|
Satyros
Satyros or Satyrus was a Greek architect in the 4th century BC. Along with Pythius of Priene, he designed and oversaw the construction of the Mausoleum at Halicarnassus. Mausolus, the satrap of Caria in southwest Anatolia died in 353 BC, and his widow, Artemisia II of Caria, ordered the construction of a huge marble tomb in his memory at Halicarnassus – now Bodrum, Turkey – which was completed about 350 BC. Its name, the Mausoleum, became the generic term for monumental tombs. It was one of the Seven Wonders of the Ancient World, and was eventually destroyed by an earthquake An earthquake (also known as a quake, tremor or temblor) is the shaking of the surface of the Earth resulting from a sudden release of energy in the Earth's lithosphere that creates seismic waves. Earthquakes can range in intensity, from .... References ;Notes Ancient Greek architects 4th-century BC Greek people {{AncientGreece-bio-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mausoleum At Halicarnassus
The Mausoleum at Halicarnassus or Tomb of Mausolus ( grc, Μαυσωλεῖον τῆς Ἁλικαρνασσοῦ; tr, Halikarnas Mozolesi) was a tomb built between 353 and 350 BC in Halicarnassus (present Bodrum, Turkey) for Mausolus, an Anatolian from Caria and a satrap in the Achaemenid Empire, and his sister-wife Artemisia II of Caria. The structure was designed by the Greek architects Satyros and Pythius of Priene. Its elevated tomb structure is derived from the tombs of neighbouring Lycia, a territory Mausolus had invaded and annexed c. 360 BC, such as the Nereid Monument. The Mausoleum was approximately in height, and the four sides were adorned with sculptural reliefs, each created by one of four Greek sculptors: Leochares, Bryaxis, Scopas of Paros, and Timotheus. The mausoleum was considered to be such an aesthetic triumph that Antipater of Sidon identified it as one of his Seven Wonders of the Ancient World. It was destroyed by successive earthquakes from the 1 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pythius Of Priene
Pythius ( el, Πύθιος), also known as Pytheos ( el, Πυθεός) or Pythis, was a Greek architect, architecture theorist, and sculptor of the 4th century BC. He designed the Temple of Athena Polias at Priene and the Mausoleum at Halicarnassus, which was regarded in antiquity among the Seven Wonders of the World. It is presumed that he came from the Greek city of Priene. The first-century BC Roman architect Vitruvius called Pythius a "celebrated builder" (''de Architectura'' I.1.12) and referenced lost treatises on architecture written in Greek by Pythius as sources for his Latin architecture manual ''de Architectura'' (I.1.15). Architectural theory The Discipline of Architecture Pythius' ''Commentaries'' are lost, but Vitruvius paraphrases his philosophy of architectural education, in which the architect should aim to be a polymath knowledgeable "in all the arts and sciences (''De architectura'' I.1.12)." Pythius was a pioneer because he "propounded the importance ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mausolus
Mausolus ( grc, Μαύσωλος or , xcr, ���𐊠���𐊸𐊫𐊦 ''Mauśoλ'') was a ruler of Caria (377–353 BCE) and a satrap of the Achaemenid Empire. He enjoyed the status of king or dynast by virtue of the powerful position created by his father Hecatomnus ( xcr, 𐊴𐊭𐊪𐊳𐊫 ), who had succeeded the assassinated Persian Satrap Tissaphernes as the first satrap of Caria and founded the hereditary Hecatomnid dynasty. Alongside Caria, Mausolus also ruled Lycia and parts of Ionia and the Dodecanese islands. He is best known for the monumental shrine, the Mausoleum at Halicarnassus, erected and named for him by order of his widow (who was also his sister) Artemisia. Name Mausolus' name is only known directly in Greek ( grc, Μαύσωλος or ). It is clearly of Carian origin, though, and would have been written as *𐊪𐊠𐊲𐊸𐊫𐊦 (''*Mauśoλ'') or similar. This is a compound name perhaps meaning "much blessed". The first part, ''*Ma-'', may mean "much ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bodrum
Bodrum () is a port city in Muğla Province, southwestern Turkey, at the entrance to the Gulf of Gökova. Its population was 35,795 at the 2012 census, with a total of 136,317 inhabitants residing within the district's borders. Known in ancient times as Halicarnassus, the city was once home to the Mausoleum at Halicarnassus, also known as the tomb of Mausolus, one of the Seven Wonders of the Ancient World. The city was founded by Dorian Greeks. It later fell under Persian rule and became the capital city of the satrapy of Caria. Mausolus ruled Caria from here, and after his death in 353 BC, his wife Artemisia built a tomb, called the Mausoleum, for him. Macedonian forces laid siege to the city and captured it in 334 BCE. After Alexander's death, the city passed to successive Hellenistic rulers and was briefly an independent kingdom until 129 BCE, when it came under Roman rule. A series of natural disasters and repeated pirate attacks wreaked havoc on the area, and the city lost ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Seven Wonders Of The Ancient World
The Seven Wonders of the Ancient World, also known as the Seven Wonders of the World or simply the Seven Wonders, is a list of seven notable structures present during classical antiquity. The first known list of seven wonders dates back to the 2nd–1st century BC. While the entries have varied over the centuries, the seven traditional wonders are the Great Pyramid of Giza, the Colossus of Rhodes, the Lighthouse of Alexandria, the Mausoleum at Halicarnassus, the Temple of Artemis, the Statue of Zeus at Olympia, and the Hanging Gardens of Babylon. Using modern-day countries, two of the wonders were located in Greece, two in Turkey, two in Egypt, and one in Iraq. Of the seven wonders, only the Pyramid of Giza, which is also by far the oldest of the wonders, still remains standing, with the others being destroyed over the centuries. There is scholarly debate over the exact nature of the Hanging Gardens, and there is doubt as to whether they existed at all. Background Alexander ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Architecture Of Ancient Greece
Ancient Greek architecture came from the Greek-speaking people (''Hellenic'' people) whose culture flourished on the Greek mainland, the Peloponnese, the Aegean Islands, and in colonies in Anatolia and Italy for a period from about 900 BC until the 1st century AD, with the earliest remaining architectural works dating from around 600 BC. Ancient Greek architecture is best known from its temples, many of which are found throughout the region, with the Parthenon regarded, now as in ancient times, as the prime example. Most remains are very incomplete ruins, but a number survive substantially intact, mostly outside modern Greece. The second important type of building that survives all over the Hellenic world is the open-air theatre, with the earliest dating from around 525–480 BC. Other architectural forms that are still in evidence are the processional gateway (''propylon''), the public square (''agora'') surrounded by storied colonnade (''stoa''), the town council building ( ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Satrap
A satrap () was a governor of the provinces of the ancient Median and Achaemenid Empires and in several of their successors, such as in the Sasanian Empire and the Hellenistic empires. The satrap served as viceroy to the king, though with considerable autonomy. The word came to suggest tyranny or ostentatious splendour, and in modern usage refers to any subordinate or local ruler, usually with unfavourable connotations of corruption. A satrapy is the territory governed by a satrap. Etymology The word is derived via Latin from Greek ''satrápes'' (), itself borrowed from an Old Iranian ''*khshathra-pa''. In Old Persian, which was the native language of the Achaemenids, it is recorded as ''khshathapavan'' (, literally "protector of the province"). The Median form is reconstructed as ''*khshathrapavan-''. It is cognate with Sanskrit ''kshetrapal'' (). The Biblical Hebrew form is ''aḥashdarpan'' , as found in . In the Parthian (language of the Arsacid Empire) and Middle Persia ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Caria
Caria (; from Greek: Καρία, ''Karia''; tr, Karya) was a region of western Anatolia extending along the coast from mid-Ionia (Mycale) south to Lycia and east to Phrygia. The Ionians, Ionian and Dorians, Dorian Greeks colonized the west of it and joined the Carian population in forming Greek-dominated states there. Carians were described by Herodotus as being of Minoan civilization, Minoan descent,''The Histories'', Book I Section 171. while he reports that the Carians themselves maintained that they were Anatolian mainlanders intensely engaged in seafaring and were akin to the Mysians and the Lydians. The Carians spoke Carian language, Carian, a native Anatolian language closely related to Luwian language, Luwian. Also closely associated with the Carians were the Leleges, which could be an earlier name for Carians. Municipalities of Caria Cramer's detailed catalog of Carian towns in classical Greece is based entirely on ancient sources. The multiple names of towns and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Anatolia
Anatolia, tr, Anadolu Yarımadası), and the Anatolian plateau, also known as Asia Minor, is a large peninsula in Western Asia and the westernmost protrusion of the Asian continent. It constitutes the major part of modern-day Turkey. The region is bounded by the Turkish Straits to the northwest, the Black Sea to the north, the Armenian Highlands to the east, the Mediterranean Sea to the south, and the Aegean Sea to the west. The Sea of Marmara forms a connection between the Black and Aegean seas through the Bosporus and Dardanelles straits and separates Anatolia from Thrace on the Balkan peninsula of Southeast Europe. The eastern border of Anatolia has been held to be a line between the Gulf of Alexandretta and the Black Sea, bounded by the Armenian Highlands to the east and Mesopotamia to the southeast. By this definition Anatolia comprises approximately the western two-thirds of the Asian part of Turkey. Today, Anatolia is sometimes considered to be synonymous with Asian ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Artemisia II Of Caria
Artemisia II of Caria (Ancient Greek, Greek: Ἀρτεμισία; died 350 BC) was a naval strategist, commander and Sibling marriage#Sibling marriage and incest, the sister (and later spouse) and the successor of Mausolus, ruler of Caria. Mausolus was a satrap of the Achaemenid Empire, yet enjoyed the status of king or dynast of the Hecatomnid dynasty. After the death of her brother/husband, Artemisia reigned for two years, from 353 to 351 BCE. Her ascension to the throne prompted a revolt in some of the island and coastal cities under her command due to their objection to a female ruler. Her administration was conducted on the same principles as that of her husband; in particular, she supported the Oligarchy, oligarchical party on the island of Rhodes. Because of Artemisia's grief for her brother-husband, and the extravagant and bizarre forms it took, she became to later ages "a lasting example of chaste widowhood and of the purest and rarest kind of love", in the words of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
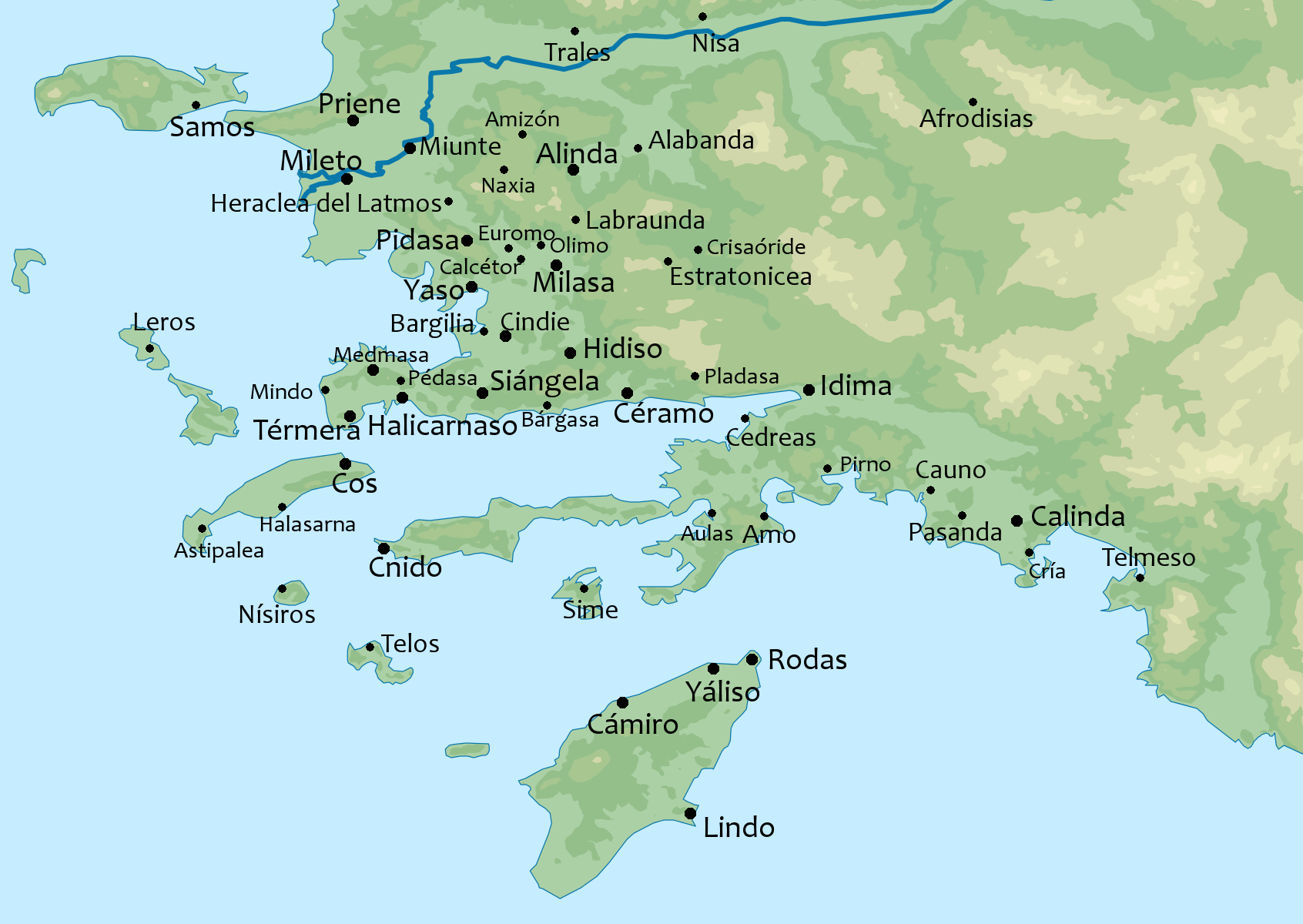
Halicarnassus
Halicarnassus (; grc, Ἁλικαρνᾱσσός ''Halikarnāssós'' or ''Alikarnāssós''; tr, Halikarnas; Carian: 𐊠𐊣𐊫𐊰 𐊴𐊠𐊥𐊵𐊫𐊰 ''alos k̂arnos'') was an ancient Greek city in Caria, in Anatolia. It was located in southwest Caria, on an advantageous site on the Gulf of Gökova, which is now in Bodrum, Turkey.} The city was famous for the Mausoleum of Halicarnassus, also known simply as the Tomb of Mausolus, whose name provided the origin of the word "mausoleum". The mausoleum, built from 353 to 350 BC, ranked as one of the seven wonders of the ancient world. Halicarnassus' history was special on two interlinked issues. Halicarnassus retained a monarchical system of government at a time when most other Greek city states had long since rid themselves of their kings. And secondly, while their Ionian neighbours rebelled against Persian rule, Halicarnassus remained loyal to the Persians and formed part of the Persian Empire until Alexander the Gre ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Turkey
Turkey ( tr, Türkiye ), officially the Republic of Türkiye ( tr, Türkiye Cumhuriyeti, links=no ), is a list of transcontinental countries, transcontinental country located mainly on the Anatolia, Anatolian Peninsula in Western Asia, with a East Thrace, small portion on the Balkans, Balkan Peninsula in Southeast Europe. It shares borders with the Black Sea to the north; Georgia (country), Georgia to the northeast; Armenia, Azerbaijan, and Iran to the east; Iraq to the southeast; Syria and the Mediterranean Sea to the south; the Aegean Sea to the west; and Greece and Bulgaria to the northwest. Cyprus is located off the south coast. Turkish people, Turks form the vast majority of the nation's population and Kurds are the largest minority. Ankara is Turkey's capital, while Istanbul is its list of largest cities and towns in Turkey, largest city and financial centre. One of the world's earliest permanently Settler, settled regions, present-day Turkey was home to important Neol ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |

.jpg)






.jpg)