|
Salampore
Salampore (salempore) was a kind of cotton cloth produced in India. It had been in use since the 17th century and was exported to Europe and Africa.''There were three staple varieties of cotton cloth manufactured in Coromandel - longcloth , salempores and moris . These three varieties accounted for by far the largest volume of export and were extensively woven in looms from North to South ...''Merchants, Companies, and Commerce on the Coromandel Coast, ...books.google.co.in › books Page 98 Exports Salempores was part of a varied collection of cloths such as long cloth, moris, and cloth with gold thread exported to various foreign locations like Bantam, Manila, and London from the Coromandel Coast. It was also exported to Africa and South America. Production Salampore was produced at various locations of India from north to down south. Pattern It was a colored woven cloth with stripe and check designs. Few sources also describe it as broad white or blue cotton fabric. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Punjum
Punjum (panjam, pŭn′jŭm; pun jum) was a type of Indian cotton cloth. It was produced in the Northern Circars, on the Coromandel Coastal region in South East India. Punjum was a kind of cotton longcloth that was produced in a variety of thread counts. Varieties of punjum Punjum was a woven fabric structure with an unusually strong texture. It was manufactured with a variety of widths from coarser to finer qualities (The finer the threads the greater number of punjums were contained in the breadth up to 40). There were Punjums available with a 120-thread count . A Punjum was regarded as a sign of quality, there were different numbers assigned for different grades ranging from 10,12,14,16, 18 up to 40.The lowest and coarse was called number 10. Later, Baramauhal successfully duplicated an imitation of Punjum which was a cloth with a lower thread count and half the length of the former. It was named Salampore. Dimensions John Forbes Watson used sample 466 to show Punjum ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Piece Goods
Piece goods were the textile materials sold in cut pieces as per the buyer's specification. The piece goods were either cut from a fabric roll or produced with a certain length, also called yard goods. Various textiles such as cotton, wool, silk, etc., were traded in terms of piece goods. The prices were determined as per the fabric quality. John Forbes Watson classified Indian textiles into two types: piece goods and loom goods. Piece goods are materials that must be cut and sewn before they can be used, whereas loom goods, such as scarves and Saris, are ready to use after leaving the loom. Production Many Indian clothes were ready to wear after leaving the loom. These were simple pieces of cloth of dimensions suited to the purposes. Lungi, Dhoti, and Sari are few specific examples of drape clothes. Other cloths produced according to specified dimensions are: * Longcloth made at Coromandel Coast was of the length of 37 yards or 37 to 40 yards. * Qutni at Damascus was we ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cotton
Cotton is a soft, fluffy staple fiber that grows in a boll, or protective case, around the seeds of the cotton plants of the genus '' Gossypium'' in the mallow family Malvaceae. The fiber is almost pure cellulose, and can contain minor percentages of waxes, fats, pectins, and water. Under natural conditions, the cotton bolls will increase the dispersal of the seeds. The plant is a shrub native to tropical and subtropical regions around the world, including the Americas, Africa, Egypt and India. The greatest diversity of wild cotton species is found in Mexico, followed by Australia and Africa. Cotton was independently domesticated in the Old and New Worlds. The fiber is most often spun into yarn or thread and used to make a soft, breathable, and durable textile. The use of cotton for fabric is known to date to prehistoric times; fragments of cotton fabric dated to the fifth millennium BC have been found in the Indus Valley civilization, as well as fabric remnants date ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
India
India, officially the Republic of India ( Hindi: ), is a country in South Asia. It is the seventh-largest country by area, the second-most populous country, and the most populous democracy in the world. Bounded by the Indian Ocean on the south, the Arabian Sea on the southwest, and the Bay of Bengal on the southeast, it shares land borders with Pakistan to the west; China, Nepal, and Bhutan to the north; and Bangladesh and Myanmar to the east. In the Indian Ocean, India is in the vicinity of Sri Lanka and the Maldives; its Andaman and Nicobar Islands share a maritime border with Thailand, Myanmar, and Indonesia. Modern humans arrived on the Indian subcontinent from Africa no later than 55,000 years ago., "Y-Chromosome and Mt-DNA data support the colonization of South Asia by modern humans originating in Africa. ... Coalescence dates for most non-European populations average to between 73–55 ka.", "Modern human beings—''Homo sapiens''—originated in Africa. Th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Europe
Europe is a large peninsula conventionally considered a continent in its own right because of its great physical size and the weight of its history and traditions. Europe is also considered a subcontinent of Eurasia and it is located entirely in the Northern Hemisphere and mostly in the Eastern Hemisphere. Comprising the westernmost peninsulas of Eurasia, it shares the continental landmass of Afro-Eurasia with both Africa and Asia. It is bordered by the Arctic Ocean to the north, the Atlantic Ocean to the west, the Mediterranean Sea to the south and Asia to the east. Europe is commonly considered to be separated from Asia by the watershed of the Ural Mountains, the Ural River, the Caspian Sea, the Greater Caucasus, the Black Sea and the waterways of the Turkish Straits. "Europe" (pp. 68–69); "Asia" (pp. 90–91): "A commonly accepted division between Asia and Europe ... is formed by the Ural Mountains, Ural River, Caspian Sea, Caucasus Mountains, and the Blac ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Africa
Africa is the world's second-largest and second-most populous continent, after Asia in both cases. At about 30.3 million km2 (11.7 million square miles) including adjacent islands, it covers 6% of Earth's total surface area and 20% of its land area.Sayre, April Pulley (1999), ''Africa'', Twenty-First Century Books. . With billion people as of , it accounts for about of the world's human population. Africa's population is the youngest amongst all the continents; the median age in 2012 was 19.7, when the worldwide median age was 30.4. Despite a wide range of natural resources, Africa is the least wealthy continent per capita and second-least wealthy by total wealth, behind Oceania. Scholars have attributed this to different factors including geography, climate, tribalism, Scramble for Africa, colonialism, the Cold War, neocolonialism, lack of democracy, and corruption. Despite this low concentration of wealth, recent economic expansion and the large and young ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Longcloth
Longcloth (or long cloth) refers to a plain cotton cloth originally made in comparatively long pieces. The name was applied particularly to cloth made in India. The long cloth made at Coromandel Coast was of the length of 37 yards. Longcloth, which is now commonly bleached, includes several various qualities. It is heavier than cambric, and finer than medium or Mexican. In the early 1900s, as it was used principally for underclothing and shirts, most of the longcloth sold in Great Britain passed through the shirt and underclothing manufacturers' hands who sold it to the shopkeepers. However, there was still considerable if decreasing retail trade-in piece-goods. In the UK in the early 20th century, the lower kinds of longcloth, which were made from American cotton, corresponded in quality to the better kinds of shirting made for the East, but the best longcloths were made from Egyptian cotton and were fine and fairly costly goods. Nowadays, longcloth designates a cotton fabric wh ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
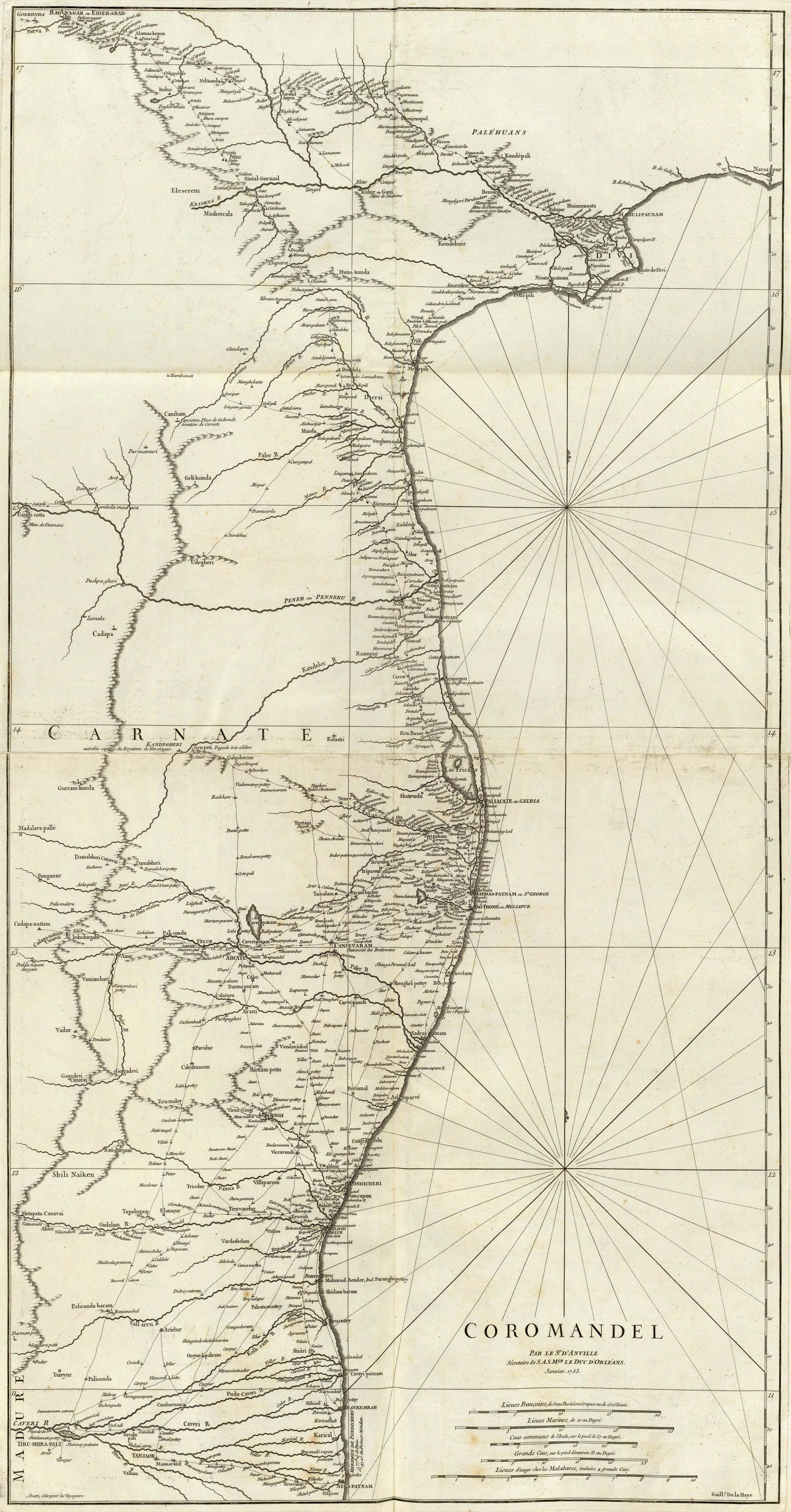
Coromandel Coast
The Coromandel Coast is the southeastern coastal region of the Indian subcontinent, bounded by the Utkal Plains to the north, the Bay of Bengal to the east, the Kaveri delta to the south, and the Eastern Ghats to the west, extending over an area of about 22,800 square kilometres. The coast has an average elevation of 80 metres and is backed by the Eastern Ghats, a chain of low lying and flat-topped hills. In historical Muslim sources from the 12th century onward, the Coromandel Coast was called Maʿbar. Etymology The land of the Chola dynasty was called ''Cholamandalam'' (சோழ மண்டலம்) in Tamil, translated as ''The realm of the Cholas'', from which the Portuguese derived the name ''Coromandel''.''The Land of the Tamulians and Its Missions'', by Eduard Raimund Baierlein, James Dunning BakerSouth Indian Coins – Page 61 by T. Desikachari – Coins, Indic – 1984Indian History – Page 112''Annals of Oriental Research'' – Page 1 by University of Madras ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
South America
South America is a continent entirely in the Western Hemisphere and mostly in the Southern Hemisphere, with a relatively small portion in the Northern Hemisphere at the northern tip of the continent. It can also be described as the southern Subregion#Americas, subregion of a single continent called Americas, America. South America is bordered on the west by the Pacific Ocean and on the north and east by the Atlantic Ocean; North America and the Caribbean Sea lie to the northwest. The continent generally includes twelve sovereign states: Argentina, Bolivia, Brazil, Chile, Colombia, Ecuador, Guyana, Paraguay, Peru, Suriname, Uruguay, and Venezuela; two dependent territory, dependent territories: the Falkland Islands and South Georgia and the South Sandwich Islands; and one administrative division, internal territory: French Guiana. In addition, the ABC islands (Leeward Antilles), ABC islands of the Kingdom of the Netherlands, Ascension Island (dependency of Saint Helena, Asce ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Woven
Woven fabric is any textile formed by weaving. Woven fabrics are often created on a loom, and made of many threads woven on a warp and a weft. Technically, a woven fabric is any fabric made by interlacing two or more threads at right angles to one another. Woven fabrics can be made of both natural and synthetic fibres, and are often made from a mixture of both. E.g. 100% Cotton or 80% Cotton & 20% polyester. 60% spandex and 40% cotton could also be woven together. Woven fabric is typically used in clothing, garments, for decoration, furniture or covering purposes such as carpets. In the Midwest, it is popular to have woven wicker furniture in sitting areas such as a patio or a dining room. Qualities Woven fabrics only stretch diagonally on the bias directions (between the warp and weft directions), unless the threads used are elastic. Woven fabric cloth usually frays at the edges, unless techniques are used to counter it, such as the use of pinking shears or hemming. Differen ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Stripe (pattern)
A stripe is a line or band that differs in color or tone from an adjacent area. Stripes are a group of such lines. Usage and appearance As a pattern (more than one stripe together), stripes are commonly seen in nature, food, emblems, clothing, and elsewhere. Two-toned stripes inherently draw one's attention, and as such are used to signal hazards. They are used in road signs, barricade tape, and thresholds. In nature, as with the zebra, stripes may have developed through natural selection to produce motion dazzle. Stripes may give appeal to certain sweets like the candy cane. For hundreds of years, stripes have been used in clothing. Striped clothing has frequently had negative symbolism in Western cultures. Historian Michel Pastoureau explores the cultural history of these design decisions in the book, '' The Devil's Cloth.'' See also * Square tiling *Sussi cloth * The Devil's Cloth * Argyle (pattern) * Racing flags * Flannel * Gingham * Madras (cloth) * Plaid (pattern) * ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Check (pattern)
Check (also checker, Brit: chequer) is a pattern of modified stripes consisting of crossed horizontal and vertical lines which form squares. The pattern typically contains two colours where a single checker (that is a single square within the check pattern) is surrounded on all four sides by a checker of a different colour. The pattern is commonly placed onto garments and is, in certain social contexts, applied to clothing which is worn to signify cultural or political affiliations. Such is the case with check in ska and on the keffiyeh. The pattern's all-pervasiveness and simple layout has lent to its practical usage in scientific experimentation and observation, optometry, technology (hardware and software), and as a symbol for responders to associate meaning with. Etymology The word is derived from the ancient Persian word ' which means "king" in the Sasanian game of Shatranj; an old form of chess which is played on a squared board of alternating coloured checkers. It is m ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |