|
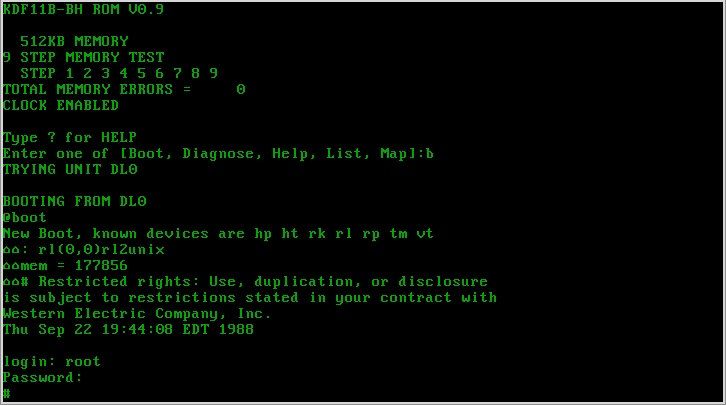
SUN OS
SunOS is a Unix-branded operating system developed by Sun Microsystems for their workstation and server (computing), server computer systems. The ''SunOS'' name is usually only used to refer to versions 1.0 to 4.1.4, which were based on Berkeley Software Distribution, BSD, while versions 5.0 and later are based on UNIX System V Release 4, and are marketed under the brand name ''Solaris (operating system), Solaris''. History SunOS 1 only supported the Sun-2 series systems, including Sun-1 systems upgraded with Sun-2 (Motorola 68010, 68010) CPU boards. SunOS 2 supported Sun-2 and Sun-3 (Motorola 68020, 68020) series systems. SunOS 4 supported Sun-2 (until release 4.0.3), Sun-3 (until 4.1.1), Sun386i (4.0, 4.0.1 and 4.0.2 only) and Sun-4 (SPARC) architectures. Although SunOS 4 was intended to be the first release to fully support Sun's new SPARC processor, there was also a SunOS 3.2 release with preliminary support for Sun-4 systems. SunOS 4.1.2 introduce ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sun Microsystems
Sun Microsystems, Inc. (Sun for short) was an American technology company that sold computers, computer components, software, and information technology services and created the Java programming language, the Solaris operating system, ZFS, the Network File System (NFS), and SPARC microprocessors. Sun contributed significantly to the evolution of several key computing technologies, among them Unix, RISC processors, thin client computing, and virtualized computing. Notable Sun acquisitions include Cray Business Systems Division, Storagetek, and ''Innotek GmbH'', creators of VirtualBox. Sun was founded on February 24, 1982. At its height, the Sun headquarters were in Santa Clara, California (part of Silicon Valley), on the former west campus of the Agnews Developmental Center. Sun products included computer servers and workstations built on its own RISC-based SPARC processor architecture, as well as on x86-based AMD Opteron and Intel Xeon processors. Sun also developed its own ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
System V Release 4
Unix System V (pronounced: "System Five") is one of the first commercial versions of the Unix operating system. It was originally developed by AT&T and first released in 1983. Four major versions of System V were released, numbered 1, 2, 3, and 4. System V Release 4 (SVR4) was commercially the most successful version, being the result of an effort, marketed as ''Unix System Unification'', which solicited the collaboration of the major Unix vendors. It was the source of several common commercial Unix features. System V is sometimes abbreviated to SysV. , the AT&T-derived Unix market is divided between four System V variants: IBM's AIX, Hewlett Packard Enterprise's HP-UX and Oracle's Solaris, plus the free-software illumos forked from OpenSolaris. Overview Introduction System V was the successor to 1982's UNIX System III. While AT&T developed and sold hardware that ran System V, most customers ran a version from a reseller, based on AT&T's reference implementation. A s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Virtual File System
A virtual file system (VFS) or virtual filesystem switch is an abstract layer on top of a more concrete file system. The purpose of a VFS is to allow client applications to access different types of concrete file systems in a uniform way. A VFS can, for example, be used to access local and network storage devices transparently without the client application noticing the difference. It can be used to bridge the differences in Windows, classic Mac OS/macOS and Unix filesystems, so that applications can access files on local file systems of those types without having to know what type of file system they are accessing. A VFS specifies an interface (or a "contract") between the kernel and a concrete file system. Therefore, it is easy to add support for new file system types to the kernel simply by fulfilling the contract. The terms of the contract might change incompatibly from release to release, which would require that concrete file system support be recompiled, and possibly mo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
External Data Representation
External Data Representation (XDR) is a standard data serialization format, for uses such as computer network protocols. It allows data to be transferred between different kinds of computer systems. Converting from the local representation to XDR is called ''encoding''. Converting from XDR to the local representation is called ''decoding''. XDR is implemented as a software library of functions which is portable between different operating systems and is also independent of the transport layer. XDR uses a base unit of 4 bytes, serialized in big-endian order; smaller data types still occupy four bytes each after encoding. Variable-length types such as string and opaque are padded to a total divisible by four bytes. Floating-point numbers are represented in IEEE 754 format. History XDR was developed in the mid 1980s at Sun Microsystems, and first widely published in 1987. XDR became an IETF standard in 1995. The XDR data format is in use by many systems, including: * Network File ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Remote Procedure Call
In distributed computing, a remote procedure call (RPC) is when a computer program causes a procedure (subroutine) to execute in a different address space (commonly on another computer on a shared network), which is coded as if it were a normal (local) procedure call, without the programmer explicitly coding the details for the remote interaction. That is, the programmer writes essentially the same code whether the subroutine is local to the executing program, or remote. This is a form of client–server interaction (caller is client, executor is server), typically implemented via a request–response message-passing system. In the object-oriented programming paradigm, RPCs are represented by remote method invocation (RMI). The RPC model implies a level of location transparency, namely that calling procedures are largely the same whether they are local or remote, but usually, they are not identical, so local calls can be distinguished from remote calls. Remote calls are usually orde ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Network Information Service
The Network Information Service, or NIS (originally called Yellow Pages or YP), is a client–server directory service protocol for distributing system configuration data such as user and host names between computers on a computer network. Sun Microsystems developed the NIS; the technology is licensed to virtually all other Unix vendors. Because British Telecom PLC owned the name "Yellow Pages" as a registered trademark in the United Kingdom for its paper-based, commercial telephone directory, Sun changed the name of its system to NIS, though all the commands and functions still start with "yp". A NIS/YP system maintains and distributes a central directory of user and group information, hostnames, e-mail aliases and other text-based tables of information in a computer network. For example, in a common UNIX environment, the list of users for identification is placed in and secret authentication hashes in . NIS adds another "global" user list which is used for identifying user ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Network File System (protocol)
Network File System (NFS) is a distributed file system protocol originally developed by Sun Microsystems (Sun) in 1984, allowing a user on a client computer to access files over a computer network much like local storage is accessed. NFS, like many other protocols, builds on the Open Network Computing Remote Procedure Call (ONC RPC) system. NFS is an open IETF standard defined in a Request for Comments (RFC), allowing anyone to implement the protocol. Versions and variations Sun used version 1 only for in-house experimental purposes. When the development team added substantial changes to NFS version 1 and released it outside of Sun, they decided to release the new version as v2, so that version interoperation and RPC version fallback could be tested. NFSv2 Version 2 of the protocol (defined in RFC 1094, March 1989) originally operated only over User Datagram Protocol (UDP). Its designers meant to keep the server side stateless, with locking (for example) i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sun-2
The Sun-2 series of UNIX workstations and servers was launched by Sun Microsystems in November 1983. As the name suggests, the Sun-2 represented the second generation of Sun systems, superseding the original Sun-1 series. The Sun-2 series used a 10 MHz Motorola 68010 microprocessor with a proprietary Sun-2 Memory Management Unit (MMU), which enabled it to be the first Sun architecture to run a full virtual memory UNIX implementation, SunOS 1.0, based on 4.1BSD. Early Sun-2 models were based on the Intel Multibus architecture, with later models using VMEbus, which continued to be used in the successor Sun-3 and Sun-4 families. Sun-2 systems were supported in SunOS until version 4.0.3. A port to support Multibus Sun-2 systems in NetBSD was begun in January 2001 from the Sun-3 support in the NetBSD 1.5 release. Code supporting the Sun-2 began to be merged into the NetBSD tree in April 2001. sun2 is considered a tier 2 support platform as of NetBSD 7.0.1. Sun-2 models Models ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Motorola 68010
The Motorola MC68010 processor is a 16/32-bit microprocessor from Motorola, released in 1982 as the successor to the Motorola 68000. It fixes several small flaws in the 68000, and adds a few features. The 68010 is pin-compatible with the 68000, but is not 100% software compatible. Some of the differences were: * The MOVE from SR instruction is now privileged (it may only be executed in supervisor mode). This means that the 68010 meets Popek and Goldberg virtualization requirements. Because the 68000 offers an unprivileged MOVE from SR, it does not meet them. * The MOVE from CCR instruction was added to partially compensate for the removal of the user-mode MOVE from SR. * It can recover from bus faults, and re-run the last instruction, allowing it to implement virtual memory. * The exception stack frame is different. * It introduced a 22-bit Vector Base Register (VBR) that holds A 1:10of the 1 KiB-aligned base address for the exception vector table. The 68000 vector table was al ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sun-1
Sun-1 was the first generation of UNIX computer workstations and servers produced by Sun Microsystems, launched in May 1982. These were based on a CPU board designed by Andy Bechtolsheim while he was a graduate student at Stanford University and funded by DARPA. The Sun-1 systems ran SunOS 0.9, a port of UniSoft's UniPlus V7 port of Seventh Edition UNIX to the Motorola 68000 microprocessor, with no window system. Early Sun-1 workstations and servers used the original Sun logo, a series of red "U"s laid out in a square, rather than the more familiar purple diamond shape used later. The first Sun-1 workstation was sold to Solo Systems in May 1982. The Sun-1/100 was used in the original Lucasfilm EditDroid non-linear editing system. Models Hardware The Sun-1 workstation was based on the Stanford University SUN workstation designed by Andy Bechtolsheim (advised by Vaughan Pratt and Forest Baskett), a graduate student and co-founder of Sun Microsystems. At the heart of this de ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Motorola 68000
The Motorola 68000 (sometimes shortened to Motorola 68k or m68k and usually pronounced "sixty-eight-thousand") is a 16/32-bit complex instruction set computer (CISC) microprocessor, introduced in 1979 by Motorola Semiconductor Products Sector. The design implements a 32-bit instruction set, with 32-bit registers and a 16-bit internal data bus. The address bus is 24 bits and does not use memory segmentation, which made it easier to program for. Internally, it uses a 16-bit data arithmetic logic unit (ALU) and two more 16-bit ALUs used mostly for addresses, and has a 16-bit external data bus. For this reason, Motorola termed it a 16/32-bit processor. As one of the first widely available processors with a 32-bit instruction set, and running at relatively high speeds for the era, the 68k was a popular design through the 1980s. It was widely used in a new generation of personal computers with graphical user interfaces, including the Macintosh 128K, Amiga, Atari ST, and X68000. Th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Version 7 Unix
Seventh Edition Unix, also called Version 7 Unix, Version 7 or just V7, was an important early release of the Unix operating system. V7, released in 1979, was the last Bell Laboratories release to see widespread distribution before the commercialization of Unix by AT&T Corporation in the early 1980s. V7 was originally developed for Digital Equipment Corporation's PDP-11 minicomputers and was later ported to other platforms. Overview Unix versions from Bell Labs were designated by the edition of the user's manual with which they were accompanied. Released in 1979, the Seventh Edition was preceded by Sixth Edition, which was the first version licensed to commercial users. Development of the Research Unix line continued with the Eighth Edition, which incorporated development from 4.1BSD, through the Tenth Edition, after which the Bell Labs researchers concentrated on developing Plan 9. V7 was the first readily portable version of Unix. As this was the era of minicomputers, with ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |