PMA-2 on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
The Pressurized Mating Adapter (PMA) is a class of spacecraft adapters that convert the
 The three PMAs are identical, but they have slightly different uses. All three perform the same basic function of connecting a
The three PMAs are identical, but they have slightly different uses. All three perform the same basic function of connecting a
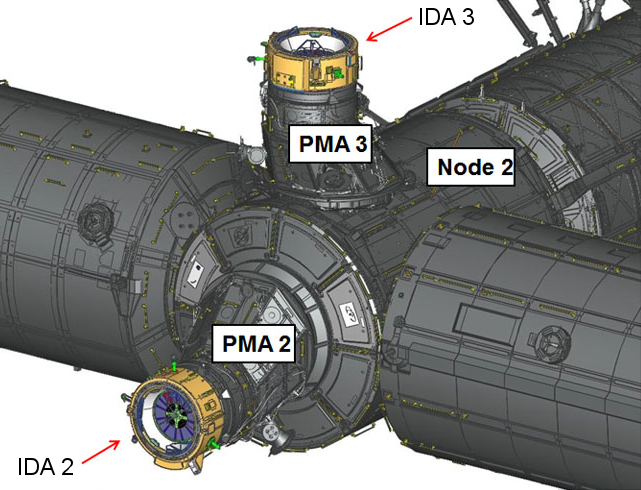 PMA-2 is mounted on the forward port of the ''
PMA-2 is mounted on the forward port of the ''
YouTube animation
Canadarm2 and Dextre move the PMA-3 between locations, one of the five times it was moved so that modules could use a Common Berthing Mechanism port instead of PMA-3. {{ISS modules Components of the International Space Station
Common Berthing Mechanism
The Common Mechanism (CBM) connects habitable elements in the US Orbital Segment (USOS) of the International Space Station (ISS). The CBM has two distinct sides that, once mated, form a cylindrical vestibule between modules. The vestibule is ...
(CBM) used on the US Orbital Segment
The US Orbital Segment (USOS) is the name given to the components of the International Space Station (ISS) constructed and operated by the United States National Aeronautics and Space Administration (NASA), European Space Agency (ESA), Canadia ...
to APAS-95
The terms Androgynous Peripheral Attach System (APAS), Androgynous Peripheral Assembly System (APAS) and Androgynous Peripheral Docking System (APDS), are used interchangeably to describe a family of spacecraft docking mechanisms, and are also so ...
docking ports. There are three PMAs located on the International Space Station
The International Space Station (ISS) is the largest Modular design, modular space station currently in low Earth orbit. It is a multinational collaborative project involving five participating space agencies: NASA (United States), Roscosmos ( ...
(ISS); the first two were launched with the ''Unity'' connecting module in 1998 aboard STS-88
STS-88 was the first Space Shuttle mission to the International Space Station (ISS). It was flown by Space Shuttle ''Endeavour'', and took the first American module, the ''Unity'' node, to the station.
The seven-day mission was highlighted by ...
, and the third was launched in 2000 aboard STS-92
STS-92 was a Space Shuttle mission to the International Space Station (ISS) flown by Space Shuttle '' Discovery''. STS-92 marked the 100th mission of the Space Shuttle. It was launched from Kennedy Space Center, Florida, 11 October 2000.
Crew
...
. All three of the PMAs are now used to permanently connect parts of the ISS, so they are no longer available as docking ports for visiting spacecraft.
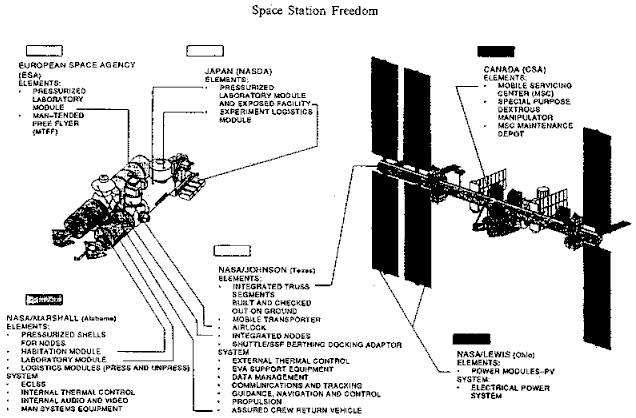
Design/History
Its origins lie in designs for the Pressurized Docking Mast, consisting of an off-axis frustoconical docking tunnel contained within a framework and a retractable coupling mechanism, later part of the Pressurized Berthing Adapter assembly that appeared in designs forSpace Station Freedom
Space Station ''Freedom'' was a NASA project to construct a permanently crewed Earth-orbiting space station in the 1980s. Although approved by then-president Ronald Reagan and announced in the 1984 State of the Union address, ''Freedom'' was ...
1987, and the reduced design referred to as 'Fred' 1991.
After 1992-93 and the Russian integration into the International Space Station Alpha project, this NASA docking design abruptly disappeared from all concepts. This was due to the availability of Russian docking hardware and experience, brought together during the Shuttle-Mir program. Russian APAS
The terms Androgynous Peripheral Attach System (APAS), Androgynous Peripheral Assembly System (APAS) and Androgynous Peripheral Docking System (APDS), are used interchangeably to describe a family of spacecraft docking mechanisms, and are also som ...
docking technology originally planned for the then defunct Soviet space shuttle program was integrated into the US Space Shuttle ODS (Orbital/Orbiter Docking System). This could hard dock with the space station through a structural interface, which became the PMA. With both the Russian docking ring and the CBM integrated into the PMA, this became the link between the USOS and the ROS from 1993.
Fabrication completed in 1995 with tests and mating tests with Node STA throughout 1996-97.

Uses
 The three PMAs are identical, but they have slightly different uses. All three perform the same basic function of connecting a
The three PMAs are identical, but they have slightly different uses. All three perform the same basic function of connecting a CBM CBM may refer to:
Businesses and corporations
* Cambrex Corporation (NYSE: CBM)
* CBM (AM), a radio station in Montreal now known as CBME-FM
* CBM-FM, a radio station in Montreal
* CBM TV, a scrapped Freeview channel
* Central Bank of Myanmar
* Che ...
port of an ISS module to an APAS-95
The terms Androgynous Peripheral Attach System (APAS), Androgynous Peripheral Assembly System (APAS) and Androgynous Peripheral Docking System (APDS), are used interchangeably to describe a family of spacecraft docking mechanisms, and are also so ...
docking port of another module or visiting spacecraft. For this purpose, the PMAs carry a passive CBM port and a passive APAS port. The PMAs are pressurized and heated from the inside, and they allow for power and data communications transfer through docking rings and external connections.
PMA-1
This was one of the first components of the International Space Station. PMA-1 joins the Russian side of the station with the US side. OnSTS-88
STS-88 was the first Space Shuttle mission to the International Space Station (ISS). It was flown by Space Shuttle ''Endeavour'', and took the first American module, the ''Unity'' node, to the station.
The seven-day mission was highlighted by ...
, the crew used the shuttle's robotic arm
A robotic arm is a type of mechanical arm, usually programmable, with similar functions to a human arm; the arm may be the sum total of the mechanism or may be part of a more complex robot. The links of such a manipulator are connected by join ...
to attach the '' Zarya'' control module to PMA-1, which was already connected to the aft berthing port of ''Unity''. These first two station components are permanently connected by PMA-1.
PMA-2
 PMA-2 is mounted on the forward port of the ''
PMA-2 is mounted on the forward port of the ''Harmony
In music, harmony is the process by which individual sounds are joined together or composed into whole units or compositions. Often, the term harmony refers to simultaneously occurring frequencies, pitches ( tones, notes), or chords. Howev ...
'' connecting node, and was used when Space Shuttle
The Space Shuttle is a retired, partially reusable low Earth orbital spacecraft system operated from 1981 to 2011 by the U.S. National Aeronautics and Space Administration (NASA) as part of the Space Shuttle program. Its official program na ...
orbiters docked at the ISS. It was outfitted with Station-to-Shuttle Power Transfer System (SSPTS) hardware to allow the shuttles to stay docked longer to the space station.
PMA-2 was moved several times as part of the space station assembly process. It was originally connected to the forward hatch of ''Unity'', but when STS-98 delivered the ''Destiny
Destiny, sometimes referred to as fate (from Latin ''fatum'' "decree, prediction, destiny, fate"), is a predetermined course of events. It may be conceived as a predetermined future, whether in general or of an individual.
Fate
Although oft ...
'' module in February 2001, PMA-2 was moved to the berthing ring of the Z1 truss so that ''Destiny'' could be berthed to the forward hatch of ''Unity''. PMA-2 was finally moved to the forward hatch of ''Destiny''. (The removal of PMA-2 from ''Unity'' was the first time the CBM had been used to disconnect two ISS components.) After STS-120
STS-120 was a Space Shuttle mission to the International Space Station (ISS) that launched on 23 October 2007 from the Kennedy Space Center, Florida. The mission is also referred to as ISS-10A by the ISS program. STS-120 delivered the ''Harmon ...
had delivered ''Harmony'' to the space station in October 2007, Canadarm2
The Mobile Servicing System (MSS), is a robotic system on board the International Space Station (ISS). Launched to the ISS in 2001, it plays a key role in station assembly and maintenance; it moves equipment and supplies around the station, su ...
repositioned PMA-2 at the forward port of ''Harmony'' on November 12, 2007. Two days later, the combined package of ''Harmony'' and PMA-2 was moved to its final location, the forward hatch of ''Destiny''. On July 18, 2016, International Docking Adapter
The International Docking Adapter (IDA) is a spacecraft docking system adapter developed to convert APAS-95 to the NASA Docking System (NDS). An IDA is placed on each of the International Space Station's (ISS) two open Pressurized Mating Adap ...
-2 was launched on SpaceX CRS-9. It was attached and permantly connected to the APAS-95 port of PMA-2 during a spacewalk on August 19, 2016. As of 2020, PMA-2 is expected to stay berthed at the forward port of ''Harmony'' with the IDA connected for the remaining duration of the ISS.
When a shuttle docked with the station, its "final approach asat a relative velocity of one-tenth of a foot per second. s it made
S, or s, is the nineteenth letter in the Latin alphabet, used in the modern English alphabet, the alphabets of other western European languages and others worldwide. Its name in English is ''ess'' (pronounced ), plural ''esses''.
History ...
contact with Pressurized Mating Adapter 2 atchesautomatically attached the two spacecraft together. Once relative motion between the spacecraft stopped, Shuttle astronaut retractedthe docking ring on he Shuttle'smechanism, closing latches to firmly secure the shuttle to the station."
PMA-3
PMA-3 was brought to the ISS bySTS-92
STS-92 was a Space Shuttle mission to the International Space Station (ISS) flown by Space Shuttle '' Discovery''. STS-92 marked the 100th mission of the Space Shuttle. It was launched from Kennedy Space Center, Florida, 11 October 2000.
Crew
...
in October 2000, mounted on a Spacelab
Spacelab was a reusable laboratory developed by European Space Agency (ESA) and used on certain spaceflights flown by the Space Shuttle. The laboratory comprised multiple components, including a pressurized module, an unpressurized carrier, ...
pallet. It was initially attached to the nadir
The nadir (, ; ar, نظير, naẓīr, counterpart) is the direction pointing directly ''below'' a particular location; that is, it is one of two vertical directions at a specified location, orthogonal to a horizontal flat surface.
The direc ...
(bottom, or Earth-facing) hatch of ''Unity''. About six weeks later, when STS-97
STS-97 was a Space Shuttle mission to the International Space Station (ISS) flown by Space Shuttle '' Endeavour''. The crew installed the first set of solar arrays to the ISS, prepared a docking port for arrival of the Destiny Laboratory Module ...
delivered the P6 solar array truss structure, ''Endeavour'' docked at PMA-3. When STS-98 moved PMA-2 from ''Unity'' to ''Destiny'' via the Z1 truss in February 2001, ''Atlantis'' was docked at PMA-3. For the remainder of the shuttle's operation, PMA-3 was not used for shuttle dockings. PMA-3 was moved in March 2001 to ''Unity''s port hatch by the crew of STS-102 to make room for the docking of a Multi-Purpose Logistics Module
A Multi-Purpose Logistics Module (MPLM) is a large pressurized container that was used on Space Shuttle missions to transfer cargo to and from the International Space Station (ISS). Two MPLMs made a dozen trips in the Shuttle cargo bay and init ...
(MPLM).
On August 30, 2007, PMA-3 was returned to the nadir port of ''Unity'' to make room for the temporary docking of the new '' Harmony (Node 2)'' module that was delivered by STS-120
STS-120 was a Space Shuttle mission to the International Space Station (ISS) that launched on 23 October 2007 from the Kennedy Space Center, Florida. The mission is also referred to as ISS-10A by the ISS program. STS-120 delivered the ''Harmon ...
. ''Harmony'' was transferred to the forward port of ''Destiny'', while PMA-3 was moved back to the port berthing mechanism of ''Unity'' on August 7, 2009, to accommodate reconfiguration of the ''Unity'' port bulkhead by crew members in a pressurized environment. On January 25, 2010, PMA-3 was moved from the port berthing mechanism of ''Unity'' to the zenith (space-facing) port of ''Harmony'' to make room for the new '' Tranquility (Node 3)'' module which was added to the station during STS-130. After activation of ''Tranquility'', PMA-3 was moved again on February 16, 2010, to the port location on ''Tranquility'' where the Cupola
In architecture, a cupola () is a relatively small, most often dome-like, tall structure on top of a building. Often used to provide a lookout or to admit light and air, it usually crowns a larger roof or dome.
The word derives, via Italian, fr ...
observatory module had been docked for launch.
PMA-3 was robotically removed from ''Tranquility'' on March 26, 2017, and attached to ''Harmony'' after being prepared during a successful spacewalk on March 24, 2017. A second spacewalk was conducted on March 30, 2017, to finalize the PMA-3 cable connections on ''Harmony''. PMA-3 received International Docking Adapter-3 in August 2019.
References
External links
YouTube animation
Canadarm2 and Dextre move the PMA-3 between locations, one of the five times it was moved so that modules could use a Common Berthing Mechanism port instead of PMA-3. {{ISS modules Components of the International Space Station