|
Salan
] Salan, Salanus or Zalan ( Bulgarian language, Bulgarian and Serbian Cyrillic: Салан or Залан; hu, Zalán; ro, Salanus) was, according to the Gesta Hungarorum, a local Bulgarianhttp://keptar.niif.hu/000500/000586/magyaro-honf-terkep_nagykep.jpg voivod (duke) who ruled in the 9th century between Danube and Tisa rivers in the south and Carpathians in the north. The capital of his voivodship (duchy) was Titel. The exact border of his duchy is not clear: according to some sources, his duchy included present-day northern Serbia, much of present-day central Hungary, present-day eastern Slovakia and part of present-day western Ukraine and northern Romania, while according to other sources his duchy included only present-day Bačka/Bácska region of Serbia and Hungary. His name comes from the toponym Szalánkemén (archaically ''Zoloncaman'', today Stari Slankamen). History According to Gesta Hungarorum, Salan (Salanus) was an Orthodox vassal of the Byzantine Empire or ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Salan
] Salan, Salanus or Zalan ( Bulgarian language, Bulgarian and Serbian Cyrillic: Салан or Залан; hu, Zalán; ro, Salanus) was, according to the Gesta Hungarorum, a local Bulgarianhttp://keptar.niif.hu/000500/000586/magyaro-honf-terkep_nagykep.jpg voivod (duke) who ruled in the 9th century between Danube and Tisa rivers in the south and Carpathians in the north. The capital of his voivodship (duchy) was Titel. The exact border of his duchy is not clear: according to some sources, his duchy included present-day northern Serbia, much of present-day central Hungary, present-day eastern Slovakia and part of present-day western Ukraine and northern Romania, while according to other sources his duchy included only present-day Bačka/Bácska region of Serbia and Hungary. His name comes from the toponym Szalánkemén (archaically ''Zoloncaman'', today Stari Slankamen). History According to Gesta Hungarorum, Salan (Salanus) was an Orthodox vassal of the Byzantine Empire or ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bačka
Bačka ( sr-cyrl, Бачка, ) or Bácska () is a geographical and historical area within the Pannonian Plain bordered by the river Danube to the west and south, and by the river Tisza to the east. It is divided between Serbia and Hungary. Most of the area is located within the Vojvodina region in Serbia and Novi Sad, the capital of Vojvodina, lies on the border between Bačka and Syrmia. The smaller northern part of the geographical area is located within Bács-Kiskun County in Hungary. Name According to Serbian historians, Bačka is a typical Slavic name form, created from "Bač" (name of historical town in Bačka) and suffix "ka" (which designates "the land that belongs to Bač"). The name of " Bač" (Bács) town is of uncertain origin and its existence was recorded among Vlachs, Slavs and Hungarians in the Middle Ages. The origin of the name could be Paleo-Balkanic, Romanian, Slavic, or Old Turkic. According to Hungarian historians, the denominator of the landscap ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bulgarian–Hungarian Wars
The Bulgarian–Hungarian wars were a series of conflicts that occurred during the 9th–14th centuries between the Bulgarian Empire and the Kingdom of Hungary. The nearly 500-year conflict encompassed the northern and western Balkans, or what is known today as north-western Serbia, Romania and northern Bulgaria. The first clashes occurred in the late 9th century, in which the Hungarians were pushed west. Later, during the 10th century, the Hungarians overran the Bulgarian dukes in what is now Transylvania and conquered the eastern parts of the Pannonian Plain. Their raids against Bulgaria continued until the middle of the century when peace was restored. Both countries sustained friendly relations until 1003 when another war broke out, further diminishing Bulgarian power in Eastern Europe. In 1185, after the re-establishment of the Bulgarian Empire, both states fought numerous conflicts for control over the provinces of Belgrade, Braničevo, Vidin and the Severin. Hungaria ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Titel
Titel ( sr-Cyrl, Тител, hu, Titel) is a town and municipality located in the South Bačka District of the province of Vojvodina, Serbia. The town of Titel has a population of 5,247, while the population of the municipality of Titel is 15,738. It is located in southeastern part of the geographical region of Bačka, known as Šajkaška. Name In Serbian, the town is known as ''Titel'' (Тител), in Hungarian as ''Titel'', in German as ''Titel'' (and sometimes ''Theisshügel''), and in Latin as ''Titulium''. History The Titel Plateau is an elevated region between the Danube and Tisza rivers, close to the confluence; about ; roughly . It has an ellipsoid form and is characterized by steep slopes at the margins. It has a substantial loess cover and is often called the Titel Loess Plateau; the loess on the plateau is considered to contain the most detailed terrestrial palaeoclimate records in Europe, with a thick and apparently continuous record extending to the middle and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gesta Hungarorum
''Gesta Hungarorum'', or ''The Deeds of the Hungarians'', is the earliest book about Hungarian history which has survived for posterity. Its genre is not chronicle, but ''gesta'', meaning "deeds" or "acts", which is a medieval entertaining literature. It was written in Latin by an unidentified author who has traditionally been called Anonymus in scholarly works. According to most historians, the work was completed between around 1200 and 1230. The ''Gesta'' exists in a sole manuscript from the second part of the 13th century, which was for centuries held in Vienna. It is part of the collection of Széchényi National Library in Budapest. The principal subject of the ''Gesta'' is the Hungarian conquest of the Carpathian Basin at the turn of the 9th and 10th centuries, and it writes of the origin of the Hungarians, identifying the Hungarians' ancestors with the ancient Scythians. Many of its sources—including the Bible, Isidore of Seville's ''Etymologiae'', the 7th-century ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Stari Slankamen
Stari Slankamen ( sr-cyrl, Стари Сланкамен), also known as Slankamen ( sr-cyrl, Сланкамен), is a village located in the Inđija municipality, in the Syrmia District of Serbia. It is situated in the Autonomous Province of Vojvodina. Before the Yugoslav war ethnic Croats made up 38,78% of the population. The population of the village numbers 674 people, of whom 485 are ethnic Serbs (2002 census). Name Its name means "Old Slankamen", while the name of the neighbouring village, Novi Slankamen, means "New Slankamen". The name "Slankamen" itself means "the salty stone" in Serbo-Croatian. In Hungarian the village is known as ''Szalánkemén'' or ''Sztari Szlankamen'' (formerly also: ''Zalánkemén''), in German as ''Alt-Slankamen'', and in Turkish as ''Salankamen''. History In the 3rd century BC, the area was inhabited by Celtic Scordisci. In the first century BC, the fort was conquered by Romans and the settlement was known as Acumincum (''acumen'', point) ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tsar
Tsar ( or ), also spelled ''czar'', ''tzar'', or ''csar'', is a title used by East Slavs, East and South Slavs, South Slavic monarchs. The term is derived from the Latin word ''Caesar (title), caesar'', which was intended to mean "emperor" in the European medieval sense of the term—a ruler with the same rank as a Roman emperor, holding it by the approval of another emperor or a supreme ecclesiastical official (the Pope or the Ecumenical Patriarch)—but was usually considered by western Europeans to be equivalent to "king". It lends its name to a system of government, tsarist autocracy or tsarism. "Tsar" and its variants were the official titles of the following states: * Bulgarian Empire (First Bulgarian Empire in 681–1018, Second Bulgarian Empire in 1185–1396), and also used in Kingdom of Bulgaria, Tsardom of Bulgaria, in 1908–1946 * Serbian Empire, in 1346–1371 * Tsardom of Russia, in 1547–1721 (replaced in 1721 by ''imperator'' in Russian Empire, but still re ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Attila The Hun
Attila (, ; ), frequently called Attila the Hun, was the ruler of the Huns from 434 until his death in March 453. He was also the leader of a tribal empire consisting of Huns, Ostrogoths, Alans, and Bulgars, among others, in Central and Eastern Europe. During his reign, he was one of the most feared enemies of the Western and Eastern Roman Empires. He crossed the Danube twice and plundered the Balkans, but was unable to take Constantinople. His unsuccessful campaign in Persia was followed in 441 by an invasion of the Eastern Roman (Byzantine) Empire, the success of which emboldened Attila to invade the West. He also attempted to conquer Roman Gaul (modern France), crossing the Rhine in 451 and marching as far as Aurelianum (Orléans), before being stopped in the Battle of the Catalaunian Plains. He subsequently invaded Italy, devastating the northern provinces, but was unable to take Rome. He planned for further campaigns against the Romans, but died in 453. After Attila' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
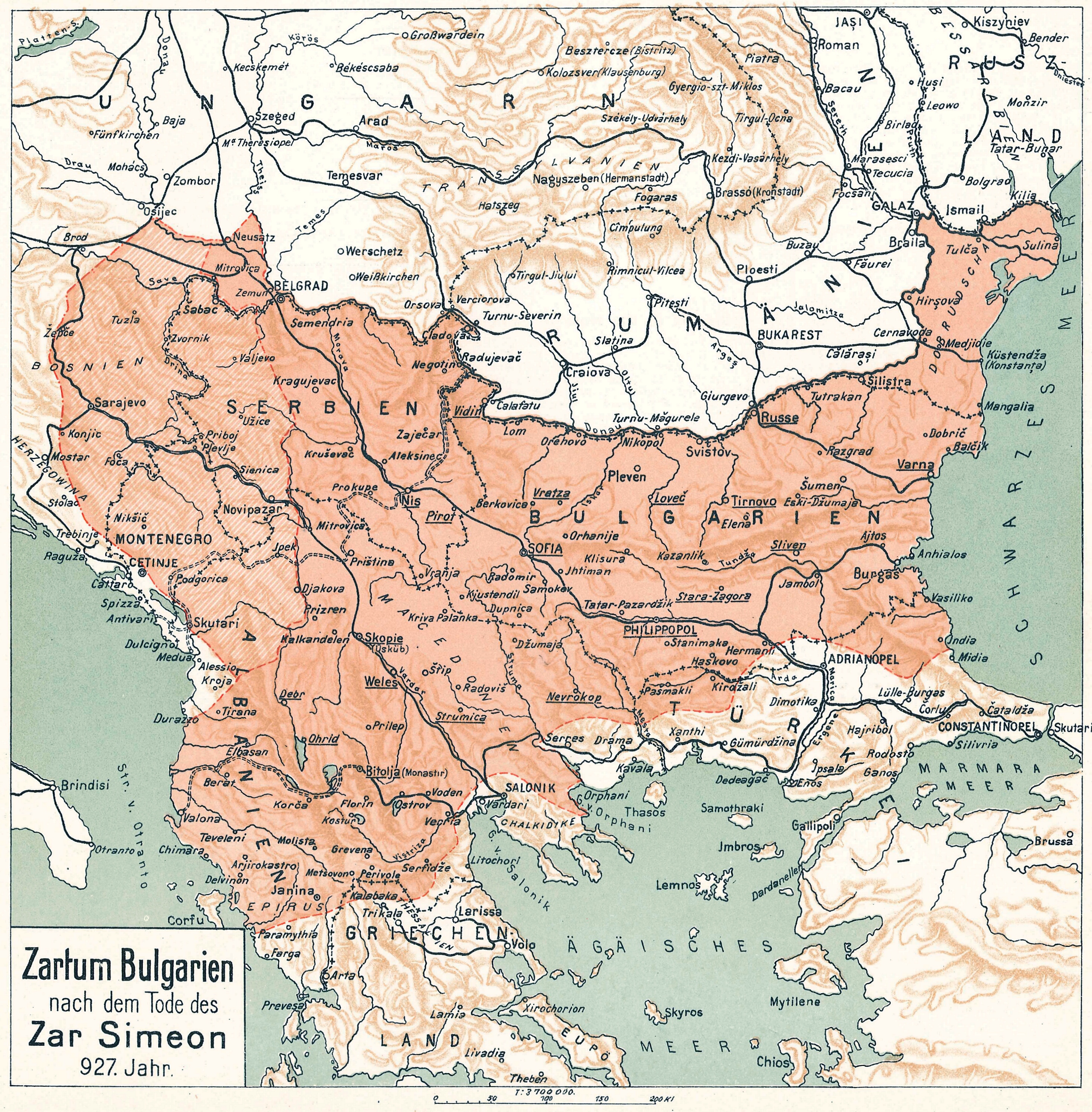
Simeon I Of Bulgaria
Tsar Simeon (also Symeon) I the Great ( cu, цѣсар҄ь Сѷмеѡ́нъ А҃ Вели́къ, cěsarĭ Sỳmeonŭ prĭvŭ Velikŭ bg, цар Симеон I Велики, Simeon I Veliki el, Συμεών Αʹ ὁ Μέγας, Sumeṓn prôtos ho Mégas) ruled over Bulgaria from 893 to 927,Lalkov, ''Rulers of Bulgaria'', pp. 23–25. during the First Bulgarian Empire. Simeon's successful campaigns against the Byzantines, Magyars and Serbs led Bulgaria to its greatest territorial expansion ever, making it the most powerful state in contemporary Eastern and Southeast Europe. His reign was also a period of unmatched cultural prosperity and enlightenment later deemed the Golden Age of Bulgarian culture. During Simeon's rule, Bulgaria spread over a territory between the Aegean, the Adriatic and the Black Sea.Bakalov, ''Istorija na Bǎlgarija'', "Simeon I Veliki". The newly independent Bulgarian Orthodox Church became the first new patriarchate besides the Pentarchy, and Bulgarian ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Byzantine Empire
The Byzantine Empire, also referred to as the Eastern Roman Empire or Byzantium, was the continuation of the Roman Empire primarily in its eastern provinces during Late Antiquity and the Middle Ages, when its capital city was Constantinople. It survived the fragmentation and fall of the Western Roman Empire in the 5th century AD and continued to exist for an additional thousand years until the fall of Constantinople to the Ottoman Empire in 1453. During most of its existence, the empire remained the most powerful economic, cultural, and military force in Europe. The terms "Byzantine Empire" and "Eastern Roman Empire" were coined after the end of the realm; its citizens continued to refer to their empire as the Roman Empire, and to themselves as Romans—a term which Greeks continued to use for themselves into Ottoman times. Although the Roman state continued and its traditions were maintained, modern historians prefer to differentiate the Byzantine Empire from Ancient Rome ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gesta Hungarorum Map
Gesta may refer to: Titles of works Gesta is the Latin word for "deeds" or "acts", and Latin titles, especially of medieval chronicles, frequently begin with the word, which thus is also a generic term for medieval biographies: *Gesta Adalberonis or Gesta Alberonis, "Deeds of Albero", Archbishop of Trier (1131–52) * Gesta Berengarii imperatoris, "Deeds of the Emperor Berengar", epic poem chronicling the career of Berengar of Friuli from c.874 to 915 *Gesta comitum Barcinonensium et regum Aragoniae, "Deeds of the counts of Barcelona and kings of Aragon", 14th century *Gesta Cnutonis Regis or Encomium Emmae Reginae, "Deeds of King Canute" 11th-century, also covers Queen Emma of Normandy *Gesta Danorum, "Deeds of the Danes", 12th century *Dei gesta per Francos, "Deeds of God through the Franks", 12th century, a narrative of the First Crusade *Gesta Francorum, "The Deeds of the Franks", in full Gesta Francorum et aliorum Hierosolimitanorum ("The deeds of the Franks and the other pilgr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hungarians
Hungarians, also known as Magyars ( ; hu, magyarok ), are a nation and ethnic group native to Hungary () and historical Hungarian lands who share a common culture, history, ancestry, and language. The Hungarian language belongs to the Uralic language family. There are an estimated 15 million ethnic Hungarians and their descendants worldwide, of whom 9.6 million live in today's Hungary. About 2–3 million Hungarians live in areas that were part of the Kingdom of Hungary before the Treaty of Trianon in 1920 and are now parts of Hungary's seven neighbouring countries, Slovakia, Ukraine, Romania, Serbia, Croatia, Slovenia, and Austria. Significant groups of people with Hungarian ancestry live in various other parts of the world, most of them in the United States, Canada, Germany, France, the United Kingdom, Chile, Brazil, Australia, and Argentina. Hungarians can be divided into several subgroups according to local linguistic and cultural characteristics; subgroups with distinc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |