|
Sandia Base
Sandia Base was the principal nuclear weapons installation of the United States Department of Defense from 1946 to 1971. It was located on the southeastern edge of Albuquerque, New Mexico. For 25 years, the top-secret Sandia Base and its subsidiary installation, Manzano Base, carried on the atomic weapons research, development, design, testing, and training commenced by the Manhattan Project during World War II. Fabrication, assembly, and storage of nuclear weapons was also done at Sandia Base. The base played a key role in the United States nuclear deterrence capability during the Cold War. In 1971 it was merged into Kirtland Air Force Base. Geography Sandia Base was located at about 35° 02' 25" N, 106° 32' 59" W at an elevation above sea level. It was in the southeast quadrant of Albuquerque, bounded roughly by Louisiana Boulevard SE and Kirtland Air Force Base on the west, and Eubank Avenue SE and the Sandia Mountains on the east, and Isleta Pueblo lands on the south. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nuclear Weapons
A nuclear weapon is an explosive device that derives its destructive force from nuclear reactions, either fission (fission bomb) or a combination of fission and fusion reactions ( thermonuclear bomb), producing a nuclear explosion. Both bomb types release large quantities of energy from relatively small amounts of matter. The first test of a fission ("atomic") bomb released an amount of energy approximately equal to . The first thermonuclear ("hydrogen") bomb test released energy approximately equal to . Nuclear bombs have had yields between 10 tons TNT (the W54) and 50 megatons for the Tsar Bomba (see TNT equivalent). A thermonuclear weapon weighing as little as can release energy equal to more than . A nuclear device no larger than a conventional bomb can devastate an entire city by blast, fire, and radiation. Since they are weapons of mass destruction, the proliferation of nuclear weapons is a focus of international relations policy. Nuclear weapons have been deplo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bomb
A bomb is an explosive weapon that uses the exothermic reaction of an explosive material to provide an extremely sudden and violent release of energy. Detonations inflict damage principally through ground- and atmosphere-transmitted mechanical stress, the impact and penetration of pressure-driven projectiles, pressure damage, and explosion-generated effects. Bombs have been utilized since the 11th century starting in East Asia. The term bomb is not usually applied to explosive devices used for civilian purposes such as construction or mining, although the people using the devices may sometimes refer to them as a "bomb". The military use of the term "bomb", or more specifically aerial bomb action, typically refers to airdropped, unpowered explosive weapons most commonly used by air forces and naval aviation. Other military explosive weapons not classified as "bombs" include shells, depth charges (used in water), or land mines. In unconventional warfare, other names can r ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Naval Weapons Evaluation Facility
The Naval Weapons Evaluation Facility (NWEF) operated through the Cold War investigating aircraft-weapon interfaces to provide United States Navy aircraft with nuclear weapons delivery capability. History The United States Army Air Corps began using Kirtland Field south of Albuquerque, New Mexico, in the early years of World War II. The adjacent Sandia Base was created as a training facility. Several units from the Los Alamos Scientific Laboratory were relocated to the Sandia Base in 1945 to use the Kirtland Field flight test facilities. Kirtland Field was designated Kirtland Air Force Base in 1947, and the Armed Forces Special Weapons Project (AFSWP) operated on Sandia Base. When the United States Air Force established the Air Force Special Weapons Command at Kirtland Air Force Base in 1949, the United States Navy formed a detachment to investigate nuclear capabilities for naval aircraft and assist the AFSWP with naval equipment for demonstrations and training. This detachment ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nevada Test Site
The Nevada National Security Site (N2S2 or NNSS), known as the Nevada Test Site (NTS) until 2010, is a United States Department of Energy (DOE) reservation located in southeastern Nye County, Nevada, about 65 miles (105 km) northwest of the city of Las Vegas. Formerly known as the Nevada Proving Grounds, the site was established in 1951 for the testing of nuclear devices. It covers approximately 1,360 square miles (3,500 km2) of desert and mountainous terrain. Nuclear weapons testing at the site began with a 1-kiloton-of-TNT (4.2 TJ) bomb dropped on Frenchman Flat on January 27, 1951. Over the subsequent four decades, over 1,000 nuclear explosions were detonated at the site. Many of the iconic images of the nuclear era come from the site. During the 1950s, the mushroom clouds from the 100 atmospheric tests could be seen from almost away. The city of Las Vegas experienced noticeable seismic effects, and the mushroom clouds, which could be seen from the downtown ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Boeing B-50 Superfortress
The Boeing B-50 Superfortress is an American strategic bomber. A post– World War II revision of the Boeing B-29 Superfortress, it was fitted with more powerful Pratt & Whitney R-4360 radial engines, stronger structure, a taller tail fin, and other improvements. It was the last piston-engined bomber built by Boeing for the United States Air Force, and was further refined into Boeing's final such design, the B-54. Although not as well known as its direct predecessor, the B-50 was in USAF service for nearly 20 years. After its primary service with Strategic Air Command (SAC) ended, B-50 airframes were modified into aerial tankers for Tactical Air Command (TAC) (KB-50) and as weather reconnaissance aircraft (WB-50) for the Air Weather Service. Both the tanker and hurricane hunter versions were retired in March 1965 due to metal fatigue and corrosion found in the wreckage of KB-50J, ''48-065'', which crashed on 14 October 1964. Design and development Development of an impro ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Frenchman Flat
Frenchman Flat is a hydrographic basin in the Nevada National Security Site south of Yucca Flat and north of Mercury, Nevada. The flat was used as an American nuclear test site and has a dry lake bed (Frenchman Lake) that was used as a 1950s airstrip before it was chosen after the start of the Korean War for the Nevada Proving Grounds. Nellis Air Force Base land was transferred to the Atomic Energy Commission on which Site Mercury was constructed on the flat for supporting American nuclear explosive tests. The 1951 Operation Ranger "Able" test (ground zero at UTM Coordinates 923758 on the flat) was the first continental US nuclear detonation after the 1945 Trinity test, and Frenchman Flat also had the only detonation of an American artillery-fired nuclear projectile in the 1953 Upshot-Knothole Grable test using the M65 Atomic Cannon. Area 5 Area 5 consists of of the southeastern portion of NTS, north of the town of Mercury, and includes the Area 5 Radioactive Waste M ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nevada
Nevada ( ; ) is a state in the Western region of the United States. It is bordered by Oregon to the northwest, Idaho to the northeast, California to the west, Arizona to the southeast, and Utah to the east. Nevada is the 7th-most extensive, the 32nd-most populous, and the 9th-least densely populated of the U.S. states. Nearly three-quarters of Nevada's people live in Clark County, which contains the Las Vegas–Paradise metropolitan area, including three of the state's four largest incorporated cities. Nevada's capital is Carson City. Las Vegas is the largest city in the state. Nevada is officially known as the "Silver State" because of the importance of silver to its history and economy. It is also known as the "Battle Born State" because it achieved statehood during the Civil War (the words "Battle Born" also appear on its state flag); as the " Sagebrush State", for the native plant of the same name; and as the " Sage-hen State". The name means "snowy" in Spanish, re ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Marshall Islands
The Marshall Islands ( mh, Ṃajeḷ), officially the Republic of the Marshall Islands ( mh, Aolepān Aorōkin Ṃajeḷ),'' () is an independent island country and microstate near the Equator in the Pacific Ocean, slightly west of the International Date Line. Geographically, the country is part of the larger island group of Micronesia. The country's population of 58,413 people (at the 2018 World Bank Census) is spread out over five islands and 29 coral atolls, comprising 1,156 individual islands and islets. The capital and largest city is Majuro. It has the largest portion of its territory composed of water of any sovereign state, at 97.87%. The islands share maritime boundaries with Wake Island to the north, Kiribati to the southeast, Nauru to the south, and Federated States of Micronesia to the west. About 52.3% of Marshall Islanders (27,797 at the 2011 Census) live on Majuro. In 2016, 73.3% of the population were defined as being "urban". The UN also indicates a popu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
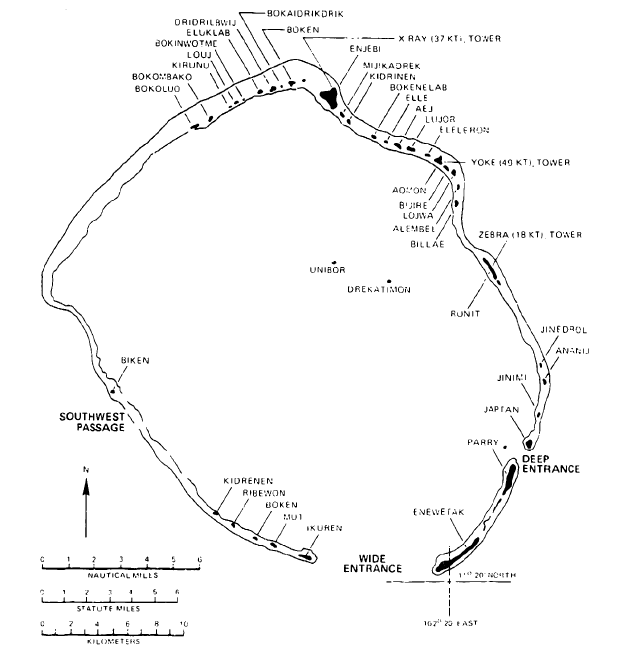
Eniwetok Atoll
Enewetak Atoll (; also spelled Eniwetok Atoll or sometimes Eniewetok; mh, Ānewetak, , or , ; known to the Japanese as Brown Atoll or Brown Island; ja, ブラウン環礁) is a large coral atoll of 40 islands in the Pacific Ocean and with its 664 people (as of 2011) forms a legislative district of the Ralik Chain of the Marshall Islands. With a land area total less than , it is no higher than and surrounds a deep central lagoon, in circumference. It is the second-westernmost atoll of the Ralik Chain and is west from Bikini Atoll. It was held by the Japanese from 1914 until its capture by the United States in February 1944, during World War II, then became Naval Base Eniwetok. Nuclear testing by the US totaling the equivalent of over 30 megatons of TNT took place during the Cold War; in 1977–1980, a concrete dome (the Runit Dome) was built on Runit Island to deposit radioactive soil and debris. The Runit Dome is deteriorating and could be breached by a typhoon, t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Operation Sandstone
Operation Sandstone was a series of nuclear weapon tests in 1948. It was the third series of American tests, following Trinity in 1945 and Crossroads in 1946, and preceding Ranger. Like the Crossroads tests, the Sandstone tests were carried out at the Pacific Proving Grounds, although at Enewetak Atoll rather than Bikini Atoll. They differed from Crossroads in that they were conducted by the Atomic Energy Commission, with the armed forces having only a supporting role. The purpose of the Sandstone tests was also different: they were primarily tests of new bomb designs rather than of the effects of nuclear weapons. Three tests were carried out in April and May 1948 by Joint Task Force 7, with a work force of 10,366 personnel, of whom 9,890 were military. The successful testing of the new cores in the Operation Sandstone tests rendered every component of the old weapons obsolete. Even before the third test had been carried out, production of the old cores was halted, and all e ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Roswell, New Mexico
Roswell () is a city in, and the seat of, Chaves County in the U.S. state of New Mexico. Chaves County forms the entirety of the Roswell micropolitan area. As of the 2020 census it had a population of 48,422, making it the fifth-largest city in New Mexico. It is home of the New Mexico Military Institute (NMMI), founded in 1891. The city is also the location of an Eastern New Mexico University campus. Bitter Lake National Wildlife Refuge is located a few miles northeast of the city on the Pecos River. Bottomless Lakes State Park is located east of Roswell on US 380. The Roswell incident was named after the town, though the crash site of the alleged UFO was some from Roswell and closer to Corona. The investigation and debris recovery was handled by the local Roswell Army Air Field. On the 50th anniversary of the Roswell UFO incident the UFO Festival was started. In the 1930s, Roswell was a site for much of Robert H. Goddard's early rocketry work. The Roswell Museum and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |





.png)