|
Scalindua Wagneri
''Candidatus'' Scalindua wagneri is a Gram-negative coccoid-shaped bacterium that was first isolated from a wastewater treatment plant. This bacterium is an obligate anaerobic chemolithotroph that undergoes anaerobic ammonium oxidation (anammox). It can be used in the wastewater treatment industry in nitrogen reactors to remove nitrogenous wastes from wastewater without contributing to fixed nitrogen loss and greenhouse gas emission. Characterization ''Candidatus'' Scalindua wagneri is a coccoid-shaped bacterium with a diameter of 1 μm. Like other Planctomycetota, ''S. wagneri'' is Gram-negative and does not have peptidoglycan in its cell wall. In addition, the bacterium contains two inner membranes instead of having one inner membrane and one outer membrane that surrounds the cell wall. Some of the near neighbors are other species within the new ''Scalindua'' genus, such as "''Candidatus'' S. sorokinii" and "''Candidatus'' S. brodae". Other neighbors include "''Candidatus'' Ku ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bacteria
Bacteria (; singular: bacterium) are ubiquitous, mostly free-living organisms often consisting of one biological cell. They constitute a large domain of prokaryotic microorganisms. Typically a few micrometres in length, bacteria were among the first life forms to appear on Earth, and are present in most of its habitats. Bacteria inhabit soil, water, acidic hot springs, radioactive waste, and the deep biosphere of Earth's crust. Bacteria are vital in many stages of the nutrient cycle by recycling nutrients such as the fixation of nitrogen from the atmosphere. The nutrient cycle includes the decomposition of dead bodies; bacteria are responsible for the putrefaction stage in this process. In the biological communities surrounding hydrothermal vents and cold seeps, extremophile bacteria provide the nutrients needed to sustain life by converting dissolved compounds, such as hydrogen sulphide and methane, to energy. Bacteria also live in symbiotic and parasitic relationsh ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pitsea
Pitsea is a small town and former civil parish, now in the unparished area of Basildon, in south Essex, England. It comprises five sub-districts: Eversley, Northlands Park Neighbourhood (previously known as Felmores), Chalvedon, Pitsea Mount and Burnt Mills. It is part of the new town of Basildon. In 1931 the parish had a population of 3414. During the creation of the new town of Basildon in the late 1940s and early 1950s, "Pitsea", "Vange" and "Laindon" were considered as possible names for the new town. As Basildon village was central to the district, the town was eventually named "Basildon". Before the new town regeneration, Pitsea itself was made up of unbuilt plot lands and was regarded as underdeveloped and run down. The Cinema Museum (London), Cinema Museum in London holds extensive home movies from the Jefree family of Pitsea in the 50's. Ref HMO353 History There is little known history about Pitsea but its earliest recorded name is Piceseia which was in 1086 and proba ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
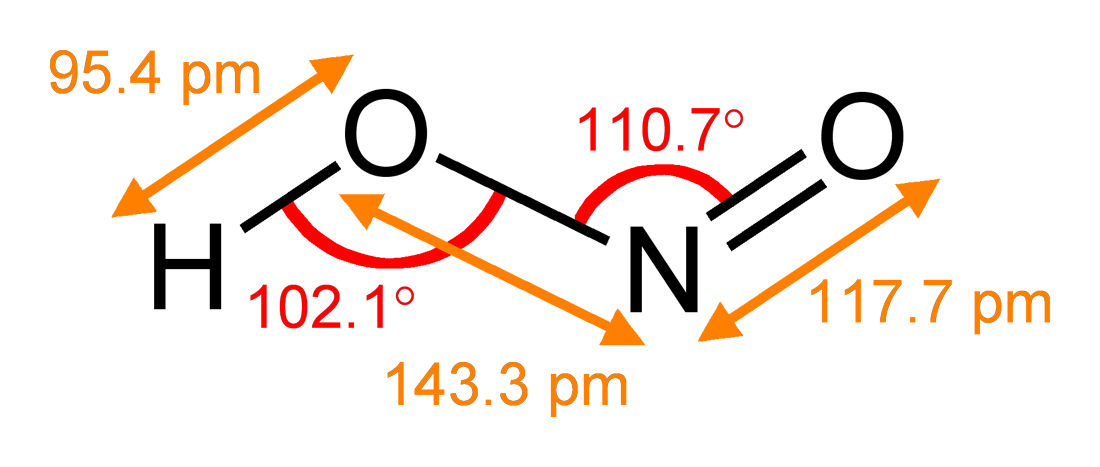
Nitrite
The nitrite polyatomic ion, ion has the chemical formula . Nitrite (mostly sodium nitrite) is widely used throughout chemical and pharmaceutical industries. The nitrite anion is a pervasive intermediate in the nitrogen cycle in nature. The name nitrite also refers to organic compounds having the –ONO group, which are esters of nitrous acid. Production Sodium nitrite is made industrially by passing a mixture of nitrogen oxides into aqueous sodium hydroxide or sodium carbonate solution: : The product is purified by recrystallization. Alkali metal nitrites are thermally stable up to and beyond their melting point (441 °C for KNO2). Ammonium nitrite can be made from dinitrogen trioxide, N2O3, which is formally the anhydride of nitrous acid: :2 NH3 + H2O + N2O3 → 2 NH4NO2 Structure The nitrite ion has a symmetrical structure (C2v molecular point group, symmetry), with both N–O bonds having equal length and a bond angle of about 115°. In valence bond theory, it is des ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ammonium
The ammonium cation is a positively-charged polyatomic ion with the chemical formula or . It is formed by the protonation of ammonia (). Ammonium is also a general name for positively charged or protonated substituted amines and quaternary ammonium cations (), where one or more hydrogen atoms are replaced by organic groups (indicated by R). Acid–base properties The ammonium ion is generated when ammonia, a weak base, reacts with Brønsted acids (proton donors): :H+ + NH3 -> H4 The ammonium ion is mildly acidic, reacting with Brønsted bases to return to the uncharged ammonia molecule: : H4 + B- -> HB + NH3 Thus, treatment of concentrated solutions of ammonium salts with strong base gives ammonia. When ammonia is dissolved in water, a tiny amount of it converts to ammonium ions: :H2O + NH3 OH- + H4 The degree to which ammonia forms the ammonium ion depends on the pH of the solution. If the pH is low, the equilibrium shifts to the right: more ammonia molecules are co ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Anaerobic Ammonium Oxidation
Anammox, an abbreviation for anaerobic ammonium oxidation, is a globally important microbial process of the nitrogen cycle that takes place in many natural environments. The bacteria mediating this process were identified in 1999, and were a great surprise for the scientific community. In the anammox reaction, nitrite and ammonium ions are converted directly into diatomic nitrogen and water. The bacteria that perform the anammox process are genera that belong to the bacterial phylum Planctomycetota. The anammox bacteria all possess one anammoxosome, a lipid bilayer membrane-bound compartment inside the cytoplasm in which the anammox process takes place. The anammoxosome membranes are rich in ladderane lipids; the presence of these lipids is so far unique in biology. "Anammox" is also the trademarked name for an anammox-based ammonium removal technology developedJetten Michael Silvester Maria, Van Loosdrecht Marinus Corneli; Technische Universiteit Delftpatent WO9807664/ref> by ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chemolithoautotroph
A lithoautotroph is an organism which derives energy from reactions of reduced compounds of mineral (inorganic) origin. Two types of lithoautotrophs are distinguished by their energy source; photolithoautotrophs derive their energy from light while chemolithoautotrophs (chemolithotrophs or chemoautotrophs) derive their energy from chemical reactions. Chemolithoautotrophs are exclusively microbes. Photolithoautotrophs include macroflora such as plants; these do not possess the ability to use mineral sources of reduced compounds for energy. Most chemolithoautotrophs belong to the domain Bacteria, while some belong to the domain Archaea. Lithoautotrophic bacteria can only use inorganic molecules as substrates in their energy-releasing reactions. The term "lithotroph" is from Greek ''lithos'' (''λίθος'') meaning "rock" and ''trōphos'' (τροφοσ) meaning "consumer"; literally, it may be read "eaters of rock". The "lithotroph" part of the name refers to the fact that these org ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ecologist
Ecology () is the study of the relationships between living organisms, including humans, and their physical environment. Ecology considers organisms at the individual, population, community, ecosystem, and biosphere level. Ecology overlaps with the closely related sciences of biogeography, evolutionary biology, genetics, ethology, and natural history. Ecology is a branch of biology, and it is not synonymous with environmentalism. Among other things, ecology is the study of: * The abundance, biomass, and distribution of organisms in the context of the environment * Life processes, antifragility, interactions, and adaptations * The movement of materials and energy through living communities * The successional development of ecosystems * Cooperation, competition, and predation within and between species * Patterns of biodiversity and its effect on ecosystem processes Ecology has practical applications in conservation biology, wetland management, natural resource managemen ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Genome
In the fields of molecular biology and genetics, a genome is all the genetic information of an organism. It consists of nucleotide sequences of DNA (or RNA in RNA viruses). The nuclear genome includes protein-coding genes and non-coding genes, other functional regions of the genome such as regulatory sequences (see non-coding DNA), and often a substantial fraction of 'junk' DNA with no evident function. Almost all eukaryotes have mitochondria and a small mitochondrial genome. Algae and plants also contain chloroplasts with a chloroplast genome. The study of the genome is called genomics. The genomes of many organisms have been sequenced and various regions have been annotated. The International Human Genome Project reported the sequence of the genome for ''Homo sapiens'' in 200The Human Genome Project although the initial "finished" sequence was missing 8% of the genome consisting mostly of repetitive sequences. With advancements in technology that could handle sequenci ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cloning Vector
A cloning vector is a small piece of DNA that can be stably maintained in an organism, and into which a foreign DNA fragment can be inserted for cloning purposes. The cloning vector may be DNA taken from a virus, the cell of a higher organism, or it may be the plasmid of a bacterium. The vector contains features that allow for the convenient insertion of a DNA fragment into the vector or its removal from the vector, for example through the presence of restriction sites. The vector and the foreign DNA may be treated with a restriction enzyme that cuts the DNA, and DNA fragments thus generated contain either blunt ends or overhangs known as sticky ends, and vector DNA and foreign DNA with compatible ends can then be joined together by molecular ligation. After a DNA fragment has been cloned into a cloning vector, it may be further subcloned into another vector designed for more specific use. There are many types of cloning vectors, but the most commonly used ones are genetically ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
TOPO Cloning
TOPO cloning is a molecular biology technique in which DNA fragments are cloned into specific vectors without the requirement for DNA ligases. Taq polymerase has a nontemplate-dependent terminal transferase activity that adds a single deoxyadenosine (A) to the 3'-end of the PCR products. This characteristic is exploited in "sticky end" TOPO TA cloning. For "blunt end" TOPO cloning, the recipient vector does not have overhangs and blunt-ended DNA fragments can be cloned. Principle The technique utilises the inherent biological activity of DNA topoisomerase I. The biological role of topoisomerase is to cleave and rejoin supercoiled DNA ends to facilitate replication. Vaccinia virus topoisomerase I specifically recognises DNA sequence 5´-(C/T)CCTT-3'. During replication, the enzyme digests DNA specifically at this sequence, unwinds the DNA and re-ligates it again at the 3' phosphate group of the thymidine Thymidine (symbol dT or dThd), also known as deoxythymidine, deoxyribos ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gel Electrophoresis
Gel electrophoresis is a method for separation and analysis of biomacromolecules ( DNA, RNA, proteins, etc.) and their fragments, based on their size and charge. It is used in clinical chemistry to separate proteins by charge or size (IEF agarose, essentially size independent) and in biochemistry and molecular biology to separate a mixed population of DNA and RNA fragments by length, to estimate the size of DNA and RNA fragments or to separate proteins by charge. Nucleic acid molecules are separated by applying an electric field to move the negatively charged molecules through a matrix of agarose or other substances. Shorter molecules move faster and migrate farther than longer ones because shorter molecules migrate more easily through the pores of the gel. This phenomenon is called sieving. Proteins are separated by the charge in agarose because the pores of the gel are too small to sieve proteins. Gel electrophoresis can also be used for the separation of nanoparticles. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Polymerase Chain Reaction
The polymerase chain reaction (PCR) is a method widely used to rapidly make millions to billions of copies (complete or partial) of a specific DNA sample, allowing scientists to take a very small sample of DNA and amplify it (or a part of it) to a large enough amount to study in detail. PCR was invented in 1983 by the American biochemist Kary Mullis at Cetus Corporation; Mullis and biochemist Michael Smith (chemist), Michael Smith, who had developed other essential ways of manipulating DNA, were jointly awarded the Nobel Prize in Chemistry in 1993. PCR is fundamental to many of the procedures used in genetic testing and research, including analysis of Ancient DNA, ancient samples of DNA and identification of infectious agents. Using PCR, copies of very small amounts of DNA sequences are exponentially amplified in a series of cycles of temperature changes. PCR is now a common and often indispensable technique used in medical laboratory research for a broad variety of applications ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |




.jpg)

