|
STS-88
STS-88 was the first Space Shuttle mission to the International Space Station (ISS). It was flown by Space Shuttle ''Endeavour'', and took the first American module, the ''Unity'' node, to the station. The seven-day mission was highlighted by the mating of the U.S.-built ''Unity'' node to the Functional Cargo Block (''Zarya'' module) already in orbit, and three spacewalks to connect power and data transmission cables between the Node and the FGB. ''Zarya'', built by Boeing and the Russian Space Agency, was launched on a Russian Proton rocket from the Baikonur Cosmodrome in Kazakhstan in November 1998. Other payloads on the STS-88 mission included the IMAX Cargo Bay Camera (ICBC), the Argentine Scientific Applications Satellite-S (SAC-A), the MightySat 1 Hitchhiker payload, the Space Experiment Module (SEM-07) and Getaway Special G-093 sponsored by the University of Michigan. Crew Launch attempts Mission highlights Node 1, named ''Unity'', was the first space station ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
STS-88 Launches
STS-88 was the first Space Shuttle mission to the International Space Station (ISS). It was flown by Space Shuttle ''Endeavour'', and took the first American module, the ''Unity'' node, to the station. The seven-day mission was highlighted by the mating of the U.S.-built ''Unity'' node to the Functional Cargo Block (''Zarya'' module) already in orbit, and three spacewalks to connect power and data transmission cables between the Node and the FGB. ''Zarya'', built by Boeing and the Russian Space Agency, was launched on a Russian Proton rocket from the Baikonur Cosmodrome in Kazakhstan in November 1998. Other payloads on the STS-88 mission included the IMAX Cargo Bay Camera (ICBC), the Argentine Scientific Applications Satellite-S (SAC-A), the MightySat 1 Hitchhiker payload, the Space Experiment Module (SEM-07) and Getaway Special G-093 sponsored by the University of Michigan. Crew Launch attempts Mission highlights Node 1, named ''Unity'', was the first space station ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
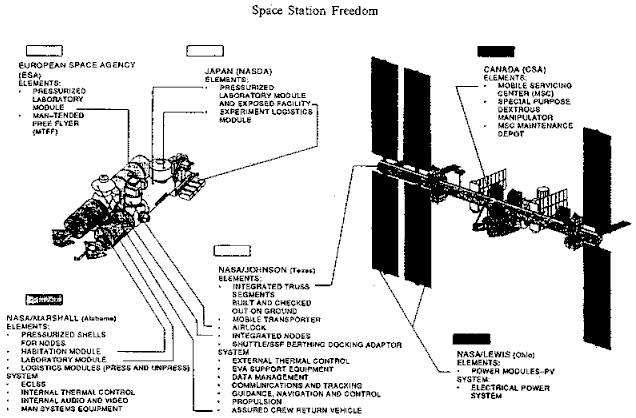
International Space Station
The International Space Station (ISS) is the largest modular space station currently in low Earth orbit. It is a multinational collaborative project involving five participating space agencies: NASA (United States), Roscosmos (Russia), JAXA (Japan), ESA (Europe), and CSA (Canada). The ownership and use of the space station is established by intergovernmental treaties and agreements. The station serves as a microgravity and space environment research laboratory in which scientific research is conducted in astrobiology, astronomy, meteorology, physics, and other fields. The ISS is suited for testing the spacecraft systems and equipment required for possible future long-duration missions to the Moon and Mars. The ISS programme evolved from the Space Station ''Freedom'', a 1984 American proposal to construct a permanently crewed Earth-orbiting station, and the contemporaneous Soviet/Russian '' Mir-2'' proposal from 1976 with similar aims. The ISS is the ninth space station to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Zarya (ISS Module)
''Zarya'' (russian: Заря, , Dawn), also known as the Functional Cargo Block or FGB (from the russian: "Функционально-грузовой блок", , ''Funktsionalno-gruzovoy blok'' or ''ФГБ''), is the first module of the International Space Station to have been launched.NASA, International Space StationZarya(accessed 19 Apr. 2014) The FGB provided electrical power, storage, propulsion, and guidance to the ISS during the initial stage of assembly. With the launch and assembly in orbit of other modules with more specialized functionality, it is primarily used for storage, both inside the pressurized section and in the externally mounted fuel tanks. The ''Zarya'' is a descendant of the TKS spacecraft designed for the Russian ''Salyut'' program. The name ''Zarya'' ("Dawn") was given to the FGB because it signified the dawn of a new era of international cooperation in space. Although it was built by a Russian company, it is owned by the United States. Construct ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
STS-95
STS-95 was a Space Shuttle mission launched from Kennedy Space Center, Florida on 29 October 1998, using the orbiter ''Discovery''. It was the 25th flight of ''Discovery'' and the 92nd mission flown since the start of the Space Shuttle program in April 1981. It was a highly publicized mission due to former Project Mercury astronaut and United States Senator John H. Glenn Jr.'s return to space for his second space flight. At age 77, Glenn became the oldest person to go into space, a record that remained unbroken for 23 years until 82-year-old Wally Funk flew on a suborbital flight on Blue Origin NS-16, launching on 20 July 2021, which in turn was broken by William Shatner at age 90 on 13 October 2021. Glenn, however, remains the oldest person to reach Earth orbit. This mission is also noted for inaugurating ATSC HDTV broadcasting in the U.S., with live coast-to-coast coverage of the launch. In another first, Pedro Duque became the first Spaniard in space. The mission's objectiv ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
PMA-1
The Pressurized Mating Adapter (PMA) is a class of spacecraft adapters that convert the Common Berthing Mechanism (CBM) used on the US Orbital Segment to APAS-95 docking ports. There are three PMAs located on the International Space Station (ISS); the first two were launched with the ''Unity'' connecting module in 1998 aboard STS-88, and the third was launched in 2000 aboard STS-92. All three of the PMAs are now used to permanently connect parts of the ISS, so they are no longer available as docking ports for visiting spacecraft. Design/History Its origins lie in designs for the Pressurized Docking Mast, consisting of an off-axis frustoconical docking tunnel contained within a framework and a retractable coupling mechanism, later part of the Pressurized Berthing Adapter assembly that appeared in designs for Space Station Freedom 1987, and the reduced design referred to as 'Fred' 1991. After 1992-93 and the Russian integration into the International Space Station Alpha proj ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Unity (ISS Module)
upright=1.0, The ''Unity'' module as seen in May 2011 The ''Unity'' connecting module, also known as Node 1, is the first U.S.-built component of the International Space Station (ISS). It connects the Russian and United States segments of the station, and is where crew eat meals together. The module is cylindrical in shape, with six berthing locations (forward, aft, port, starboard, zenith, and nadir) facilitating connections to other modules. ''Unity'' measures in diameter, is long, made of steel, and was built for NASA by Boeing in a manufacturing facility at the Marshall Space Flight Center in Huntsville, Alabama. ''Unity'' is the first of the three connecting modules; the other two are '' Harmony'' and ''Tranquility''. Launch and initial berthing ''Unity'' (with its two attached PMAs) was carried into orbit as the primary cargo of the Space Shuttle ''Endeavour'' (OV 105) on STS-88, the first Space Shuttle mission dedicated to assembly of the station. On 6 Decemb ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
PMA-2
The Pressurized Mating Adapter (PMA) is a class of spacecraft adapters that convert the Common Berthing Mechanism (CBM) used on the US Orbital Segment to APAS-95 docking ports. There are three PMAs located on the International Space Station (ISS); the first two were launched with the ''Unity'' connecting module in 1998 aboard STS-88, and the third was launched in 2000 aboard STS-92. All three of the PMAs are now used to permanently connect parts of the ISS, so they are no longer available as docking ports for visiting spacecraft. Design/History Its origins lie in designs for the Pressurized Docking Mast, consisting of an off-axis frustoconical docking tunnel contained within a framework and a retractable coupling mechanism, later part of the Pressurized Berthing Adapter assembly that appeared in designs for Space Station Freedom 1987, and the reduced design referred to as 'Fred' 1991. After 1992-93 and the Russian integration into the International Space Station Alpha proj ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
STS-96
STS-96 was a Space Shuttle mission to the International Space Station (ISS) flown by Space Shuttle '' Discovery'', and the first shuttle flight to dock at the International Space Station. The shuttle carried the Spacehab module in the payload, filled with cargo for station outfitting. STS-96 launched from Kennedy Space Center, Florida, on 27 May 1999 at 06:49:42 AM EDT and returned to Kennedy on 6 June 1999, 2:02:43 AM EDT. Crew Space walk *'' Jernigan and Barry '' – EVA 1 *EVA 1 Start: 30 May 1999 – 02:56 UTC *EVA 1 End: 30 May 1999 – 10:51 UTC *Duration: 7 hours, 55 minutes Mission highlights ISSafterSTS96.jpg, Illustration of the International Space Station (ISS) during Space Shuttle flight STS-96 01 ICC STS-96.jpg, Integrated Cargo Carrier (ICC), with among other the Russian cargo crane "STRELA", which was mounted on the ISS STS-96 was a logistics and resupply mission for the International Space Station carrying the Spacehab Double Module (DM) 13th Spacehab overa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Space Shuttle Endeavour
Space Shuttle ''Endeavour'' (Orbiter Vehicle Designation: OV-105) is a retired orbiter from NASA's Space Shuttle program and the fifth and final operational Shuttle built. It embarked on its first mission, STS-49, in May 1992 and its 25th and final mission, STS-134, in May 2011. STS-134 was expected to be the final mission of the Space Shuttle program, but with the authorization of STS-135 by the United States Congress, Space Shuttle Atlantis, ''Atlantis'' became the last shuttle to fly. The United States Congress approved the construction of ''Endeavour'' in 1987 to replace the Space Shuttle Challenger, Space Shuttle ''Challenger'', which was Space Shuttle Challenger disaster, destroyed in 1986. NASA chose, on cost grounds, to build much of ''Endeavour'' from spare parts rather than refitting the Space Shuttle Enterprise, Space Shuttle ''Enterprise'', and used structural spares built during the construction of ''Space Shuttle Discovery, Discovery'' and Space Shuttle Atlantis, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Getaway Special
Getaway Special was a NASA program that offered interested individuals, or groups, opportunities to fly small experiments aboard the Space Shuttle. Over the 20-year history of the program, over 170 individual missions were flown. The program, which was officially known as the ''Small, Self-Contained Payloads program'', was canceled following the Space Shuttle ''Columbia'' disaster on February 1, 2003. History The program was conceived by NASA's Shuttle program manager John Yardley, and announced in the fall of 1976. The "Getaway Special" nickname originated from a special vacation fare for flights between Los Angeles and Honolulu being advertised by Trans World Airlines at the time around the program's conception. The first Getaway Special was purchased by Gilbert Moore of Thiokol on October 12, 1976, and donated to Utah State University. It was flown on '' Columbia'' during STS-4 in June/July 1982. The program was canceled after the Space Shuttle ''Columbia'' disaster on F ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Russian Federal Space Agency
The State Space Corporation "Roscosmos" (russian: Государственная корпорация по космической деятельности «Роскосмос»), commonly known simply as Roscosmos (russian: Роскосмос), is a state corporation of the Russian Federation responsible for space flights, cosmonautics programs, and aerospace research. Originating from the Soviet space program founded in the 1950s, Roscosmos emerged following the dissolution of the Soviet Union in 1991. It initially began as the Russian Space Agency, which was established on 25 February 1992russian: Российское космическое агентство, ''Rossiyskoye kosmicheskoye agentstvo'', or RKA (russian: РКА). and restructured in 1999 and 2004, as the Russian Aviation and Space Agencyrussian: Российское авиационно-космическое агентство, ''Rossiyskoye aviatsionno-kosmicheskoye agentstvo'', commonly known as (rus ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Russian Space Agency
The State Space Corporation "Roscosmos" (russian: Государственная корпорация по космической деятельности «Роскосмос»), commonly known simply as Roscosmos (russian: Роскосмос), is a state corporation of the Russian Federation responsible for space flights, cosmonautics programs, and aerospace research. Originating from the Soviet space program founded in the 1950s, Roscosmos emerged following the dissolution of the Soviet Union in 1991. It initially began as the Russian Space Agency, which was established on 25 February 1992russian: Российское космическое агентство, ''Rossiyskoye kosmicheskoye agentstvo'', or RKA (russian: РКА). and restructured in 1999 and 2004, as the Russian Aviation and Space Agencyrussian: Российское авиационно-космическое агентство, ''Rossiyskoye aviatsionno-kosmicheskoye agentstvo'', commonly known as (russ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |