalchenie Peak and east-northeast of Silverstein Peak Silverstein Peak is a prominent, peak on the west edge of the ice-covered Vinson Plateau in the Sentinel Range of Ellsworth Mountains, Antarctica. It surmounts Roché Glacier to the north and Zapol Glacier to the southwest. The peak was named .... US mapping in 1961, updated in 1988. Maps Vinson Massif. Sc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vinson Plateau
Vinson Plateau is the summit plateau of Vinson Massif, Sentinel Range in Ellsworth Mountains, Antarctica. It extends for 9 km between Goodge Col and Hammer Col linking it to the north-central part of Sentinel Range to the north-northwest and to Craddock Massif to the south-southeast respectively, and 4.5 km wide between Branscomb Peak and Silverstein Peak to the west and Schoening Peak and Marts Peak to the east. Elevation from 4000 m to 4600 m above sea level. Rising from the plateau is the summit of Antarctica Mount Vinson (4892 m), and several other peaks higher than 4700 m, albeit of modest prominence: Clinch Peak (4841 m), Corbet Peak (4822 m), Silverstein Peak (4790 m), Schoening Peak (4743 m) and Hollister Peak (Antarctica), Hollister Peak (4729 m). The lower peaks of Fukushima Peak, Fukushima (4634 m) and Opalchenie Peak, Opalchenie (4500 m) stand at the south extremity of the plateau. Its central part is drained by Roché Glacier and a tributary glacier in J ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sentinel Range
The Sentinel Range is a major mountain range situated northward of Minnesota Glacier and forming the northern half of the Ellsworth Mountains in Antarctica. The range trends NNW-SSE for about and is 24 to 48 km (15 to 30 mi) wide. Many peaks rise over and Vinson Massif (4892 m) in the southern part of the range is the highest elevation on the continent.Sentinel Range. SCAR Composite Antarctic Gazetteer. Sentinel Range comprises a main ridge (featuring Vinson Massif in its southern portion) and a number of distinct heights, ridges and mountains on its east side, including (south to north) , [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ellsworth Mountains
The Ellsworth Mountains are the highest mountain ranges in Antarctica, forming a long and wide chain of mountains in a north to south configuration on the western margin of the Ronne Ice Shelf in Marie Byrd Land. They are bisected by Minnesota Glacier to form the Sentinel Range to the north and the Heritage Range to the south. The former is by far the higher and more spectacular with Mount Vinson () constituting the highest point on the continent.Bockheim, J.G., Schaefer, C.E., 2015. ''Soils of Ellsworth Land, the Ellsworth Mountains''. In: Bockheim, J.G. (Ed.), ''The Soils of Antarctica. World Soils Book Series'', Springer, Switzerland, pp. 169–181. The mountains are located within the Chilean Antarctic territorial claim but outside of the Argentinian and British ones. Discovery The mountains were discovered on November 23, 1935, by Lincoln Ellsworth in the course of a trans-Antarctic flight from Dundee Island to the Ross Ice Shelf. He gave them the descriptive name Sentinel ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Antarctica
Antarctica () is Earth's southernmost and least-populated continent. Situated almost entirely south of the Antarctic Circle and surrounded by the Southern Ocean, it contains the geographic South Pole. Antarctica is the fifth-largest continent, being about 40% larger than Europe, and has an area of . Most of Antarctica is covered by the Antarctic ice sheet, with an average thickness of . Antarctica is, on average, the coldest, driest, and windiest of the continents, and it has the highest average elevation. It is mainly a polar desert, with annual precipitation of over along the coast and far less inland. About 70% of the world's freshwater reserves are frozen in Antarctica, which, if melted, would raise global sea levels by almost . Antarctica holds the record for the lowest measured temperature on Earth, . The coastal regions can reach temperatures over in summer. Native species of animals include mites, nematodes, penguins, seals and tardigrades. Where vegetation o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hinkley Glacier
Hinkley Glacier () is a glacier flowing northeastward from Corbet Peak and Schoening Peak, Vinson Massif on the east slope of Sentinel Range in the Ellsworth Mountains, Antarctica, and continuing between Mount Segers and Zinsmeister Ridge to enter Dater Glacier southeast of Nebeska Peak and northwest of Sipey Bluff. It was named by US-ACAN (2006) after Todd K. Hinkley, Technical Director, National Ice Core Laboratory, U.S. Geological Survey, Denver, CO,2001-06. See also * List of glaciers in the Antarctic * Glaciology Maps Vinson Massif. Scale 1:250 000 topographic map. Reston, Virginia: US Geological Survey, 1988. Antarctic Digital Database (ADD).Scale 1:250000 topographic map of Antarctica. Scientific Committee on Antarctic Research (SCAR). Since 1993, regularly updated. References * External links Hinkley GlacierSCAR A scar (or scar tissue) is an area of fibrous tissue that replaces normal skin after an injury. Scars result from the biological process of w ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dater Glacier
The Dater Glacier is a steep valley glacier in Antarctica, long and from wide, flowing northeast in a sinuous course from the eastern slopes of the Vinson Massif between Sullivan Heights and Veregava Ridge to Rutford Ice Stream which borders the eastern flank of the Sentinel Range, Ellsworth Mountains. At the lower end the Dater Glacier coalesces with the terminus of the Ellen Glacier, the two emerging from the Sentinel Range as one stream just north of the Flowers Hills. The glacier was discovered by U.S. Navy Squadron VX-6 on photographic flights of December 14–15, 1959, and mapped from these photographs by the United States Geological Survey. It was named by the Advisory Committee on Antarctic Names after Henry M. Dater, a historian on the staff of the U.S. Antarctic Projects Officer and the U.S. Naval Support Force Antarctica. Tributary glaciers * Hansen Glacier * Berisad Glacier * Orizari Glacier * Hinkley Glacier * Strinava Glacier Maps * Vinson Massif. S ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
US-ACAN
The Advisory Committee on Antarctic Names (ACAN or US-ACAN) is an advisory committee of the United States Board on Geographic Names responsible for recommending commemorative names for features in Antarctica. History The committee was established in 1943 as the Special Committee on Antarctic Names (SCAN). It became the Advisory Committee on Antarctic Names in 1947. Fred G. Alberts was Secretary of the Committee from 1949 to 1980. By 1959, a structured nomenclature was reached, allowing for further exploration, structured mapping of the region and a unique naming system. A 1990 ACAN gazeeter of Antarctica listed 16,000 names. Description The United States does not recognise territorial boundaries within Antarctica, so ACAN assigns names to features anywhere within the continent, in consultation with other national nomenclature bodies where appropriate, as defined by the Antarctic Treaty System. The research and staff support for the ACAN is provided by the United States Geolog ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pete Schoening
Peter Kittilsby Schoening (July 30, 1927 – September 22, 2004) was an American mountaineer. Schoening and Andrew Kauffman was two Americans to first successfully climb the Pakistani peak Gasherbrum I in 1958, and was one of the first to summit Mount Vinson in Antarctica in 1966. Schoening is perhaps best remembered for his heroics during "The Belay" while part of the American K2 expedition in 1953, where he single-handedly averted the loss of the entire expedition. Biography Early years Schoening was born July 30, 1927, in Seattle, Washington to John and Gudrun Schoening, and grew up in Seattle. He dropped out of school to serve in the US Navy in the last year of the World War II. Later, he earned a degree in chemical engineering from the University of Washington, where he became involved in mountain climbing. The Belay In August 1953, the same year that Sir Edmund Hillary and Tenzing Norgay climbed Everest, an American team of seven set out to climb K2 led by Charles H ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mount Vinson
Vinson Massif () is a large mountain massif in Antarctica that is long and wide and lies within the Sentinel Range of the Ellsworth Mountains. It overlooks the Ronne Ice Shelf near the base of the Antarctic Peninsula. The massif is located about from the South Pole. Vinson Massif was discovered in January 1958 by U.S. Navy aircraft. In 1961, the Vinson Massif was named by the Advisory Committee on Antarctic Names (US-ACAN), after Carl G. Vinson, United States congressman from the state of Georgia, for his support for Antarctic exploration. On November 1, 2006, US-ACAN declared Mount Vinson and Vinson Massif to be separate entities.Stewart, J. (2011) ''Antarctic An Encyclopedia'' McFarland & Company Inc, New York. 1776 pp. . Vinson Massif lies within the Chilean claim under the Antarctic Treaty System. Mount Vinson is the highest peak in Antarctica, at . It lies in the north part of Vinson Massif's summit plateau in the south portion of the main ridge of the Sentinel Range ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Marts Peak
Marts Peak is a high, small and sharp peak at the east edge of the ice-covered Vinson Plateau in the Sentinel Range of the Ellsworth Mountains, Antarctica. It surmounts Dater Glacier to the northeast and Hammer Col to the south. The peak was named by US-ACAN in 2006 after Brian Marts, a member of the 1966–67 American Antarctic Mountaineering Expedition that made the first ascent of Mount Vinson, the summit of Antarctica, and other high mountains in the Sentinel Range. Location Marts Peak is located at , which is east-southeast of Mount Vinson, northeast of Opalchenie Peak and east by north of Silverstein Peak, according to US maps made in 1961 and updated in 1988. See also * Mountains in Antarctica This is a list of all the Ultra prominent peaks (with topographic prominence greater than 1,500 metres) in Antarctica. Some islands in the South Atlantic have also been included and can be found at the end of the list. Antarctica South Atl ... Maps Vinson Massif. S ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |