|
Sary-Shagan
Sary Shagan ( rus, Сары-Шаган; kz, Сарышаған) is an anti-ballistic missile testing range located in Kazakhstan. On 17 August 1956 the Council of Ministers of the Soviet Union authorized plans for an experimental facility for missile defense located at Sary Shagan, on the west bank of Lake Balkhash. The first missile launched from the facility was a V-1000 on 16 October 1958, but the facilities for full-scale testing were not ready until 1961. Sary Shagan remains in use to this day, with the latest known launch on 2 December 2022. The town of Sary Shagan was a closed city until 2005. The administrative center, Priozersk remained a closed city. The length of the site is 480 km. The Sary Shagan range was the intended landing site for the sample return canister of the Russian Fobos-Grunt mission. History The first and only one in Eurasia test site for the development and testing of anti-missile weapons. In USSR, the official name of the test site was ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Anti-ballistic Missile
An anti-ballistic missile (ABM) is a surface-to-air missile designed to counter ballistic missiles (missile defense). Ballistic missiles are used to deliver nuclear weapon, nuclear, Chemical weapon, chemical, Bioagent, biological, or conventional weapon, conventional warheads in a ballistics, ballistic flight trajectory. The term "anti-ballistic missile" is a generic term conveying a system designed to intercept and destroy any type of ballistic threat; however, it is commonly used for systems specifically designed to counter intercontinental ballistic missiles (ICBMs). Current counter-ICBM systems There are a limited number of systems worldwide that can intercept intercontinental ballistic missiles: * The Russian A-135 anti-ballistic missile system (renamed in 2017 to A-235) is used for the defense of Moscow. It became operational in 1995 and was preceded by the A-35 anti-ballistic missile system. The system uses ABM-4 Gorgon, Gorgon and Gazelle (missile), Gazelle missiles pre ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
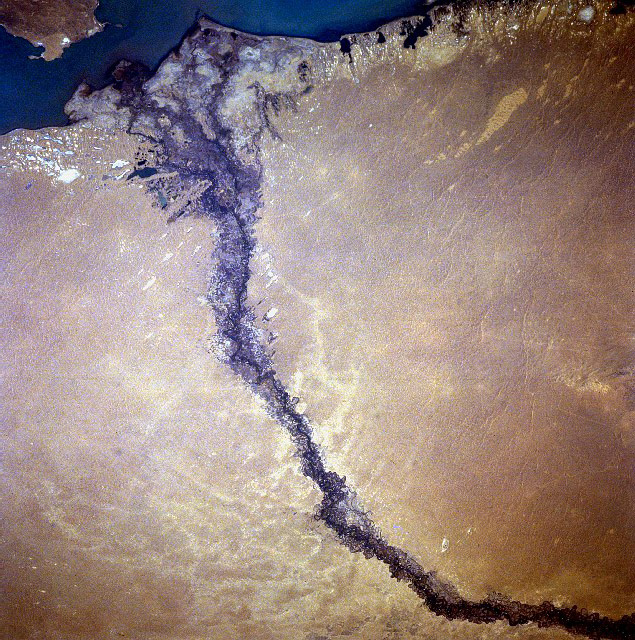
Lake Balkhash
Lake Balkhash ( kk, Балқаш көлі, ''Balqaş kóli'', ; russian: озеро Балхаш, ozero Balkhash) is a lake in southeastern Kazakhstan, one of the largest lakes in Asia and the 15th largest in the world. It is located in the eastern part of Central Asia and sits in the Balkhash-Alakol Basin, an endorheic (closed) basin. The basin drains seven rivers, the primary of which is the Ili, bringing most of the riparian inflow; others, such as the Karatal, bring surface and subsurface flow. The Ili is fed by precipitation, largely vernal snowmelt, from the mountains of China's Xinjiang region. The lake currently covers about . However, like the Aral Sea, it is shrinking due to diversion and extraction of water from its feeders. The lake has a narrow, quite central, strait. The lake's western part is fresh water. The lake's eastern half is saline. The east is on average 1.7 times deeper than the west. The largest shore city is named Balkhash and has about 66,000 inhab ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fakel V-1000
An anti-ballistic missile (ABM) is a surface-to-air missile designed to counter ballistic missiles (missile defense). Ballistic missiles are used to deliver nuclear, chemical, biological, or conventional warheads in a ballistic flight trajectory. The term "anti-ballistic missile" is a generic term conveying a system designed to intercept and destroy any type of ballistic threat; however, it is commonly used for systems specifically designed to counter intercontinental ballistic missiles (ICBMs). Current counter-ICBM systems There are a limited number of systems worldwide that can intercept intercontinental ballistic missiles: * The Russian A-135 anti-ballistic missile system (renamed in 2017 to A-235) is used for the defense of Moscow. It became operational in 1995 and was preceded by the A-35 anti-ballistic missile system. The system uses Gorgon and Gazelle missiles previously armed with nuclear warheads. These missiles have been updated (2017) and use non-nuclear kinetic int ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
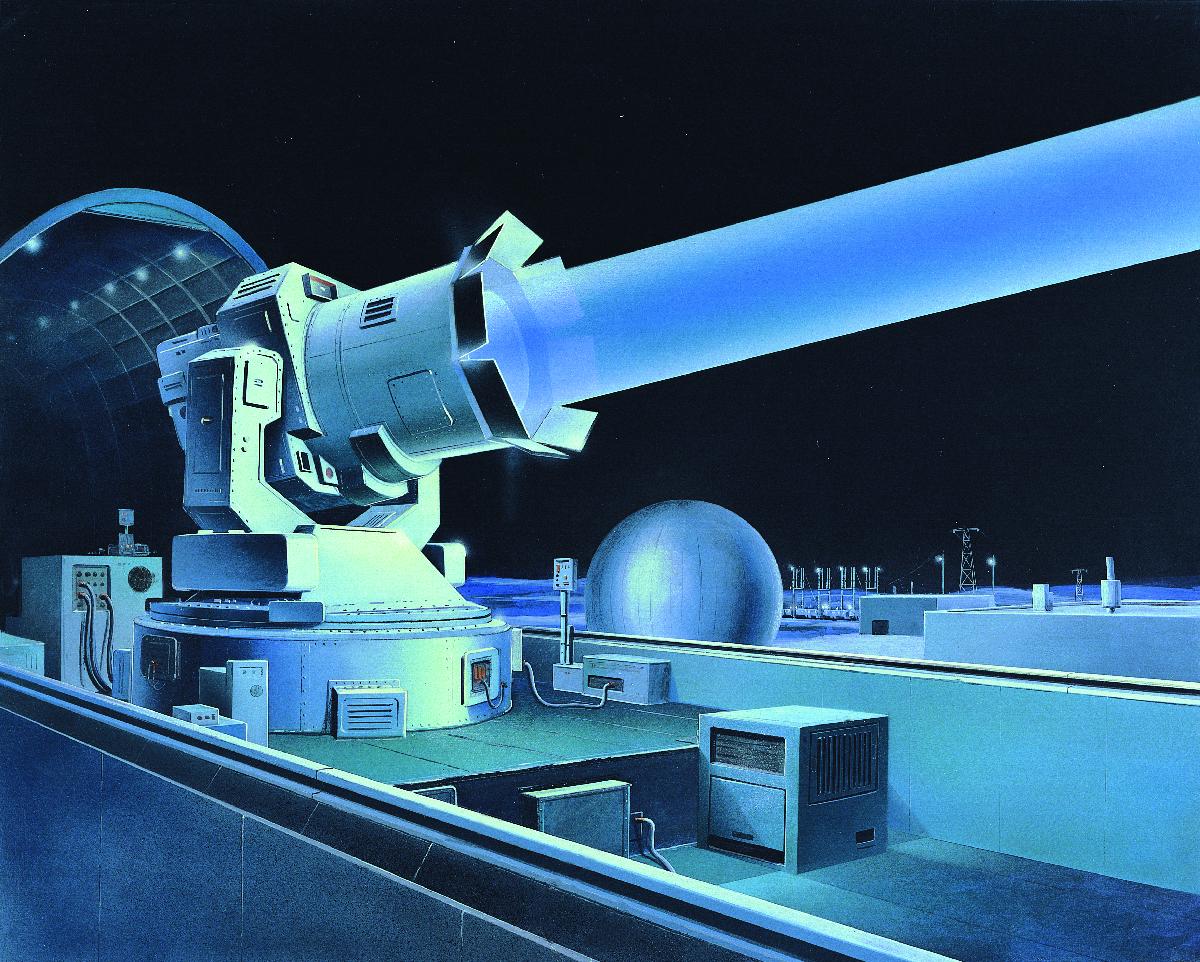
Omega (laser)
Omega (Russian: омега) (1965-) was a Soviet program for developing high-power laser weapons for air defense purposes, similar to the Terra-3 laser. The scientific director of the Omega program was A. M. Prokhorov. Practical work was carried out by Strela Design Bureau, (later - Almaz). History Boris Vasilyevich Bunkin (Raspletin's deputy) and his brother Fedor Vasilievich Bunkin (employee of Prokhorov) showed that low-flying targets could be destroyed with a neodymium-emitting glass laser with an active medium volume of approximately . General Designer of the KB-1 Academician Alexander Andreevich Raspletina and Prokhorov raised the idea before the CPSU Central Committee and the USSR Council of Ministers. The proposal received support in the defense department of CPSU-CC and in the Military-Industrial Commission (MIC) of the USSR Council of Ministers. On February 23, 1967, a Decree was issued, and on June 26 the MIC signed on. These documents determined the direction of w ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kapustin Yar
Kapustin Yar (russian: Капустин Яр) is a Russian rocket launch complex in Astrakhan Oblast, about 100 km east of Volgograd. It was established by the Soviet Union on 13 May 1946. In the beginning, Kapustin Yar used technology, material, and scientific support gained from the defeat of Germany in World War II. Numerous launches of test rockets for the Russian military were carried out at the site, as well as satellite and sounding rocket launches. The towns of Znamensk and Kapustin Yar (air base) were built nearby to serve the missile test range. Name The nearby village, Kapustin Yar, was used as the operations base in the early days of the testing site. The actual name can be translated as "cabbage ravine". In public opinion, Kapustin Yar is often referred to as the "Russian Roswell"—the place where the USSR discovered, investigated, or captured alien ships (UFOs). Due to its role as a development site for new technology, Kapustin Yar is also the site of numero ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Priozersk, Kazakhstan
Priozersk ( kz, Priozersk; russian: Приозёрск, ''Priozyorsk'') is a closed city at Lake Balkhash, Kazakhstan. It serves as the administrative center of Sary Shagan anti-ballistic missile testing site. Priozersk is located in Karaganda Region (central Kazakhstan), approximately 620 kilometers to the south-east of the Karaganda and 747 kilometers from Astana. The Cambala Airport lies in the suburbs. Population: By nationality, the city is 46% Russian, 39% Kazakh, 6% Ukrainian, and 9% other. The town is closed to visits by foreign citizens. History Tens of thousands of workers and hundreds of missile experts and army officers arrived after the Soviet government decided to establish a secret military base in the Kazakh Steppe. This testing site for the soviet missile defense system was one of such centers, which had led to construction of anti-ballistic missiles and to attain parity in the arms race between the USSR and United States. After the Soviet Union's co ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Soviet Project K Nuclear Tests
The Soviet Union's K project nuclear test series was a group of five nuclear tests conducted in 1961–1962. These tests followed the 1961 Soviet nuclear tests series and preceded the 1962 Soviet nuclear tests series. The K project nuclear testing series were all high altitude tests fired by missiles from the Kapustin Yar launch site in Russia across central Kazakhstan toward the Sary Shagan test range (see map below). Two of the tests were 1.2 kiloton warheads tested in 1961. The remaining three tests were of 300 kiloton warheads in 1962. Electromagnetic pulse The worst effects of a Soviet high altitude test were from the electromagnetic pulse of the nuclear test on 22 October 1962 (during the Cuban Missile Crisis). In that Operation K high altitude test, a 300 kiloton missile-warhead detonated west of Jezkazgan (also called Dzhezkazgan or Zhezqazghan) at an altitude of . The Soviet scientists instrumented a section of telephone line in the area that they expected to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lavochkin
NPO Lavochkin (russian: НПО Лавочкина, OKB-301, also called Lavochkin Research and Production Association or shortly Lavochkin Association, LA) is a Russian aerospace company. It is a major player in the Russian space program, being the developer and manufacturer of the Fregat upper stage, as well as interplanetary probes such as Fobos-Grunt. As of 2015, it was headed by Sergei Lemeshevskii. On August 10, 2017 the Lavochkin Association's Board of Directors appointed Vladimir Kolmykov Director General of the enterprise. Overview The company develops and manufactures spacecraft such as the Fregat rocket upper stages, satellites and interplanetary probes. It is a contractor for a number of military programs, such as the Oko early warning satellite, Prognoz and Araks programmes as well as the civilian program Kupon. One of the company's most notable projects was the participation in the failed Fobos-Grunt sample return mission. NPO Lavochkin has also developed the Elektr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Semyon Lavochkin
Semyon Alekseyevich Lavochkin (russian: Семён Алексе́евич Ла́вочкин; 11 September 1900 - 9 June 1960) was a Soviet aerospace engineer, Soviet aircraft designer who founded the Lavochkin aircraft design bureau. Many of his fighter designs were produced in large numbers for Soviet forces during World War II. Biography Lavochkin was born to a family of teachers in Smolensk. After graduation in 1918, he enlisted in the Red Army and served in the infantry in the Russian Civil War. In 1920, he began studies at the Moscow State Technical University, from which he graduated in 1927. He then served for two years as an intern at the design department of the Central Aerohydrodynamic Institute under the direction of Andrei Tupolev, where he assisted in the design of the Tupolev TB-3 heavy bomber. While at TsAGI, his colleagues included the French seaplane designer Paul Richard, as well as Mikhail Gurevich and Nikolay Kamov. In the early 1930s, he transferred to the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Missile Defense
Missile defense is a system, weapon, or technology involved in the detection, tracking, interception, and also the destruction of attacking missiles. Conceived as a defense against nuclear-armed intercontinental ballistic missiles (ICBMs), its application has broadened to include shorter-ranged non-nuclear tactical and theater missiles. China, France, India, Iran, Israel, Italy, Russia, Taiwan, the United Kingdom and the United States have all developed such air defense systems. Missile defense categories Missile defense can be divided into categories based on various characteristics: type/range of missile intercepted, the trajectory phase where the intercept occurs, and whether intercepted inside or outside the Earth's atmosphere: Type/range of missile intercepted These types/ranges include strategic, theater and tactical. Each entails unique requirements for intercept, and a defensive system capable of intercepting one missile type frequently cannot intercept others. H ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Terra (laser)
Terra-3 (Russian: терра–3) was a Soviet laser testing centre, located on the Sary Shagan anti-ballistic missile (ABM) testing range in the Karaganda Region of Kazakhstan. It was originally built to test missile defense concepts, but these attempts were dropped after the Anti-Ballistic Missile Treaty was signed. The site later hosted two modest devices used primarily for experiments in space tracking. Several other laser test sites were also active during this period. During the 1980s, officials within the United States Department of Defense (DoD) suggested it was the site of a prototypical anti-satellite weapon system."Soviets could have laser able to blind US satellites" ''Gadsden Times'', 10 April 1984 The site was abandoned ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Air Defense
Anti-aircraft warfare, counter-air or air defence forces is the battlespace response to aerial warfare, defined by NATO as "all measures designed to nullify or reduce the effectiveness of hostile air action".AAP-6 It includes surface based, subsurface ( submarine launched), and air-based weapon systems, associated sensor systems, command and control arrangements, and passive measures (e.g. barrage balloons). It may be used to protect naval, ground, and air forces in any location. However, for most countries, the main effort has tended to be homeland defence. NATO refers to airborne air defence as counter-air and naval air defence as anti-aircraft warfare. Missile defence is an extension of air defence, as are initiatives to adapt air defence to the task of intercepting any projectile in flight. In some countries, such as Britain and Germany during the Second World War, the Soviet Union, and modern NATO and the United States, ground-based air defence and air defence aircraf ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |


.jpg)