|
Saint Avold
Saint-Avold (; ; Lorraine Franconian: ''Sänt Avuur'') is a commune in the Moselle department in Grand Est in north-eastern France. It is situated twenty-eight miles (45 km) east of Metz, France and seventeen miles (27 km) southwest of Saarbrücken, Germany. History The Saint-Avold area has frequently suffered invasions and since the nineteenth century has been controlled alternately by German and French authorities. The original Abbey of Saint Nabor began as an oratory for a sixth-century monastery. Gradually a complex developed after it received the relics of Saint Nabor, and the church was rebuilt in the eighteenth century, in part following Baroque style. It was designated as a basilica. During the French Revolution, the monastery and church suffered extensive damage; the cloisters were destroyed. The ancient parish church was sacrificed in exchange for keeping Saint Nabor. The abbey also suffered bombing damage during World War II, but much of the church has been ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Communes Of France
The () is a level of administrative division in the French Republic. French are analogous to civil townships and incorporated municipalities in the United States and Canada, ' in Germany, ' in Italy, or ' in Spain. The United Kingdom's equivalent are civil parishes, although some areas, particularly urban areas, are unparished. are based on historical geographic communities or villages and are vested with significant powers to manage the populations and land of the geographic area covered. The are the fourth-level administrative divisions of France. vary widely in size and area, from large sprawling cities with millions of inhabitants like Paris, to small hamlets with only a handful of inhabitants. typically are based on pre-existing villages and facilitate local governance. All have names, but not all named geographic areas or groups of people residing together are ( or ), the difference residing in the lack of administrative powers. Except for the municipal arrondi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Synagogue
A synagogue, ', 'house of assembly', or ', "house of prayer"; Yiddish: ''shul'', Ladino: or ' (from synagogue); or ', "community". sometimes referred to as shul, and interchangeably used with the word temple, is a Jewish house of worship. Synagogues have a place for prayer (the main sanctuary and sometimes smaller chapels), where Jews attend religious Services or special ceremonies (including Weddings, Bar Mitzvahs or Bat Mitzvahs, Confirmations, choir performances, or even children's plays), have rooms for study, social hall(s), administrative and charitable offices, classrooms for religious school and Hebrew school, sometimes Jewish preschools, and often have many places to sit and congregate; display commemorative, historic, or modern artwork throughout; and sometimes have items of some Jewish historical significance or history about the Synagogue itself, on display. Synagogues are consecrated spaces used for the purpose of Jewish prayer, study, assembly, and r ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Adrienne Thomas (novelist)
Adrienne Thomas was the pseudonym of Hertha A. Deutsch, ''nee'' Strauch (1897–1980), a German autobiographical novelist. Life Hertha Strauch was born in St Avold in Alsace-Lorraine, then part of Germany, on June 24, 1897. She grew up bilingual in German and French, going to school in Metz, where her family owned a small department store. During World War I she became a nurse for the Red Cross, at first in Metz and later in Berlin, where her family moved. During the 1920s she trained as a singer and actor at the Clara Lion Conservatory in Frankfurt. Writing as Adrienne Thomas, she drew on her Red Cross experiences for her semi-autobiographical anti-war novel ''Die Katrin wird Soldat'' (Katrin Becomes a Soldier), the diary of a young Jewish girl serving behind the German lines as a relief worker. Published in 1930, the book was translated into sixteen languages. When Adolf Hitler came to power in 1933 Thomas was forced to go into exile and her writings banned. After living in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Erich Isselhorst
Erich Isselhorst (5 February 1906 – 23 February 1948) was a German war criminal and ''Schutzstaffel'' (SS) member before and during World War II. Between 1942 and 1943, during the German invasion of the Soviet Union, Isselhorst was an ''Einsatzkommando'' leader, tasked with the murdering of Jews in what is now Belarus and the Baltic states. Before and after, Isselhorst held posts within the Gestapo and SS in Cologne, Munich, Stuttgart and Strasbourg. He was sentenced to death by both a British and French military court and executed in France in 1948 for ordering the execution of captured British SAS members and French civilians in 1944. Biography Early life Erich Georg Heinrich Isselhorst was born in Saint-Avold, Lorraine, in 1906, which was then part of the German Empire but is now part of France. He was educated in Dortmund, Recklinghausen and Düsseldorf, where he graduated in 1925. He was employed in a rubber factory before studying law from 1927 to 1930 in Cologne and Munic ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bronx
The Bronx () is a borough of New York City, coextensive with Bronx County, in the state of New York. It is south of Westchester County; north and east of the New York City borough of Manhattan, across the Harlem River; and north of the New York City borough of Queens, across the East River. The Bronx has a land area of and a population of 1,472,654 in the 2020 census. If each borough were ranked as a city, the Bronx would rank as the ninth-most-populous in the U.S. Of the five boroughs, it has the fourth-largest area, fourth-highest population, and third-highest population density.New York State Department of Health''Population, Land Area, and Population Density by County, New York State – 2010'' retrieved on August 8, 2015. It is the only borough of New York City not primarily on an island. With a population that is 54.8% Hispanic as of 2020, it is the only majority-Hispanic county in the Northeastern United States and the fourth-most-populous nationwide. The Bronx ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
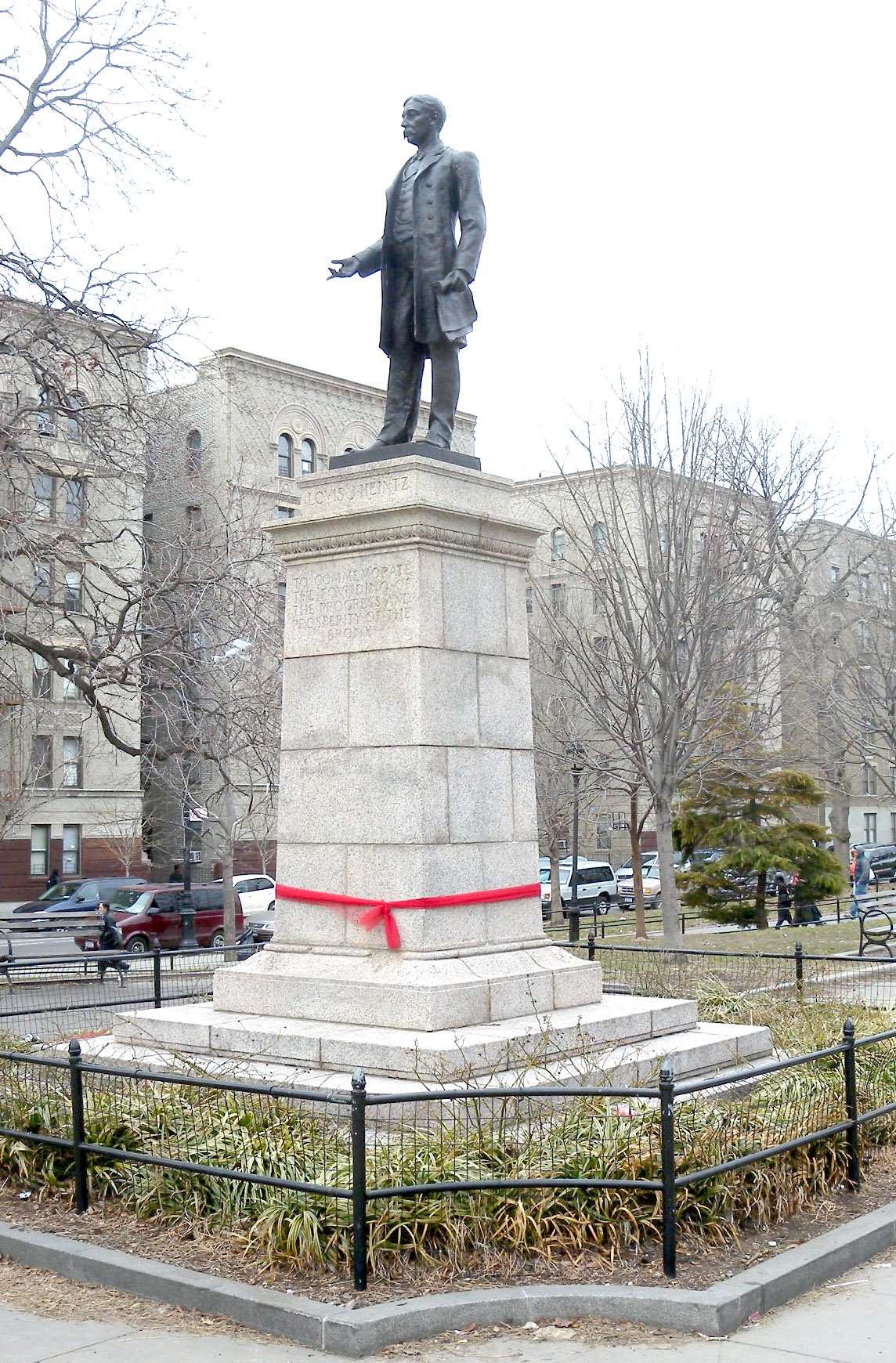
Grand Concourse (Bronx)
The Grand Concourse (also known as the Grand Boulevard and Concourse) is a thoroughfare in the borough (New York City), borough of the Bronx in New York City. Grand Concourse runs through several neighborhoods, including Bedford Park, Bronx, Bedford Park, Concourse, Bronx, Concourse, Highbridge, Bronx, Highbridge, Fordham, Bronx, Fordham, Mott Haven, Bronx, Mott Haven, Norwood, Bronx, Norwood and Tremont, Bronx, Tremont. For most of its length, the Concourse is wide, though portions of the Concourse are narrower. The Grand Concourse was designed by Louis Aloys Risse, an immigrant from Saint-Avold, Lorraine, France. Risse first conceived of the road in 1890, and the Concourse was built between 1894 and 1909, with an additional extension in 1927. The development of the Concourse led to the construction of apartment buildings surrounding the boulevard, and by 1939 it was called "the Park Avenue of middle-class Bronx residents". A period of decline followed in the 1960s and 1970s, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Włocławek
Włocławek (Polish pronunciation: ; german: Leslau) is a city located in central Poland along the Vistula (Wisła) River and is bordered by the Gostynin-Włocławek Landscape Park. As of December 2021, the population of the city is 106,928. Located in the Kuyavian-Pomeranian Voivodeship, it was the capital of Włocławek Voivodeship until 1999. The city is located in the historical region of Kuyavia and is the region's third largest city after Bydgoszcz and Toruń. History Włocławek's history dates back to the late Bronze Age – early Iron Age (1300 BCE – 500 BCE). Archaeological excavations conducted on the current city site uncovered the remains of a settlement belonging to the Lusatian culture, as well as evidence of a settlement of early Pomeranian culture which had been established. Traces of additional settlements dating to the Roman period and the early Middle Ages have also been excavated in the area. Middle Ages Precise dating of the city's founding has proven ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dudweiler
Dudweiler is a borough of Saarbrücken, on the Sulzbach creek. In 977, Dudweiler was first mentioned in official documents of German Emperor Otto II as the location of a chapel (Duodonisvillare). Dudweiler received town privileges on 12 September 1962. In 1974 it was incorporated into the city of Saarbrücken. Since then, Dudweiler has also been the name of one of the four city districts ''(Stadtbezirke)'' of Saarbrücken. The district of Dudweiler comprises four city boroughs ''(Stadtteile)'': Dudweiler, Herrensohr, Jägersfreude (both were boroughs of Dudweiler before 1974), and Scheidt (a municipality in the amt of Brebach before 1974). The coal mining industry played an important role for the growth of Dudweiler until 1968 when the last mine was closed. Today Dudweiler is characterised by its proximity to the Saarland University Saarland University (german: Universität des Saarlandes, ) is a public research university located in Saarbrücken, the capital of the German s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fayetteville, North Carolina
Fayetteville () is a city in and the county seat of Cumberland County, North Carolina, United States. It is best known as the home of Fort Bragg, a major U.S. Army installation northwest of the city. Fayetteville has received the All-America City Award from the National Civic League three times. As of the 2020 census it had a population of 208,501, It is the 6th-largest city in North Carolina. Fayetteville is in the Sandhills in the western part of the Coastal Plain region, on the Cape Fear River. With a population in 2020 of 529,252 people, the Fayetteville metropolitan area is the largest in southeastern North Carolina, and the fifth-largest in the state. Suburban areas of metro Fayetteville include Fort Bragg, Hope Mills, Spring Lake, Raeford, Pope Field, Rockfish, Stedman, and Eastover. History Early settlement The area of present-day Fayetteville was historically inhabited by various Siouan Native American peoples, such as the Eno, Shakori, Waccamaw, Keyauwee, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Oceanic Climate
An oceanic climate, also known as a marine climate, is the humid temperate climate sub-type in Köppen classification ''Cfb'', typical of west coasts in higher middle latitudes of continents, generally featuring cool summers and mild winters (for their latitude), with a relatively narrow annual temperature range and few extremes of temperature. Oceanic climates can be found in both hemispheres generally between 45 and 63 latitude, most notably in northwestern Europe, northwestern America, as well as New Zealand. Precipitation Locations with oceanic climates tend to feature frequent cloudy conditions with precipitation, low hanging clouds, and frequent fronts and storms. Thunderstorms are normally few, since strong daytime heating and hot and cold air masses meet infrequently in the region. In most areas with an oceanic climate, precipitation comes in the form of rain for the majority of the year. However, some areas with this climate see some snowfall annually during winter. M ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Köppen Climate Classification
The Köppen climate classification is one of the most widely used climate classification systems. It was first published by German-Russian climatologist Wladimir Köppen (1846–1940) in 1884, with several later modifications by Köppen, notably in 1918 and 1936. Later, the climatologist Rudolf Geiger (1894–1981) introduced some changes to the classification system, which is thus sometimes called the Köppen–Geiger climate classification system. The Köppen climate classification divides climates into five main climate groups, with each group being divided based on seasonal precipitation and temperature patterns. The five main groups are ''A'' (tropical), ''B'' (arid), ''C'' (temperate), ''D'' (continental), and ''E'' (polar). Each group and subgroup is represented by a letter. All climates are assigned a main group (the first letter). All climates except for those in the ''E'' group are assigned a seasonal precipitation subgroup (the second letter). For example, ''Af'' indi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
.jpg)