|
SagDIG
The Sagittarius Dwarf Irregular Galaxy (SagDIG) is a dwarf galaxy in the constellation of Sagittarius. (SagDIG should not be confused with the Sagittarius Dwarf Spheroidal Galaxy, SagDEG, a satellite galaxy of the Milky Way discovered decades later in the same constellation.) It lies about 3.4 million light-years away. It was discovered by Cesarsky ''et al.'' on a photographic plate taken for the ESO (B) Atlas on 13 June 1977 using the ESO 1 meter Schmidt telescope. The SagDIG is thought to be the member of the Local Group most remote from the Local Group's barycenter. It is only slightly outside the zero-velocity surface of the Local Group. SagDIG is a much more luminous galaxy than the Aquarius Dwarf and it has been through a prolonged period of star formation.Momany ''et al.'' 2005. This has resulted in it containing a rich intermediate-age population of stars. Twenty-seven candidate carbon stars have been identified inside SagDIG. Analysis shows tha ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
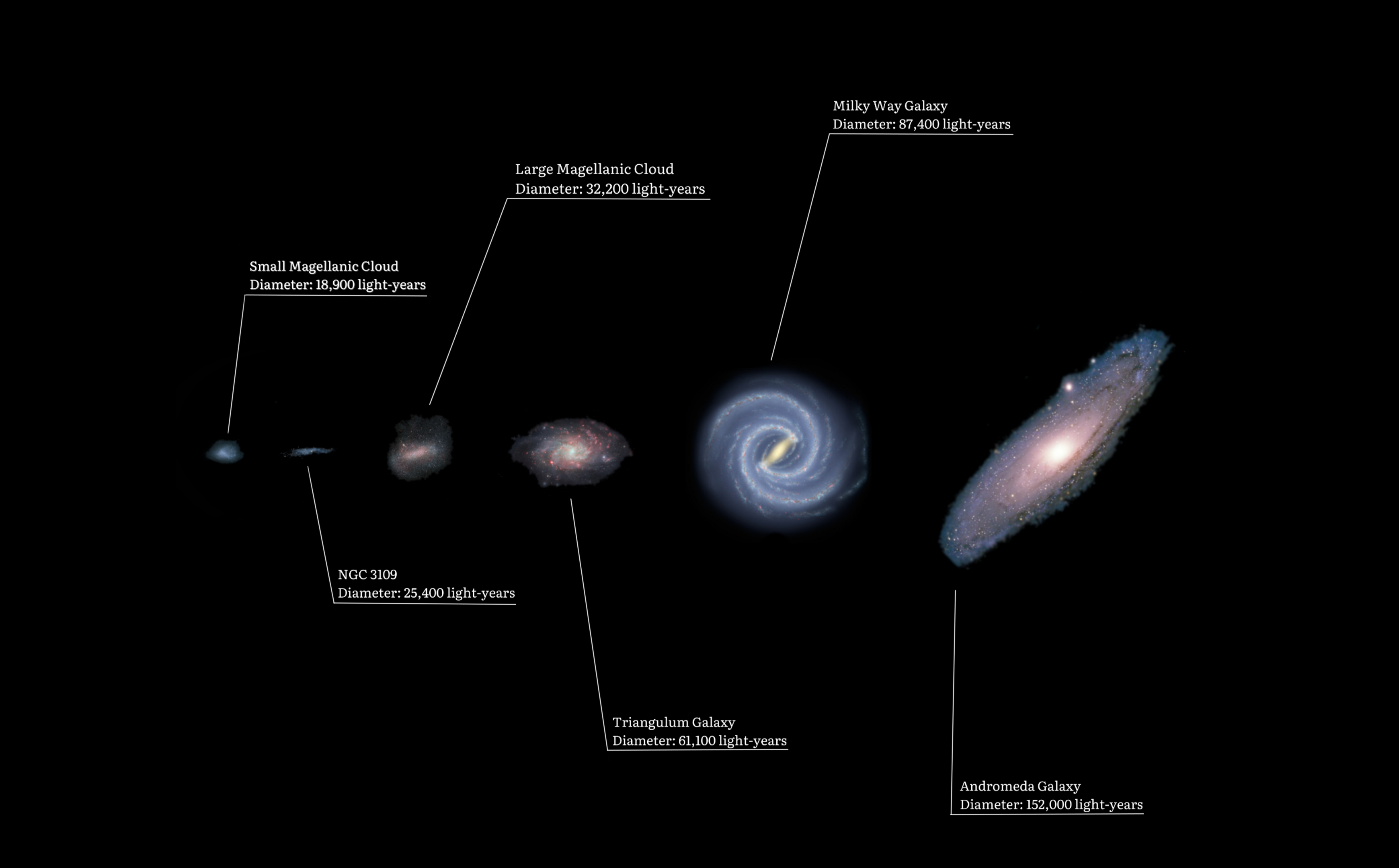
Local Group
The Local Group is the galaxy group that includes the Milky Way. It has a total diameter of roughly , and a total mass of the order of . It consists of two collections of galaxies in a "dumbbell" shape: the Milky Way and its satellites form one lobe, and the Andromeda Galaxy and its satellites constitute the other. The two collections are separated by about and are moving toward one another with a velocity of . The group itself is a part of the larger Virgo Supercluster, which may be a part of the Laniakea Supercluster. The exact number of galaxies in the Local Group is unknown as some are occluded by the Milky Way; however, at least 80 members are known, most of which are dwarf galaxies. The two largest members, the Andromeda Galaxy and the Milky Way, are both spiral galaxies with masses of about solar masses each. Each has its own system of satellite galaxies: * The Andromeda Galaxy's satellite system consists of Messier 32 (M32), Messier 110 (M110), NGC 147, NGC 185, A ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hubble Space Telescope
The Hubble Space Telescope (often referred to as HST or Hubble) is a space telescope that was launched into low Earth orbit in 1990 and remains in operation. It was not the first space telescope, but it is one of the largest and most versatile, renowned both as a vital research tool and as a public relations boon for astronomy. The Hubble telescope is named after astronomer Edwin Hubble and is one of NASA's Great Observatories. The Space Telescope Science Institute (STScI) selects Hubble's targets and processes the resulting data, while the Goddard Space Flight Center (GSFC) controls the spacecraft. Hubble features a mirror, and its five main instruments observe in the ultraviolet, visible, and near-infrared regions of the electromagnetic spectrum. Hubble's orbit outside the distortion of Earth's atmosphere allows it to capture extremely high-resolution images with substantially lower background light than ground-based telescopes. It has recorded some of the most detaile ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Photographic Plate
Photographic plates preceded photographic film as a capture medium in photography, and were still used in some communities up until the late 20th century. The light-sensitive emulsion of silver salts was coated on a glass plate, typically thinner than common window glass. History Glass plates were far superior to film for research-quality imaging because they were stable and less likely to bend or distort, especially in large-format frames for wide-field imaging. Early plates used the wet collodion process. The wet plate process was replaced late in the 19th century by gelatin dry plates. A view camera nicknamed "The Mammoth" weighing was built by George R. Lawrence in 1899, specifically to photograph "The Alton Limited" train owned by the Chicago & Alton Railway. It took photographs on glass plates measuring × . Glass plate photographic material largely faded from the consumer market in the early years of the 20th century, as more convenient and less fragile fil ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Irregular Galaxies
An irregular galaxy is a galaxy that does not have a distinct regular shape, unlike a spiral or an elliptical galaxy. Irregular galaxies do not fall into any of the regular classes of the Hubble sequence, and they are often chaotic in appearance, with neither a nuclear bulge nor any trace of spiral arm structure. Collectively they are thought to make up about a quarter of all galaxies. Some irregular galaxies were once spiral or elliptical galaxies but were deformed by an uneven external gravitational force. Irregular galaxies may contain abundant amounts of gas and dust. This is not necessarily true for dwarf irregulars. Irregular galaxies are commonly small, about one tenth the mass of the Milky Way galaxy. Due to their small sizes, they are prone to environmental effects like crashing with large galaxies and intergalactic clouds. Types There are three major types of irregular galaxies: * An Irr-I galaxy (Irr I) is an irregular galaxy that features some structure but not eno ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dwarf Irregular Galaxies
An irregular galaxy is a galaxy that does not have a distinct regular shape, unlike a Spiral galaxy, spiral or an elliptical galaxy. Irregular galaxies do not fall into any of the regular classes of the Hubble sequence, and they are often chaotic in appearance, with neither a bulge (astronomy), nuclear bulge nor any trace of spiral arm structure. Collectively they are thought to make up about a quarter of all galaxies. Some irregular galaxies were once spiral or elliptical galaxies but were deformed by an uneven external gravitational force. Irregular galaxies may contain abundant amounts of gas and dust. This is not necessarily true for dwarf irregulars. Irregular galaxies are commonly small, about one tenth the mass of the Milky Way galaxy. Due to their small sizes, they are prone to environmental effects like crashing with large galaxies and intergalactic clouds. Types There are three major types of irregular galaxies: * An Irr-I galaxy (Irr I) is an irregular galaxy that f ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Astronomy And Astrophysics
''Astronomy & Astrophysics'' is a monthly peer-reviewed scientific journal covering theoretical, observational, and instrumental astronomy and astrophysics. The journal is run by a Board of Directors representing 27 sponsoring countries plus a representative of the European Southern Observatory. The journal is published by EDP Sciences and the editor-in-chief is . History Origins ''Astronomy and Astrophysics'' (A&A) was created as an answer to the publishing scenario found in Europe in the 1960s. At that time, multiple journals were being published in several countries around the continent. These journals usually had a limited number of subscribers, and published articles in languages other than English, resulting in a small number of citations compared to American and British journals. Starting in 1963, conversations between astronomers from European countries assessed the need for a common astronomical journal. On 8 April 1968, leading astronomers from Belgium, Denmark, Fran ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Metal-poor
In astronomy, metallicity is the abundance of elements present in an object that are heavier than hydrogen and helium. Most of the normal physical matter in the Universe is either hydrogen or helium, and astronomers use the word ''"metals"'' as a convenient short term for ''"all elements except hydrogen and helium"''. This word-use is distinct from the conventional chemical or physical definition of a metal as an electrically conducting solid. Stars and nebulae with relatively high abundances of heavier elements are called "metal-rich" in astrophysical terms, even though many of those elements are nonmetals in chemistry. The presence of heavier elements hails from stellar nucleosynthesis, where the majority of elements heavier than hydrogen and helium in the Universe (''metals'', hereafter) are formed in the cores of stars as they evolve. Over time, stellar winds and supernovae deposit the metals into the surrounding environment, enriching the interstellar medium and providing re ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Stellar Population
During 1944, Walter Baade categorized groups of stars within the Milky Way into stellar populations. In the abstract of the article by Baade, he recognizes that Jan Oort originally conceived this type of classification in 1926: Baade noticed that bluer stars were strongly associated with the spiral arms, and yellow stars dominated near the central galactic bulge and within globular star clusters. Two main divisions were defined as * Population I and * Population II, with another newer, hypothetical division called * Population III added in 1978; they are often simply abbreviated as Pop. I, Pop. II, and Pop. III. Among the population types, significant differences were found with their individual observed stellar spectra. These were later shown to be very important and were possibly related to star formation, observed kinematics, stellar age, and even galaxy evolution in both spiral and elliptical galaxies. These three simple population classes use ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Carbon Stars
A carbon star (C-type star) is typically an asymptotic giant branch star, a luminous red giant, whose atmosphere contains more carbon than oxygen. The two elements combine in the upper layers of the star, forming carbon monoxide, which consumes most of the oxygen in the atmosphere, leaving carbon atoms free to form other carbon compounds, giving the star a "sooty" atmosphere and a strikingly ruby red appearance. There are also some dwarf and supergiant carbon stars, with the more common giant stars sometimes being called classical carbon stars to distinguish them. In most stars (such as the Sun), the atmosphere is richer in oxygen than carbon. Ordinary stars not exhibiting the characteristics of carbon stars but cool enough to form carbon monoxide are therefore called oxygen-rich stars. Carbon stars have quite distinctive spectral characteristics, and they were first recognized by their spectra by Angelo Secchi in the 1860s, a pioneering time in astronomical spectroscopy. Spectra ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Aquarius Dwarf
The Aquarius Dwarf is a dwarf galaxy, dwarf irregular galaxy, first catalogued in 1959 by the DDO survey. It is located within the boundaries of the constellation of Aquarius (constellation), Aquarius. It is a member of the Local Group of galaxies, albeit an extremely isolated one; it is one of only a few known Local Group members for which a past close approach to the Milky Way or Andromeda Galaxy can be ruled out, based on its current location and velocity. Local Group membership was firmly established only in 1999, with the derivation of a distance based on the tip of the red-giant branch method. Its distance from the Milky Way of 3.2 ±0.2 Mly (980 ±40 kpc) means that Aquarius Dwarf is quite isolated in space. It is one of the least luminous Local Group galaxies to contain significant amounts of neutral hydrogen and support to ongoing star formation, although it does so only at an extremely low level. Because of its large distance, the Hubble Space Telescope is required in or ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Zero-velocity Surface
The zero-velocity surface is a concept that relates to the N-body problem of gravity. It represents a surface a body of given energy cannot cross, since it would have zero velocity on the surface. It was first introduced by George William Hill. The zero-velocity surface is particularly significant when working with weak gravitational interactions among orbiting bodies. Three-body problem In the circular restricted three-body problem two heavy masses orbit each other at constant radial distance and angular velocity, and a particle of negligible mass is affected by their gravity. By shifting to a rotating coordinate system where the masses are stationary a centrifugal force is introduced. Energy and momentum are not conserved separately in this coordinate system, but the Jacobi integral remains constant: :C=\omega^2 (x^2+y^2) + 2 \left(\frac+\frac\right) - \left(\dot x^2+\dot y^2+\dot z^2\right) where \omega is the rotation rate, x,y the particle's location in the rotating coordinate ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Barycentric Coordinates (astronomy)
In astronomy, the barycenter (or barycentre; ) is the center of mass of two or more bodies that orbit one another and is the point about which the bodies orbit. A barycenter is a dynamical point, not a physical object. It is an important concept in fields such as astronomy and astrophysics. The distance from a body's center of mass to the barycenter can be calculated as a two-body problem. If one of the two orbiting bodies is much more massive than the other and the bodies are relatively close to one another, the barycenter will typically be located within the more massive object. In this case, rather than the two bodies appearing to orbit a point between them, the less massive body will appear to orbit about the more massive body, while the more massive body might be observed to wobble slightly. This is the case for the Earth–Moon system, whose barycenter is located on average from Earth's center, which is 75% of Earth's radius of . When the two bodies are of similar mass ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |


.jpg)


