|
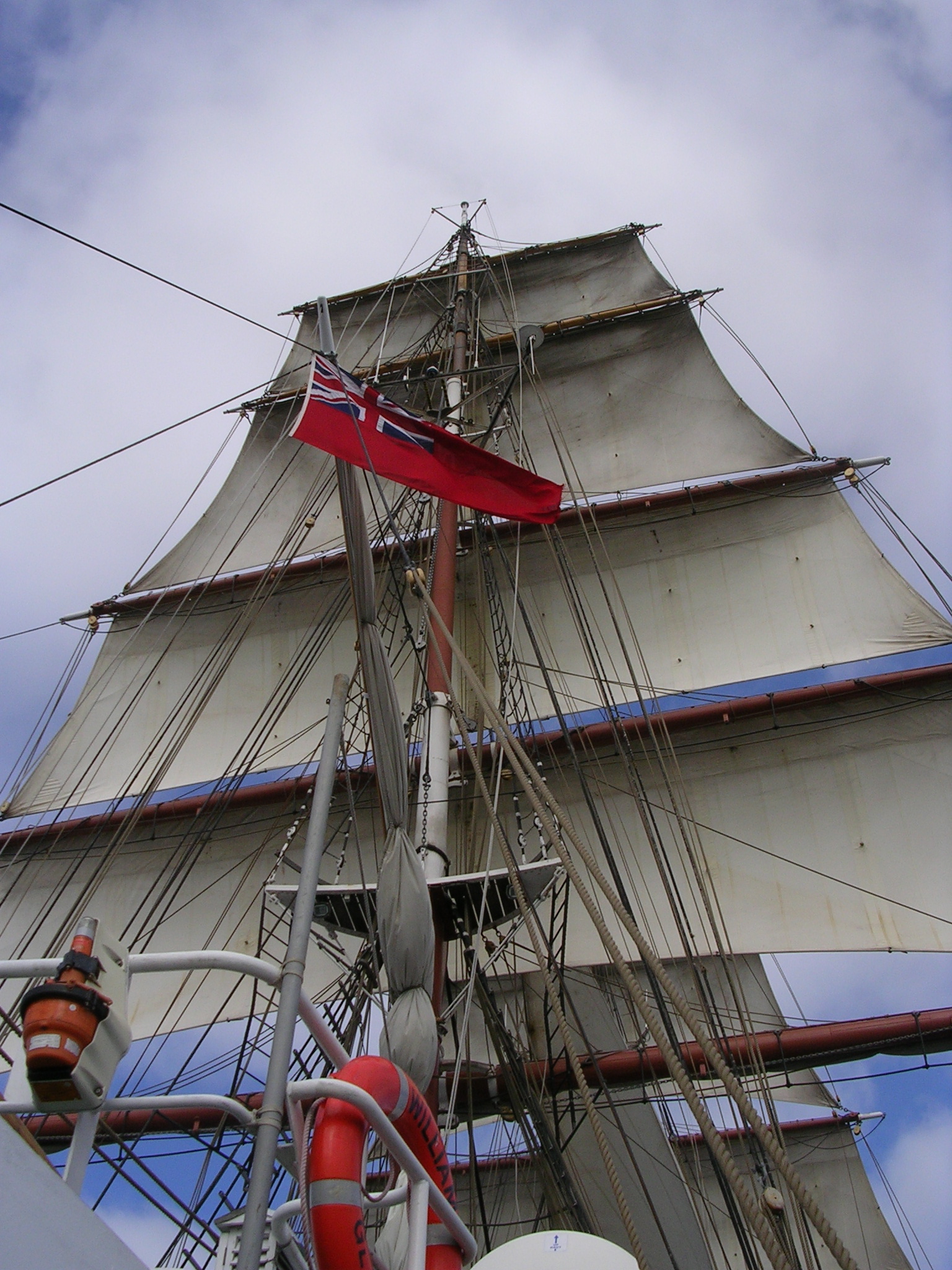
Sails
A sail is a tensile structure—which is made from fabric or other membrane materials—that uses wind power to propel sailing craft, including sailing ships, sailboats, windsurfers, ice boats, and even sail-powered land vehicles. Sails may be made from a combination of woven materials—including canvas or polyester cloth, laminated membranes or bonded filaments—usually in a three- or four-sided shape. A sail provides propulsive force via a combination of lift and drag, depending on its angle of attack—its angle with respect to the apparent wind. Apparent wind is the air velocity experienced on the moving craft and is the combined effect of the true wind velocity with the velocity of the sailing craft. Angle of attack is often constrained by the sailing craft's orientation to the wind or point of sail. On points of sail where it is possible to align the leading edge of the sail with the apparent wind, the sail may act as an airfoil, generating propulsive force as air pa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
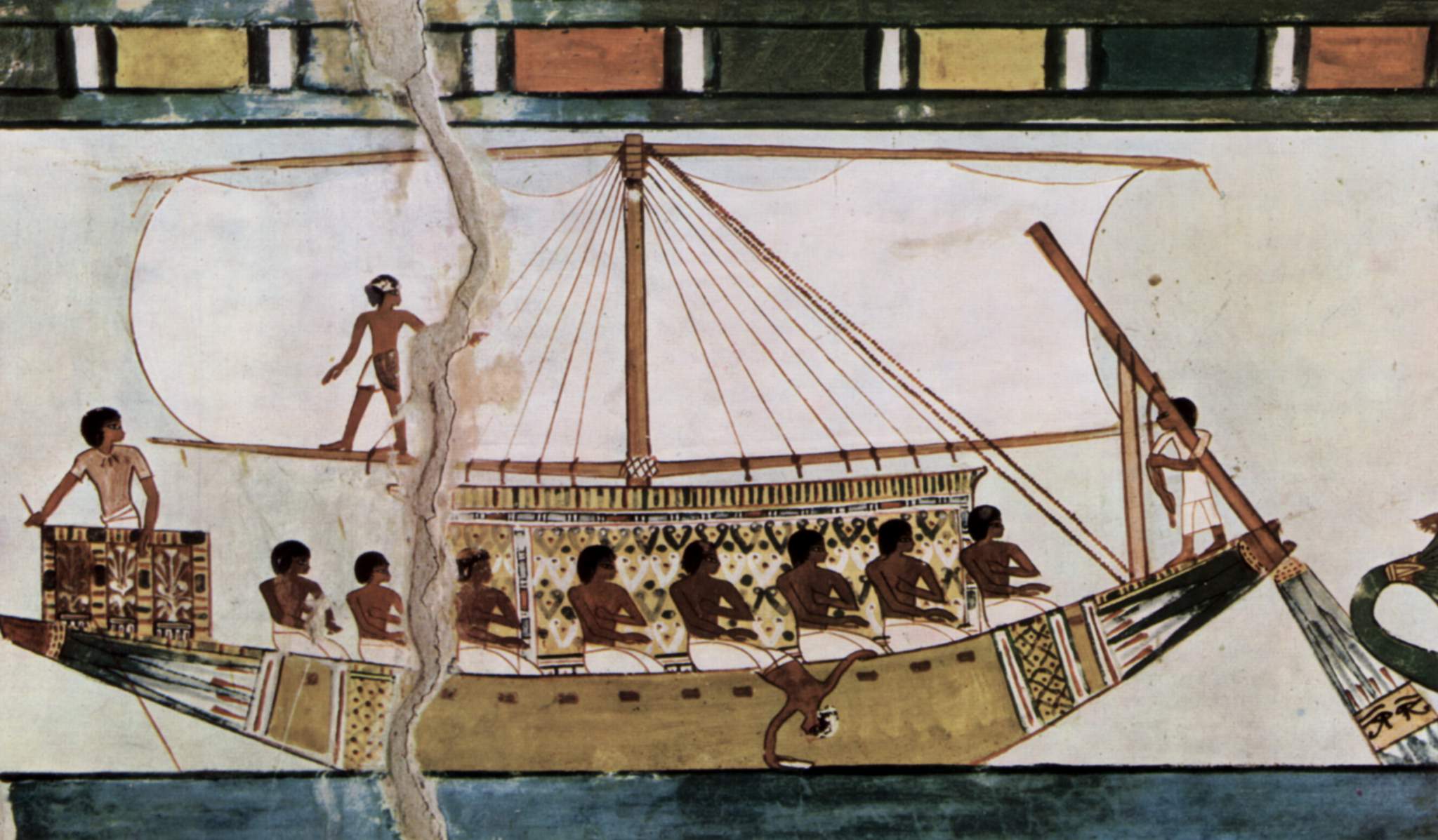
Sailing Ship
A sailing ship is a sea-going vessel that uses sails mounted on masts to harness the power of wind and propel the vessel. There is a variety of sail plans that propel sailing ships, employing square-rigged or fore-and-aft sails. Some ships carry square sails on each mast—the brig and full-rigged ship, said to be "ship-rigged" when there are three or more masts. Others carry only fore-and-aft sails on each mast, for instance some schooners. Still others employ a combination of square and fore-and-aft sails, including the barque, barquentine, and brigantine. Early sailing ships were used for river and coastal waters in Ancient Egypt and the Mediterranean. The Austronesian peoples developed maritime technologies that included the fore-and-aft crab-claw sail and with catamaran and outrigger hull configurations, which enabled the Austronesian expansion into the islands of the Indo-Pacific. This expansion originated in Taiwan BC and propagated through Island Southeast Asia ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Windsurfing
Windsurfing is a wind propelled water sport that is a combination of sailing and surfing. It is also referred to as "sailboarding" and "boardsailing", and emerged in the late 1960s from the aerospace and surf culture of California. Windsurfing gained a popular following across Europe and North America by the late 1970s and had achieved significant global popularity by the 1980s. Windsurfing became an olympic sport in 1984. Newer variants include windfoiling, kiteboarding and wingfoiling. Hydrofoil fins under the board allow the boards to safely lift out of the water and fly silently and smoothly above the surface even in lighter winds. Windsurfing is a recreational, family friendly sport, most popular at flat water locations around the world that offer safety and accessibility for beginner and intermediate participants. Technique and equipment have evolved over the years Major competitive disciplines include slalom, wave and freestyle. Increasingly, "foiling" is replacing trad ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kite Rig
Kite rigs are wind-assisted propulsion systems for propelling a vehicle. They differ from conventional sails in that they are flown from kite control lines, not supported by masts. Vehicles driven by kites include boats, buggies, and vehicles with snow and ice runners. They may be as simple as a person flying a kite while standing on a specialized skateboard, or be large, complex systems fixed to the vehicle, with powered and automated controls. They have recreational and commercial uses. Structure Current kite rigs can be sailed within 50 degrees of the wind.Skysails Captain John Konrad, Mariner's Weather Log, April 2009, Volume 53, No. 1, National Weather Service This allows them to sail upwind by tacking (sailing), tacking. A power kite is held at an angle to the wind using kite control systems, control lines. Like any other sai ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bermuda Rig
A Bermuda rig, Bermudian rig, or Marconi rig is a configuration of Mast (sailing), mast and rigging for a type of sailboat and is the typical configuration for most modern sailboats. This configuration was developed in Bermuda in the 1600s; the term ''Marconi'', a reference to the inventor of the Radio#History, radio, Guglielmo Marconi, became associated with this configuration in the early 1900s because the wires that stabilize the mast of a Bermuda rig reminded observers of the wires on early radio masts. Description The rig consists of a triangular sail set aft of the mast with its Mainsail#Bermuda rig, mainsail raised to the top of the mast; its parts of a sail, luff runs down the mast and is normally attached to it for its entire length; its Tack (sailing), tack is attached at the base of the mast; its Parts of a sail, foot (in modern versions of the rig) controlled by a Boom (sailing), boom; and its Parts of a sail, clew attached to the aft end of the boom, which is control ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Airfoil
An airfoil (American English) or aerofoil (British English) is the cross-sectional shape of an object whose motion through a gas is capable of generating significant lift, such as a wing, a sail, or the blades of propeller, rotor, or turbine. A solid body moving through a fluid produces an aerodynamic force. The component of this force perpendicular to the relative freestream velocity is called lift. The component parallel to the relative freestream velocity is called drag. An airfoil is a streamlined shape that is capable of generating significantly more lift than drag. Airfoils can be designed for use at different speeds by modifying their geometry: those for subsonic flight generally have a rounded leading edge, while those designed for supersonic flight tend to be slimmer with a sharp leading edge. All have a sharp trailing edge. Foils of similar function designed with water as the working fluid are called hydrofoils. The lift on an airfoil is primarily the result o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Angle Of Attack
In fluid dynamics, angle of attack (AOA, α, or \alpha) is the angle between a reference line on a body (often the chord line of an airfoil) and the vector representing the relative motion between the body and the fluid through which it is moving. Angle of attack is the angle between the body's reference line and the oncoming flow. This article focuses on the most common application, the angle of attack of a wing or airfoil moving through air. In aerodynamics, angle of attack specifies the angle between the chord line of the wing of a fixed-wing aircraft and the vector representing the relative motion between the aircraft and the atmosphere. Since a wing can have twist, a chord line of the whole wing may not be definable, so an alternate reference line is simply defined. Often, the chord line of the root of the wing is chosen as the reference line. Another choice is to use a horizontal line on the fuselage as the reference line (and also as the longitudinal axis). Some aut ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Square Rig
Square rig is a generic type of sail and rigging arrangement in which the primary driving sails are carried on horizontal spars which are perpendicular, or square, to the keel of the vessel and to the masts. These spars are called ''yards'' and their tips, outside the lifts, are called the ''yardarms.'' A ship mainly rigged so is called a square-rigger. The square rig is aerodynamically the most efficient running rig (i.e., sailing downwind), and stayed popular on ocean-going sailing ships until the end of the Age of Sail. The last commercial sailing ships, windjammers, were usually square-rigged four-masted barques. History The oldest archaeological evidence of use of a square-rig on a vessel is an image on a clay disk from Mesopotamia from 5000 BC. Single sail square rigs were used by the ancient Egyptians, the Phoenicians, the Greeks, the Romans, and the Celts. Later the Scandinavians, the Germanic peoples, and the Slavs adopted the single square-rigged sail, with it be ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Square Rig
Square rig is a generic type of sail and rigging arrangement in which the primary driving sails are carried on horizontal spars which are perpendicular, or square, to the keel of the vessel and to the masts. These spars are called ''yards'' and their tips, outside the lifts, are called the ''yardarms.'' A ship mainly rigged so is called a square-rigger. The square rig is aerodynamically the most efficient running rig (i.e., sailing downwind), and stayed popular on ocean-going sailing ships until the end of the Age of Sail. The last commercial sailing ships, windjammers, were usually square-rigged four-masted barques. History The oldest archaeological evidence of use of a square-rig on a vessel is an image on a clay disk from Mesopotamia from 5000 BC. Single sail square rigs were used by the ancient Egyptians, the Phoenicians, the Greeks, the Romans, and the Celts. Later the Scandinavians, the Germanic peoples, and the Slavs adopted the single square-rigged sail, with it be ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fore-and-aft Rig
A fore-and-aft rig is a sailing vessel rigged mainly with sails set along the line of the keel, rather than perpendicular to it as on a square rigged vessel. Description Fore-and-aft rigged sails include staysails, Bermuda rigged sails, gaff rigged sails, gaff sails, gunter rig, lateen sails, lug sails, tanja sails, the spanker sail on a square rig and crab claw sails. Fore-and-aft rigs include: * Rigs with one mast: the proa, the catboat, the sloop, the cutter * Rigs with two masts: the ketch, the yawl * Rigs with two or more masts: the schooner Barques and barquentines are partially square rigged and partially fore-and-aft rigged. A rig which combines both on a foremast is known as a hermaphroditic rig. History Austronesia The fore-and-aft rig is believed to have been first developed independently by the Austronesian peoples some time around 1500 BC with the invention of the crab claw sail. It is suggested that it evolved from a more primitive "V"-shaped "square" s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Spar (sailing)
A spar is a pole of wood, metal or lightweight materials such as carbon fibre used in the rigging of a sailing vessel to carry or support its sail. These include yards, booms, and masts, which serve both to deploy sail and resist compressive and bending forces, as well as the bowsprit and spinnaker pole. In larger vessels during the age of sail, spare spars could be roped together to provide a temporary surface known as a "spar deck". These served as jury-rigged repairs for permanent decks, or as an additional platform under which to shelter goods or crew. The term was also informally applied to areas of the forecastle or quarterdeck where spare spars were stored by laying them flat against the existing decking. In the modern era the term has been used to describe the uppermost deck on flush deck Flush deck is a term in naval architecture. It can refer to any deck of a ship which is continuous from stem to stern. History The flush deck design originated with rice ships built ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Spar (sailing)
A spar is a pole of wood, metal or lightweight materials such as carbon fibre used in the rigging of a sailing vessel to carry or support its sail. These include yards, booms, and masts, which serve both to deploy sail and resist compressive and bending forces, as well as the bowsprit and spinnaker pole. In larger vessels during the age of sail, spare spars could be roped together to provide a temporary surface known as a "spar deck". These served as jury-rigged repairs for permanent decks, or as an additional platform under which to shelter goods or crew. The term was also informally applied to areas of the forecastle or quarterdeck where spare spars were stored by laying them flat against the existing decking. In the modern era the term has been used to describe the uppermost deck on flush deck Flush deck is a term in naval architecture. It can refer to any deck of a ship which is continuous from stem to stern. History The flush deck design originated with rice ships built ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
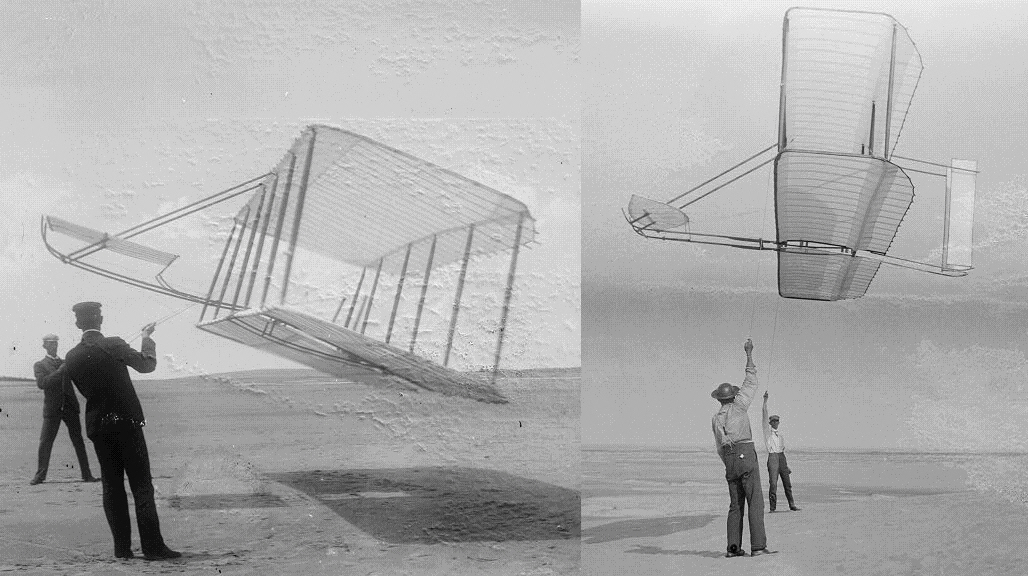
Kite
A kite is a tethered heavier than air flight, heavier-than-air or lighter-than-air craft with wing surfaces that react against the air to create Lift (force), lift and Drag (physics), drag forces. A kite consists of wings, tethers and anchors. Kites often have a bridle and tail to guide the face of the kite so the wind can lift it. Some kite designs don’t need a bridle; box kites can have a single attachment point. A kite may have fixed or moving anchors that can balance the kite. The name is derived from kite (bird), kite, the hovering bird of prey. The Lift (force), lift that sustains the kite in flight is generated when air moves around the kite's surface, producing low pressure above and high pressure below the wings. The interaction with the wind also generates horizontal Drag (physics), drag along the direction of the wind. The resultant force vector from the lift and drag force components is opposed by the tension of one or more of the rope, lines or tethers to which t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |