|
S Andromedae
SN 1885A (also S Andromedae) was a supernova in the Andromeda Galaxy, the only one seen in that galaxy so far by astronomers. It was the first supernova ever seen outside the Milky Way, though it was not appreciated at the time how far away it was. It is also known as "Supernova 1885". Discovery The supernova appears to have been seen first on August 17, 1885, by French astronomer Ludovic Gully during a public stargazing event. Gully thought it was scattered moonlight in his telescope and did not follow up on this observation. Irish amateur astronomer Isaac Ward in Belfast claimed to have seen the object on August 19, 1885, but did not immediately publish its existence. The independent detection of the supernova by Ernst Hartwig at Dorpat (Tartu) Observatory in Estonia on August 20, 1885, however, was communicated in a telegram on August 31, 1885, once Hartwig had verified in more ideal circumstances that the feature was not caused by reflected moonlight. The telegram promp ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Photometric System
In astronomy, a photometric system is a set of well-defined passbands (or optical filters), with a known sensitivity to incident radiation. The sensitivity usually depends on the optical system, detectors and filters used. For each photometric system a set of primary standard stars is provided. A commonly adopted standardized photometric system is the Johnson-Morgan or UBV photometric system (1953). At present, there are more than 200 photometric systems. Photometric systems are usually characterized according to the widths of their passbands: * broadband (passbands wider than 30 nm, of which the most widely used is Johnson-Morgan UBV system) * intermediate band (passbands between 10 and 30 nm wide) * narrow band (passbands less than 10 nm wide) Photometric letters Each letter designates a section of light of the electromagnetic spectrum; these cover well the consecutive major groups, near-ultraviolet (NUV), visible light (centered on the V band), near-infrared ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
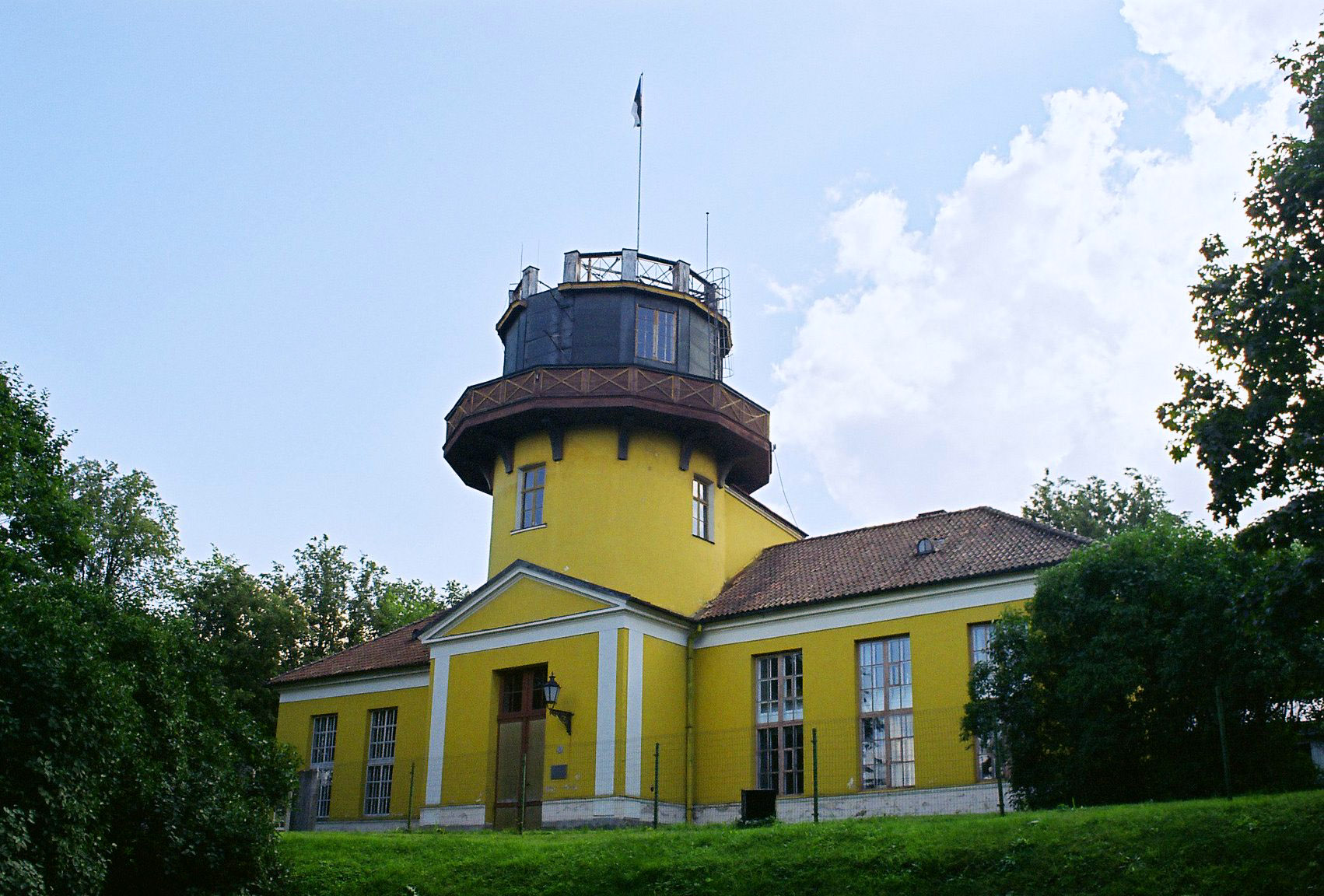
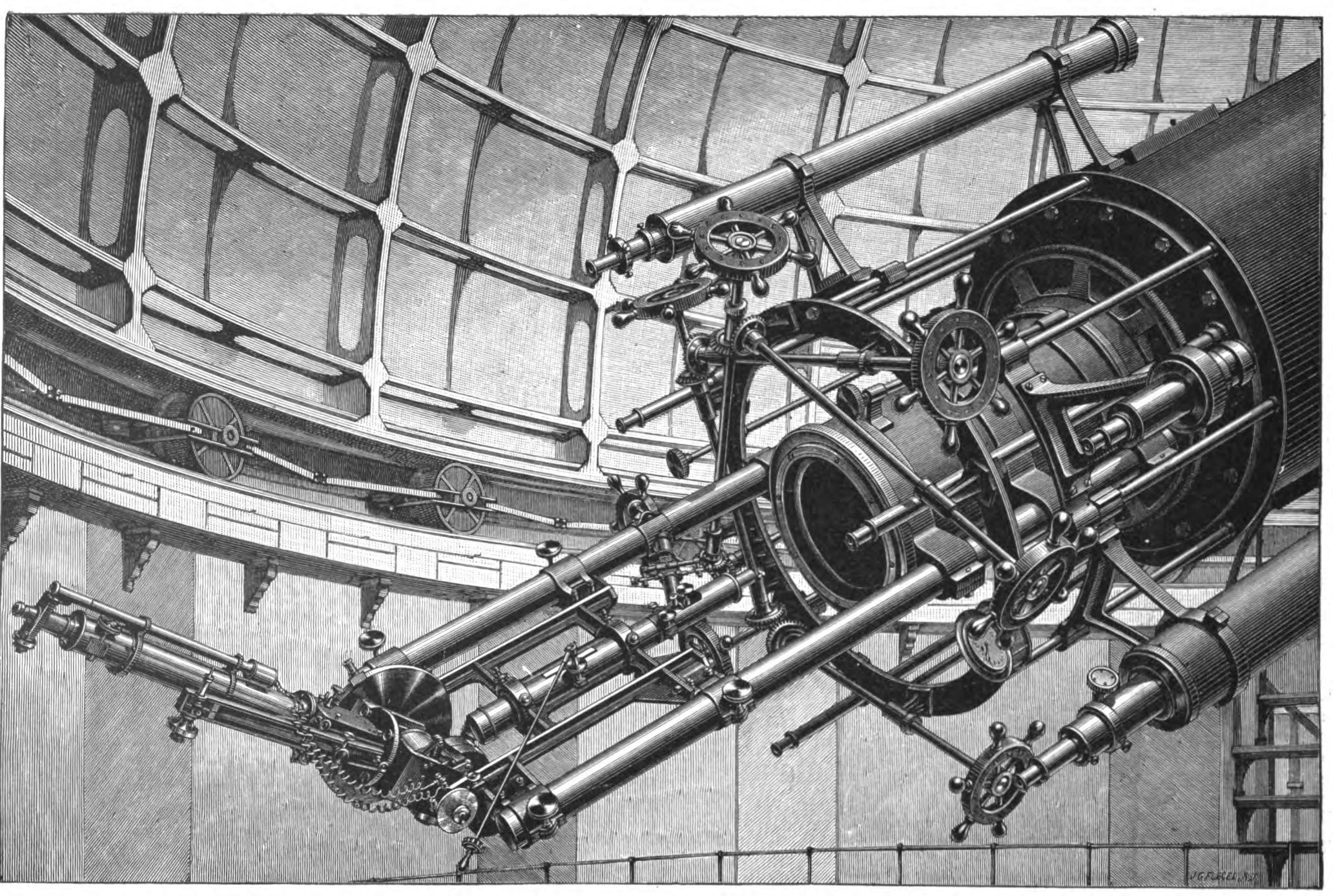
Tartu Observatory
The Tartu Observatory ( et, Tartu Observatoorium) is the largest astronomical observatory in Estonia. On 1 January 2018, Tartu Observatory was joined again to the University of Tartu, and the observatory is now an institute of the university. It is located on the Tõravere hill, about 20 km south-west of Tartu in Nõo Parish, Tartu County. The old Tartu Observatory located in Tartu city centre, is known internationally for its connection to Friedrich Georg Wilhelm von Struve and the Struve Geodetic Arc, of which it is the first reference point. History The Tartu Observatory was founded at the Imperial University of Dorpat as it was reopened in 1802. The observatory building was completed in 1810 on the Toome hill in Dorpat. The instruments were installed in 1814 by von Struve who subsequently started observations. In 1824, a 9" Fraunhofer refractor arrived, the largest achromatic telescope in the world at the time. When von Struve began assembling his Geodetic Arc in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Calcium
Calcium is a chemical element with the symbol Ca and atomic number 20. As an alkaline earth metal, calcium is a reactive metal that forms a dark oxide-nitride layer when exposed to air. Its physical and chemical properties are most similar to its heavier homologues strontium and barium. It is the fifth most abundant element in Earth's crust, and the third most abundant metal, after iron and aluminium. The most common calcium compound on Earth is calcium carbonate, found in limestone and the fossilised remnants of early sea life; gypsum, anhydrite, fluorite, and apatite are also sources of calcium. The name derives from Latin ''calx'' "lime", which was obtained from heating limestone. Some calcium compounds were known to the ancients, though their chemistry was unknown until the seventeenth century. Pure calcium was isolated in 1808 via electrolysis of its oxide by Humphry Davy, who named the element. Calcium compounds are widely used in many industries: in foods and pharma ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Iron
Iron () is a chemical element with symbol Fe (from la, ferrum) and atomic number 26. It is a metal that belongs to the first transition series and group 8 of the periodic table. It is, by mass, the most common element on Earth, right in front of oxygen (32.1% and 30.1%, respectively), forming much of Earth's outer and inner core. It is the fourth most common element in the Earth's crust. In its metallic state, iron is rare in the Earth's crust, limited mainly to deposition by meteorites. Iron ores, by contrast, are among the most abundant in the Earth's crust, although extracting usable metal from them requires kilns or furnaces capable of reaching or higher, about higher than that required to smelt copper. Humans started to master that process in Eurasia during the 2nd millennium BCE and the use of iron tools and weapons began to displace copper alloys, in some regions, only around 1200 BCE. That event is considered the transition from the Bronze Age to the Iron A ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hubble Space Telescope
The Hubble Space Telescope (often referred to as HST or Hubble) is a space telescope that was launched into low Earth orbit in 1990 and remains in operation. It was not the first space telescope, but it is one of the largest and most versatile, renowned both as a vital research tool and as a public relations boon for astronomy. The Hubble telescope is named after astronomer Edwin Hubble and is one of NASA's Great Observatories. The Space Telescope Science Institute (STScI) selects Hubble's targets and processes the resulting data, while the Goddard Space Flight Center (GSFC) controls the spacecraft. Hubble features a mirror, and its five main instruments observe in the ultraviolet, visible, and near-infrared regions of the electromagnetic spectrum. Hubble's orbit outside the distortion of Earth's atmosphere allows it to capture extremely high-resolution images with substantially lower background light than ground-based telescopes. It has recorded some of the most detaile ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kitt Peak
Kitt Peak ( ood, Ioligam) is a mountain in the U.S. state of Arizona, and at is the highest point in the Quinlan Mountains. It is the location of the Kitt Peak National Observatory. The radio telescope at the observatory is one of ten dishes comprising the Very Long Baseline Array radio telescope. The peak was named in English by county surveyor George J. Roskruge for his sister, Phillippa, who was the wife of William F. Kitt. On his 1893 Pima County Survey map, Roskruge spelled the name 'Kits'. At the request of the wife of George F. Kitt, the spelling was changed by decision in 1930. Kitt Peak is the second-highest peak on the Tohono O'odham Indian Reservation, and as such is the second-most sacred after Baboquivari Peak. Near the summit is I'itoi's Garden, the summer residence of the nation's elder brother deity. The name Ioligam means "red stick" in reference to the abundance of manzanita Manzanita is a common name for many species of the genus ''Arctostaphylos''. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nicholas U
Nicholas is a male given name and a surname. The Eastern Orthodox Church, the Roman Catholic Church, and the Anglican Churches celebrate Saint Nicholas every year on December 6, which is the name day for "Nicholas". In Greece, the name and its derivatives are especially popular in maritime regions, as St. Nicholas is considered the protector saint of seafarers. Origins The name is derived from the Greek name Νικόλαος (''Nikolaos''), understood to mean 'victory of the people', being a compound of νίκη ''nikē'' 'victory' and λαός ''laos'' 'people'.. An ancient paretymology of the latter is that originates from λᾶς ''las'' ( contracted form of λᾶας ''laas'') meaning 'stone' or 'rock', as in Greek mythology, Deucalion and Pyrrha recreated the people after they had vanished in a catastrophic deluge, by throwing stones behind their shoulders while they kept marching on. The name became popular through Saint Nicholas, Bishop of Myra in Lycia, the inspir ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
SN 2002bj
SN 2002bj was the explosion of a star in the galaxy NGC 1821, located in the constellation Lepus. The explosion was discovered by Jack Newton in scans of images produced by Tim Puckett. (It was independently discovered by the Lick/Tenagra Observatory as part of their combined supernova search program.) Initially it had an apparent magnitude of about 14.7 and was categorized as a Type IIn supernova. However, in 2008 Dovi Poznanski discovered that the spectrum more closely resembled a Type Ia supernova. Further, the energy output was much lower than a typical supernova and the luminosity dropped at a dramatic pace. A team consisting of Poznanski, Joshua Bloom, Alex Filippenko and others concluded that it was a new category of exploding star. This system is believed to consist of a binary pair of white dwarf stars, with helium being transferred from one dwarf to the other. The accreted helium exploded in a thermonuclear reaction on the surface of the more massive white dwarf, resul ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hagai Perets
Haggai (; he, חַגַּי – ''Ḥaggay''; Koine Greek: Ἀγγαῖος; la, Aggaeus) was a Hebrew prophet during the building of the Second Temple in Jerusalem, and one of the twelve minor prophets in the Hebrew Bible and the author of the Book of Haggai. He is known for his prophecy in 520 BCE, commanding the Jews to rebuild the Temple. He was the first of three post-exile prophets from the Neo-Babylonian Exile of the House of Judah (with Zechariah, his contemporary, and Malachi, who lived about one hundred years later), who belonged to the period of Jewish history which began after the return from captivity in Babylon. His name means "my holidays." The name Haggai, with various vocalizations, is also found in the Book of Esther, as a eunuch servant of the Queen. Life Scarcely anything is known of his personal history, with the book of Haggai offering no biographical details about his ancestry or anything else in his life outside the prophecies of 520 BCE. Haggai is ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dovi Poznanski
Dovi is an arrondissement in the Zou department of Benin. It is an administrative division under the jurisdiction of the commune of Zagnanado. According to the population census conducted by the Institut National de la Statistique Benin An institute is an organisational body created for a certain purpose. They are often research organisations ( research institutes) created to do research on specific topics, or can also be a professional body. In some countries, institutes can ... on February 15, 2002, the arrondissement had a total population of 4,518. accessed b Geohive accessed 4 June 2012 References [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Stellar Spectrum
Astronomical spectroscopy is the study of astronomy using the techniques of spectroscopy to measure the spectrum of electromagnetic radiation, including visible light, ultraviolet, X-ray, infrared and radio waves that radiate from stars and other celestial objects. A stellar spectrum can reveal many properties of stars, such as their chemical composition, temperature, density, mass, distance and luminosity. Spectroscopy can show the velocity of motion towards or away from the observer by measuring the Doppler shift. Spectroscopy is also used to study the physical properties of many other types of celestial objects such as planets, nebulae, galaxies, and active galactic nuclei. Background Astronomical spectroscopy is used to measure three major bands of radiation in the electromagnetic spectrum: visible light, radio waves, and X-rays. While all spectroscopy looks at specific bands of the spectrum, different methods are required to acquire the signal depending on the frequency. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |