|
Samuel Fairclough
Samuel Fairclough (1594–1677) was an English nonconformist divine. Early life Fairclough was born 29 April 1594 at Haverhill, Suffolk, the youngest of the four sons of Lawrence Fairclough, vicar of Haverhill, by his wife Mary, daughter of John Cole of that town. After some preliminary training under a Mr. Robotham, who said of him that he was the best scholar he had ever taught in the course of thirty years, he was sent to Queens' College, Cambridge, at the age of fourteen. Various stories are told of his strict life and steady attachment to moderate puritan principles. He refused on principle to take a woman's part in the comedy of ‘Ignoramus’ when about to be presented before James I. Ministry Soon after taking his B.A. degree a Mr. Allington offered him a presentation to a living in Suffolk, but not being of age to receive priest's orders he declined it, and preferred to pursue his theological studies with Richard Blackerby, then resident at Ashen, Essex, whose eldes ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Anglicanism
Anglicanism is a Western Christian tradition that has developed from the practices, liturgy, and identity of the Church of England following the English Reformation, in the context of the Protestant Reformation in Europe. It is one of the largest branches of Christianity, with around 110 million adherents worldwide . Adherents of Anglicanism are called ''Anglicans''; they are also called ''Episcopalians'' in some countries. The majority of Anglicans are members of national or regional ecclesiastical provinces of the international Anglican Communion, which forms the third-largest Christian communion in the world, after the Roman Catholic Church and the Eastern Orthodox Church. These provinces are in full communion with the See of Canterbury and thus with the Archbishop of Canterbury, whom the communion refers to as its '' primus inter pares'' (Latin, 'first among equals'). The Archbishop calls the decennial Lambeth Conference, chairs the meeting of primates, and is the pr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kedington
Kedington is a village and civil parish in the West Suffolk district of Suffolk in eastern England, located between the towns of Clare and Haverhill in the south-west of Suffolk. History Known as Kidituna in the ''Domesday Book'' (1086), there were 280 people living there at that time. Part of it was formerly in Essex. The puritan, Thomas Barnardiston studied under Calvin in Geneva during the reign of Queen Mary I, but returned to Kedington after the accession of Queen Elizabeth I in 1558 and the consequent Elizabethan Religious Settlement. Church of St Peter and St Paul Kedington's church, St Peter and St Paul, is one of the historical treasures of East Anglia, dating from the late 13th century. However, the church is built on top of a Roman villa, the remains of which can be viewed under small trap doors located in the pews towards the back of the nave. There is an Anglo-Saxon stone cross located above the altar on the east wall of the church. This was found near to the chur ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Houghton Conquest
Houghton Conquest is a village and civil parish located in the Central Bedfordshire district of Bedfordshire, England. The parish also includes the hamlet of How End. History Historically in the hundred of Redbornestoke, the name of the village originated from the Conquest family who held a manor and lands in the area from the 13th century to the 18th century. The Houghton in Houghton Conquest is pronounced 'how-ton', and this has been the official pronunciation since at least 1998. The Church of All Saints was constructed in the village during the 14th century, and is today the largest parish church in Bedfordshire. Features of interest include the wall paintings, sculpture, stained glass, benches and stalls. In 2018 all of the lead, weighing 21 tonnes, was stolen from the church roof. Manors The Conquest family owned Conquestbury, a large manor which was left to ruin when the family left the area. The Conquestbury manor house stood near the southeast end of the village on ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
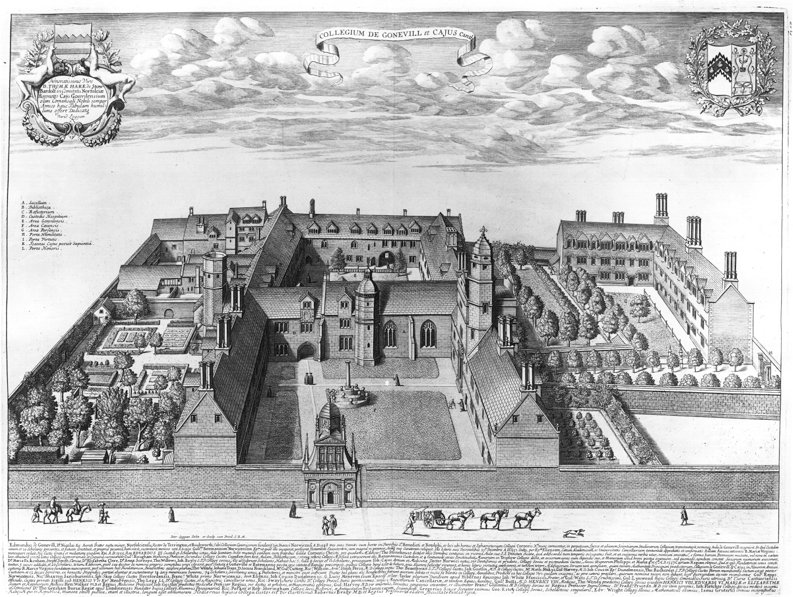
Caius College, Cambridge
Gonville and Caius College, often referred to simply as Caius ( ), is a constituent college of the University of Cambridge in Cambridge, England. Founded in 1348, it is the fourth-oldest of the University of Cambridge's 31 colleges and one of the wealthiest. The college has been attended by many students who have gone on to significant accomplishment, including fifteen Nobel Prize winners, the second-highest of any Oxbridge college after Trinity College, Cambridge. The college has long historical associations with the teaching of medicine, especially due to its prominent alumni in the medical profession. It also has globally-recognized and prestigious academic programmes in law, economics, English literature, and history. Famous Gonville and Caius alumni include physicians John Caius (who gave the college the caduceus in its insignia) and William Harvey. Other alumni in the sciences include Francis Crick (joint discoverer of the structure of DNA with James Watson), James Chad ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Stowmarket
Stowmarket ( ) is a market town in Suffolk, England,OS Explorer map 211: Bury St.Edmunds and Stowmarket Scale: 1:25 000. Publisher:Ordnance Survey – Southampton A2 edition. Publishing Date:2008. on the busy A14 road (Great Britain), A14 trunk road between Bury St Edmunds to the west and Ipswich to the southeast. The town is on the main railway line between London and Norwich, and lies on the River Gipping, which is joined by its tributary, the River Rat, to the south of the town. The town takes its name from the Old English language, Old English word ''stōw'' meaning "principal place", and was granted a market charter in 1347 by Edward III of England, Edward III. A bi-weekly market is still held there today on Thursday and Saturday. The population of the town has increased from around 6,000 in 1981 to its current level of around 19,000, with considerable further development planned for the town and surrounding villages as part of an area action plan. It is the largest town in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Heveningham, Suffolk
Heveningham is a village and civil parish in the East Suffolk district of Suffolk in eastern England. Located four miles south-west of Halesworth, in 2005 it had a population of 120. Heveningham Hall, a country house built in 1777, once belonged to the Lords Huntingfield. History In 1870–1872, John Marius Wilson's ''Imperial Gazetteer of England and Wales'' described the parish as: ”Haveningham, or Heveningham, a village and parish in Blything district, Suffolk.” Historic buildings Church of St Margaret St. Margaret's Church, built in 1539, is a Perpendicular style parish church and is now a Grade I listed building. Heveningham Hall Heveningham Hall is a Grade I listed building that stands on the site of an earlier house built for William Heveningham in 1658. Country fair The summer fair is held annually in the grounds of Heveningham Hall and is a landmark event for the Parish, as it highlights the local rural traditions. Activities include a Sheep Show, C ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kennett, Cambridgeshire
Kennett is a small village and civil parish at the very eastern tip of Cambridgeshire, England. Situated around north-east of Newmarket and north-west of Bury St Edmunds, it falls into the county of Suffolk. History The small parish of Kennett covers at the easternmost point of the spur of Cambridgeshire that stretches into Suffolk. Listed as ''Chenet'' in the Domesday Book of 1086, the village is named after the river Kennett, a tributary of the River Lark. The origin of the river's name is unclear, but it is of Celtic origin perhaps partially derived from ''cwm'' meaning "summit". The parish is roughly square in shape, and borders Suffolk to its east and south. The eastern border is largely made up of the meandering medieval course of the River Kennett, though the river has been straightened in sections since the border was defined. The border deviates to the east of the river for a kilometre or so, such that the land around Kennett Hall falls into the parish. The straig ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Finchingfield, Essex
Finchingfield is a village in the Braintree district in north-west Essex, England, a primarily rural area. It is approximately from Thaxted, farther from the larger towns of Saffron Walden and Braintree. Nearby villages include Great Bardfield, Great Sampford, and Wethersfield. History There has been a settlement in Finchingfield since historical records of the area began. Also, there is archaeological evidence for a Roman villa 400 metres south-southwest of the village church. The place-name 'Finchingfield ' is first attested in the Domesday Book of 1086, where it appears as ''Fincingefelda,'' a name that means 'the field of Finc or his people'. The village was an official stop for horse-drawn coaches travelling from London to Norwich. Spains Hall, the nearby Elizabethan country house, was built in the early fifteenth century. The hall is named after Hervey de Ispania, who held the manor at the time of the 1086 ''Domesday Book''. Since then, the land has been owned by four ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Richard Fairclough (divine)
Richard Fairclough (1621–1682) was an English nonconformist divine. Life Fairclough was the eldest son of Samuel Fairclough (1594–1677). He graduated M.A. as a member of Emmanuel College, Cambridge. While a resident in Thames Street, London, he was licensed in 1672 to be a general presbyterian teacher. He died in London 4 July 1682 and was buried in Bunhill Fields. According to John Howe, Fairclough was "a man of a clear, distinct understanding, of a very quick, discerning, and penetrating judgment, that would on a sudden … strike through knotty difficulties into the inward center of truth with such a felicity that things seem'd to offer themselves to him which are wont to cost others a troublesome search." He was author of "The nature, possibility, and duty of a true believer attaining to a certain knowledge of his effectual vocation, eternal election, and final perseverance to glory", a sermon printed in Nathaniel Vincent's ''The Morning-Exercise against Popery'', 1675, a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Trinity College, Cambridge
Trinity College is a constituent college of the University of Cambridge. Founded in 1546 by Henry VIII, King Henry VIII, Trinity is one of the largest Cambridge colleges, with the largest financial endowment of any college at either Cambridge or University of Oxford, Oxford. Trinity has some of the most distinctive architecture in Cambridge with its Trinity Great Court, Great Court said to be the largest enclosed courtyard in Europe. Academically, Trinity performs exceptionally as measured by the Tompkins Table (the annual unofficial league table of Cambridge colleges), coming top from 2011 to 2017. Trinity was the top-performing college for the 2020-21 undergraduate exams, obtaining the highest percentage of good honours. Members of Trinity have been awarded 34 Nobel Prizes out of the 121 received by members of Cambridge University (the highest of any college at either Oxford or Cambridge). Members of the college have received four Fields Medals, one Turing Award and one Abel ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Engagement Controversy
{{Use dmy dates, date=April 2022 The Engagement Controversy was a debate in England from 1649–1652 regarding loyalty to the new regime after Pride's Purge and the execution of Charles I. During this period hundreds of pamphlets were published in England supporting 'engagement' to the new regime or denying the right of English citizens to shift their allegiance from the deposed king to Oliver Cromwell and his associates. In 1650 the statement of engagement took the form: "I do declare and promise, that I will be true and faithful to the Commonwealth of England, as it is now established, without a King or House of Lords."Glenn Burgess. 'Usurpation, Obligation, and Obedience in the Thought of the Engagement Controversy.' ''The Historical Journal.'' Vol. 29, No. 3 (Sept., 1986), pp. 515-536. Participants in the debate are generally regarded either as ''de facto'' theorists or royalists. ''De facto'' theorists advocated loyalty to any government capable of taking power and maintaini ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Westminster Assembly
The Westminster Assembly of Divines was a council of Divinity (academic discipline), divines (theologians) and members of the English Parliament appointed from 1643 to 1653 to restructure the Church of England. Several Scots also attended, and the Assembly's work was adopted by the Church of Scotland. As many as 121 ministers were called to the Assembly, with nineteen others added later to replace those who did not attend or could no longer attend. It produced a new Form of Presbyterial Church Government, Form of Church Government, a Westminster Confession of Faith, Confession of Faith or statement of belief, two catechisms or manuals for religious instruction (Westminster Shorter Catechism, Shorter and Westminster Larger Catechism, Larger), and a liturgical manual, the ''Directory for Public Worship'', for the Churches of England and Scotland. The Confession and catechisms were adopted as doctrinal standards in the Church of Scotland and other Presbyterian churches, where they ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |