|
Samsung Galaxy Watch Active
The Samsung Galaxy Watch Active is a smartwatch developed by Samsung Electronics Samsung Electronics Co., Ltd. (, sometimes shortened to SEC and stylized as SΛMSUNG) is a South Korean multinational corporation, multinational electronics corporation headquartered in Yeongtong-gu, Suwon, South Korea. It is the pinnacle of .... It was announced on 20 February 2019. The Galaxy Watch Active was scheduled for availability in the United States starting on March 8, 2019. Specifications References External links Galaxy Watch Active on Samsung Newsroom Consumer electronics brands Products introduced in 2019 Smartwatches Samsung wearable devices {{tech-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Samsung Electronics
Samsung Electronics Co., Ltd. (, sometimes shortened to SEC and stylized as SΛMSUNG) is a South Korean multinational corporation, multinational electronics corporation headquartered in Yeongtong-gu, Suwon, South Korea. It is the pinnacle of the Samsung chaebol, accounting for 70% of the group's revenue in 2012. Samsung Electronics has played a key role in the group's corporate governance due to circular ownership. Samsung Electronics has Assembly line, assembly plants and sales networks in 74 countries and employs around 290,000 people. It is majority-owned by foreign investors. Samsung Electronics is the world's List of largest technology companies by revenue, second-largest technology company by revenue, and its market capitalization stood at US$520.65 billion, the 12th largest in the world. Samsung is a major manufacturer of Electronic component, Electronic Components such as lithium-ion batteries, semiconductors, image sensors, camera modules, and Display device, d ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Near-field Communication
Near-field communication (NFC) is a set of communication protocols that enables communication between two electronic devices over a distance of 4 cm (1 in) or less. NFC offers a low-speed connection through a simple setup that can be used to bootstrap more-capable wireless connections. Like other "proximity card" technologies, NFC is based on inductive coupling between two so-called antennas present on NFC-enabled devices—for example a smartphone and a printer—communicating in one or both directions, using a frequency of 13.56 MHz in the globally available unlicensed radio frequency ISM band using the ISO/IEC 18000-3 air interface standard at data rates ranging from 106 to 424 kbit/s. The standards were provided by the NFC Forum. The forum was responsible for promoting the technology and setting standards and certifies device compliance. Secure communications are available by applying encryption algorithms as is done for credit cards and if they fit the crite ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Products Introduced In 2019
Product may refer to: Business * Product (business), an item that serves as a solution to a specific consumer problem. * Product (project management), a deliverable or set of deliverables that contribute to a business solution Mathematics * Product (mathematics) Algebra * Direct product Set theory * Cartesian product of sets Group theory * Direct product of groups * Semidirect product * Product of group subsets * Wreath product * Free product * Zappa–Szép product (or knit product), a generalization of the direct and semidirect products Ring theory * Product of rings * Ideal operations, for product of ideals Linear algebra * Scalar multiplication * Matrix multiplication * Inner product, on an inner product space * Exterior product or wedge product * Multiplication of vectors: ** Dot product ** Cross product ** Seven-dimensional cross product ** Triple product, in vector calculus * Tensor product Topology * Product topology Algebraic topology * Cap product * Cup product * ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Consumer Electronics Brands
A consumer is a person or a group who intends to order, or uses purchased goods, products, or services primarily for personal, social, family, household and similar needs, who is not directly related to entrepreneurial or business activities. The term most commonly refers to a person who purchases goods and services for personal use. Consumer rights “Consumers, by definition, include us all," said President John F. Kennedy, offering his definition to the United States Congress on March 15, 1962. This speech became the basis for the creation of World Consumer Rights Day, now celebrated on March 15. In his speech : John Fitzgerald Kennedy outlined the integral responsibility to consumers from their respective governments to help exercise consumers' rights, including: *The right to safety: To be protected against the marketing of goods that are hazardous to health or life. *The right to be informed: To be protected against fraudulent, deceitful, or grossly misleading informatio ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
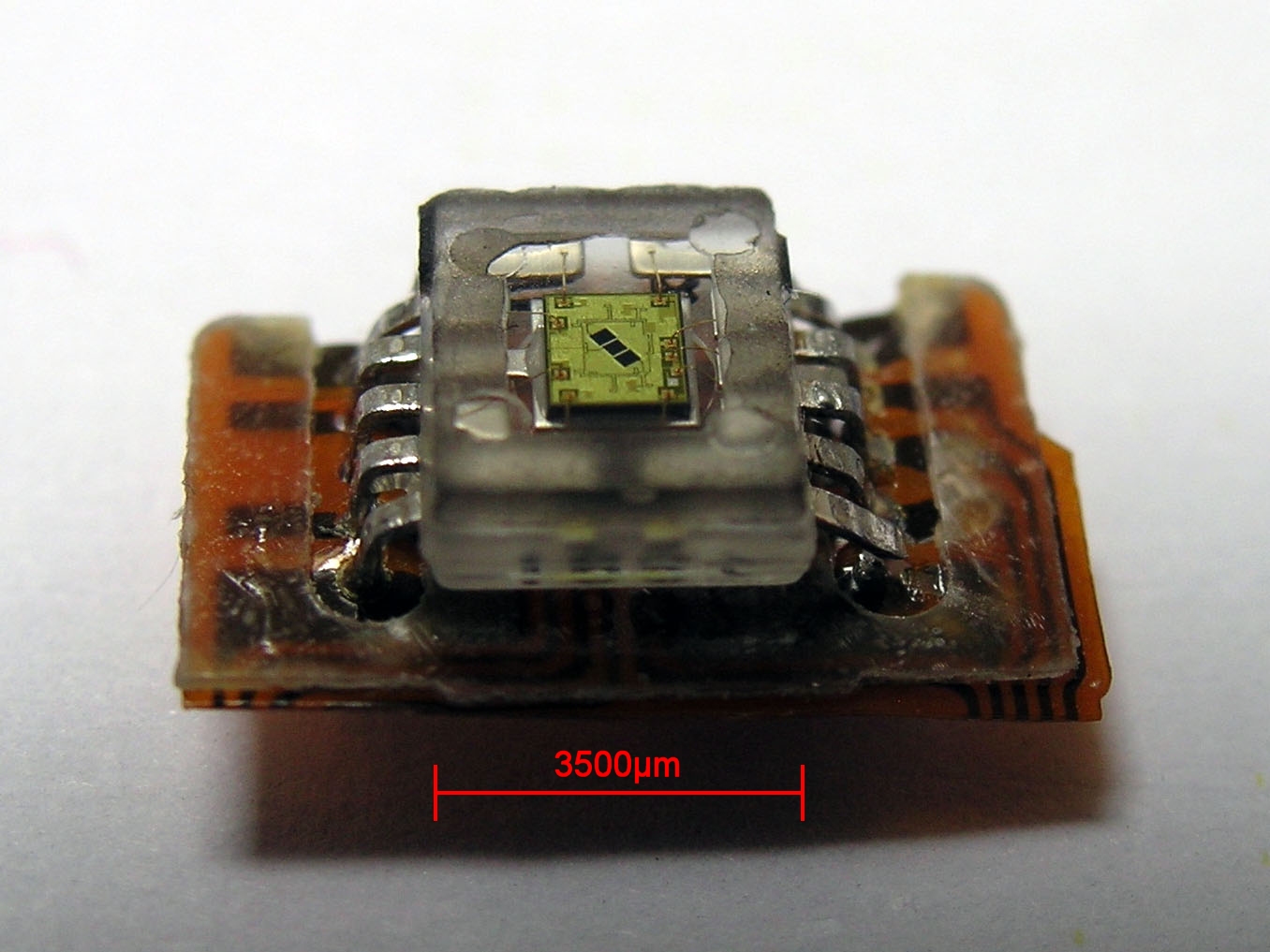
Photodetector
Photodetectors, also called photosensors, are sensors of light or other electromagnetic radiation. There is a wide variety of photodetectors which may be classified by mechanism of detection, such as Photoelectric effect, photoelectric or photochemical effects, or by various performance metrics, such as spectral response. Semiconductor-based photodetectors typically photo detector have a p–n junction that converts light photons into current. The absorbed photons make electron–hole pairs in the depletion region. Photodiodes and photo transistors are a few examples of photo detectors. Solar cells convert some of the light energy absorbed into electrical energy. Types Photodetectors may be classified by their mechanism for detection: * Photoemission or photoelectric effect: Photons cause electrons to transition from the conduction band of a material to free electrons in a vacuum or gas. * Thermal: Photons cause electrons to transition to mid-gap states then decay back to lo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Electro-optical Sensor
Electro-optical sensors are electronic detectors that convert light, or a change in light, into an electronic signal. These sensors are able to detect electromagnetic radiation from the infrared up to the ultraviolet wavelengths. They are used in many industrial and consumer applications, for example: * Lamps that turn on automatically in response to darkness * Position sensors that activate when an object interrupts a light beam * Flash detection, to synchronize one photographic flash to another * Photoelectric sensors that detect the distance, absence, or presence of an object Function An optical sensor converts light rays into electronic signals. It measures the physical quantity of light and then translates it into a form that is readable by an instrument. An optical sensor is generally part of a larger system that integrates a source of light, a measuring device and the optical sensor. This is often connected to an electrical trigger. The trigger reacts to a change in the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Barometer
A barometer is a scientific instrument that is used to measure air pressure in a certain environment. Pressure tendency can forecast short term changes in the weather. Many measurements of air pressure are used within surface weather analysis to help find surface troughs, pressure systems and frontal boundaries. Barometers and pressure altimeters (the most basic and common type of altimeter) are essentially the same instrument, but used for different purposes. An altimeter is intended to be used at different levels matching the corresponding atmospheric pressure to the altitude, while a barometer is kept at the same level and measures subtle pressure changes caused by weather and elements of weather. The average atmospheric pressure on the earth's surface varies between 940 and 1040 hPa (mbar). The average atmospheric pressure at sea level is 1013 hPa (mbar). Etymology The word ''barometer'' is derived from the Ancient Greek (), meaning "weight", and (), meaning "measure ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vibrating Structure Gyroscope
A vibrating structure gyroscope, defined by the IEEE as a Coriolis vibratory gyroscope (CVG), is a gyroscope that uses a vibrating structure to determine the rate of rotation. A vibrating structure gyroscope functions much like the halteres of flies (insects in the order Diptera). The underlying physical principle is that a vibrating object tends to continue vibrating in the same plane even if its support rotates. The Coriolis effect causes the object to exert a force on its support, and by measuring this force the rate of rotation can be determined. Vibrating structure gyroscopes are simpler and cheaper than conventional rotating gyroscopes of similar accuracy. Inexpensive vibrating structure gyroscopes manufactured with MEMS technology are widely used in smartphones, gaming devices, cameras and many other applications. Theory of operation Consider two proof masses vibrating in plane (as in the MEMS gyro) at frequency \omega_r. The Coriolis effect induces an acceleration o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
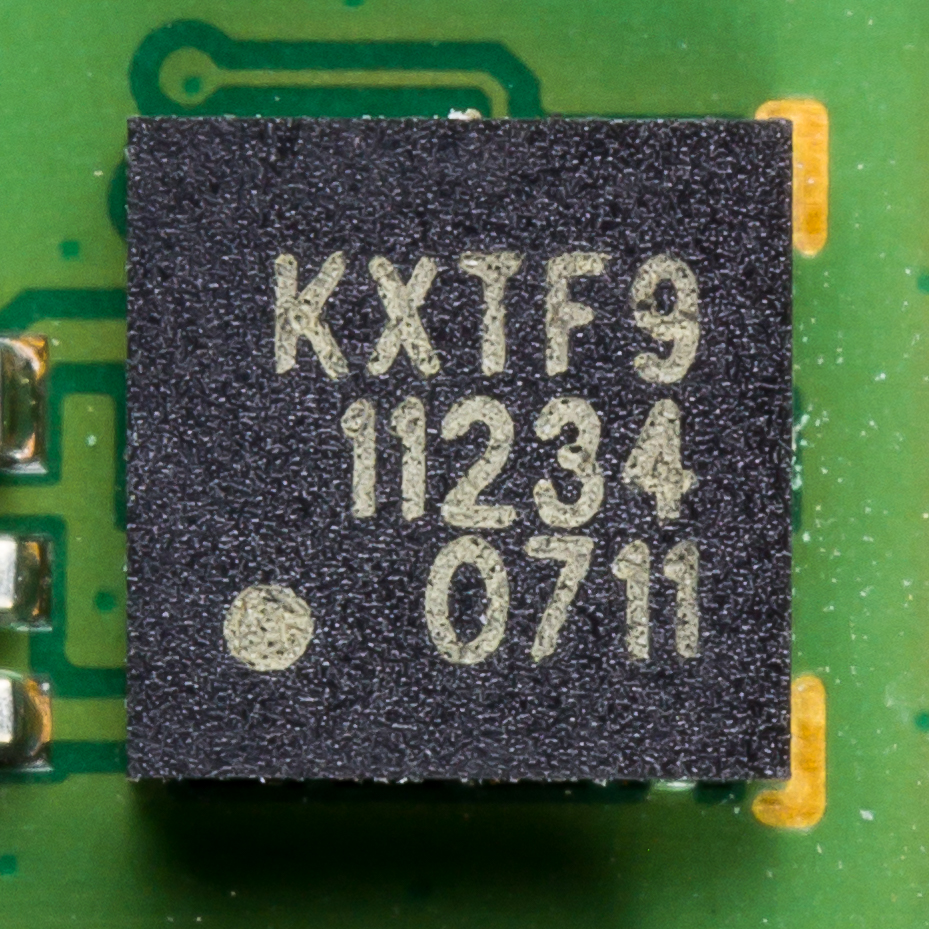
Accelerometer
An accelerometer is a tool that measures proper acceleration. Proper acceleration is the acceleration (the rate of change of velocity) of a body in its own instantaneous rest frame; this is different from coordinate acceleration, which is acceleration in a fixed coordinate system. For example, an accelerometer at rest on the surface of the Earth will measure an acceleration due to Earth's gravity, straight upwards (by definition) of g ≈ 9.81 m/s2. By contrast, accelerometers in free fall (falling toward the center of the Earth at a rate of about 9.81 m/s2) will measure zero. Accelerometers have many uses in industry and science. Highly sensitive accelerometers are used in inertial navigation systems for aircraft and missiles. Vibration in rotating machines is monitored by accelerometers. They are used in tablet computers and digital cameras so that images on screens are always displayed upright. In unmanned aerial vehicles, accelerometers help to stabilise flight. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Microelectromechanical Systems
Microelectromechanical systems (MEMS), also written as micro-electro-mechanical systems (or microelectronic and microelectromechanical systems) and the related micromechatronics and microsystems constitute the technology of microscopic devices, particularly those with moving parts. They merge at the nanoscale into nanoelectromechanical systems (NEMS) and nanotechnology. MEMS are also referred to as micromachines in Japan and microsystem technology (MST) in Europe. MEMS are made up of components between 1 and 100 micrometers in size (i.e., 0.001 to 0.1 mm), and MEMS devices generally range in size from 20 micrometres to a millimetre (i.e., 0.02 to 1.0 mm), although components arranged in arrays (e.g., digital micromirror devices) can be more than 1000 mm2. They usually consist of a central unit that processes data (an integrated circuit chip such as microprocessor) and several components that interact with the surroundings (such as microsensors). Because of the la ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Galileo
Galileo di Vincenzo Bonaiuti de' Galilei (15 February 1564 – 8 January 1642) was an Italian astronomer, physicist and engineer, sometimes described as a polymath. Commonly referred to as Galileo, his name was pronounced (, ). He was born in the city of Pisa, then part of the Duchy of Florence. Galileo has been called the "father" of observational astronomy, modern physics, the scientific method, and modern science. Galileo studied speed and velocity, gravity and free fall, the principle of relativity, inertia, projectile motion and also worked in applied science and technology, describing the properties of pendulums and "hydrostatic balances". He invented the thermoscope and various military compasses, and used the telescope for scientific observations of celestial objects. His contributions to observational astronomy include telescopic confirmation of the phases of Venus, observation of the four largest satellites of Jupiter, observation of Saturn's rings, and an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Beidou
The BeiDou Navigation Satellite System (BDS; ) is a Chinese satellite navigation system. It consists of two separate satellite constellations. The first BeiDou system, officially called the BeiDou Satellite Navigation Experimental System and also known as BeiDou-1, consisted of three satellites which, beginning in 2000, offered limited coverage and navigation services, mainly for users in China and neighboring regions. BeiDou-1 was decommissioned at the end of 2012. The second generation of the system, officially called the BeiDou Navigation Satellite System (BDS) and also known as COMPASS or BeiDou-2, became operational in China in December 2011 with a partial constellation of 10 satellites in orbit. Since December 2012, it has been offering services to customers in the Asia-Pacific region. In 2015, China launched the third generation BeiDou system (BeiDou-3) for global coverage. The first BDS-3 satellite was launched on 30 March 2015. On 27 December 2018, BeiDou Navigation ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |

_(14597240757).jpg)