|
SS LeBaron Russell Briggs
SS ''LeBaron Russell Briggs'' was a Liberty ship built in the United States during World War II. She was named after LeBaron Russell Briggs, the first Dean of Men at Harvard College and the president of Radcliffe College. Construction ''LeBaron Russell Briggs'' was laid down on 29 March 1944, under a Maritime Commission (MARCOM) contract, MC hull 2301, by J.A. Jones Construction, Panama City, Florida; she was sponsored by Mrs. George R. Smith, daughter of James Addison Jones, and launched on 12 May 1944. History She was allocated to R.A. Nichol & Company, on 31 May 1944. On 5 March 1948, she was laid up in the National Defense Reserve Fleet, in Wilmington, North Carolina. On 26 September 1957, she was relocated to the National Defense Reserve Fleet, in the Hudson River Group. On 8 December 1961, she was withdrawn from the fleet to be loaded with grain under the "Grain Program 1961". She returned loaded with grain to the fleet on 22 December 1961. On 17 June 1963, she was with ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
LeBaron Russell Briggs
LeBaron Russell Briggs (December 11, 1855 – April 24, 1934) was an American educator. He was appointed the first dean of men at Harvard College, and subsequently served as dean of the faculty until he retired. He was concurrently president of Radcliffe College and the National Collegiate Athletic Association. Early life Briggs was born in Salem, Massachusetts on December 11, 1855. He was the son of Unitarian minister George Ware Briggs and Lucia Jane (née Russell) Briggs. Among his siblings was brother George Russell Briggs. He received A.B. (in 1875) and A.M. degrees (in 1882) from Harvard University. Career After graduating from Harvard, he began teaching there; he began as a Greek tutor before moving to English, eventually becoming the Boylston Professor of Rhetoric from 1904 until 1925. Briggs was appointed dean of Harvard College in 1891 (to 1902) and dean of the Faculty of Arts and Sciences from 1902 until his retirement in 1925. His appointment as dean of men wa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
James Addison Jones
James Addison Jones, (20 August 1869 - 25 May 1950) was the founder of J.A. Jones Construction, as well as being a known philanthropist for many organizations such as the Methodist Church, the city of Charlotte, North Carolina and surrounding areas, regional hospitals and several other companies. He was the benefactor and namesake for the James Addison Jones Library at Greensboro College and the J.A. Jones Library at Brevard College. His company was also responsible for assisting in the building of the Liberty fleet during World War II. Jones was married four times in his lifetime and had fifteen children. Early life Birth and parentage James Addison Jones was born in Farmer, North Carolina, on August 20, 1869, to Robert B. Jones and Elizabeth Horney Jones (21 August 1839 – 15 June 1872). Jones had multiple siblings in descending order: John, William, Sherman and Emma. Childhood Jones was only able to attend school a few months out of the year at a local one-room c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hudson River Reserve Fleet Grain Program
Hudson may refer to: People * Hudson (given name) * Hudson (surname) * Henry Hudson, English explorer * Hudson (footballer, born 1986), Hudson Fernando Tobias de Carvalho, Brazilian football right-back * Hudson (footballer, born 1988), Hudson Rodrigues dos Santos, Brazilian football defensive midfielder * Hudson (footballer, born 1996), Hudson Felipe Gonçalves, Brazilian football midfielder Places Argentina * Hudson, Buenos Aires Province, a town in Berazategui Partido Australia * Hudson, Queensland, a locality in the Cassowardy Coast Region Canada * Hudson, Ontario * Hudson, Quebec * Hudson, Edmonton, Alberta United States * Hudson, Colorado, a town in Weld County * Hudson, Florida, a census-designated place in Pasco County * Hudson, Illinois, a town in McLean County * Hudson, Indiana, a town in Steuben County * Hudson, Iowa, a town in Black Hawk County * Hudson, Kansas, a town in Stafford County * Hudson, Maine, a town in Penobscot County * Hudson, Massachuset ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Wilmington Reserve Fleet
A Liberty ship, the most common ship stored at the Wilmington Reserve Fleet Atlantic Reserve Fleet, Wilmington was part of the United States Navy reserve fleets in Wilmington, North Carolina at . The reserve fleet was at and overflowed out of the former North Carolina Shipbuilding Company in the dredge out Brunswick River. The ships lined both sides of the Brunswick River. The freshwater of the river made a good spot to store ships. The reserve fleet was opened in 1946 to store the now many surplus ships after World War II. The ''mothball fleet'' was mostly cargo ships used in the merchant marine navy. When opened it had mostly cargo ships and a few troop ships. At its peak it had 300 Victory ships and Liberty ships, many that were built at the nearby former North Carolina Shipbuilding Company Shipyard. Some ships in the fleet were reactivated for the Korean War and Vietnam War. Atlantic Reserve Fleet, Wilmington closed in 1962, with the last ship removed in February 27, 1970. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
1944 Ships
Events Below, the events of World War II have the "WWII" prefix. January * January 2 – WWII: ** Free France, Free French General Jean de Lattre de Tassigny is appointed to command First Army (France), French Army B, part of the Sixth United States Army Group in North Africa. ** Landing at Saidor: 13,000 US and Australian troops land on Papua New Guinea, in an attempt to cut off a Japanese retreat. * January 8 – WWII: Philippine Commonwealth troops enter the province of Ilocos Sur in northern Luzon and attack Japanese forces. * January 11 ** President of the United States Franklin D. Roosevelt proposes a Second Bill of Rights for social and economic security, in his State of the Union address. ** The Nazi German administration expands Kraków-Płaszów concentration camp into the larger standalone ''Konzentrationslager Plaszow bei Krakau'' in occupied Poland. * January 12 – WWII: Winston Churchill and Charles de Gaulle begin a 2-day conference in Marrakech ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ships Built In Panama City, Florida
A ship is a large watercraft that travels the world's oceans and other sufficiently deep waterways, carrying cargo or passengers, or in support of specialized missions, such as defense, research, and fishing. Ships are generally distinguished from boats, based on size, shape, load capacity, and purpose. Ships have supported exploration, trade, warfare, migration, colonization, and science. After the 15th century, new crops that had come from and to the Americas via the European seafarers significantly contributed to world population growth. Ship transport is responsible for the largest portion of world commerce. The word ''ship'' has meant, depending on the era and the context, either just a large vessel or specifically a ship-rigged sailing ship with three or more masts, each of which is square-rigged. As of 2016, there were more than 49,000 merchant ships, totaling almost 1.8 billion dead weight tons. Of these 28% were oil tankers, 43% were bulk carriers, and 13% were cont ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Liberty Ships
Liberty ships were a ship class, class of cargo ship built in the United States during World War II under the Emergency Shipbuilding Program. Though British in concept, the design was adopted by the United States for its simple, low-cost construction. Mass-produced on an unprecedented scale, the Liberty ship came to symbolize U.S. wartime industrial output. The class was developed to meet British orders for transports to replace ships that had been lost. Eighteen American shipyards built 2,710 Liberty ships between 1941 and 1945 (an average of three ships every two days), easily the largest number of ships ever produced to a single design. Their production mirrored (albeit on a much larger scale) the manufacture of "Hog Islander" and similar standardized ship types during World War I. The immensity of the effort, the number of ships built, the role of Rosie the Riveter, female workers in their construction, and the survival of some far longer than their original five-year desig ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
The New York Times
''The New York Times'' (''the Times'', ''NYT'', or the Gray Lady) is a daily newspaper based in New York City with a worldwide readership reported in 2020 to comprise a declining 840,000 paid print subscribers, and a growing 6 million paid digital subscribers. It also is a producer of popular podcasts such as '' The Daily''. Founded in 1851 by Henry Jarvis Raymond and George Jones, it was initially published by Raymond, Jones & Company. The ''Times'' has won 132 Pulitzer Prizes, the most of any newspaper, and has long been regarded as a national " newspaper of record". For print it is ranked 18th in the world by circulation and 3rd in the U.S. The paper is owned by the New York Times Company, which is publicly traded. It has been governed by the Sulzberger family since 1896, through a dual-class share structure after its shares became publicly traded. A. G. Sulzberger, the paper's publisher and the company's chairman, is the fifth generation of the family to head the pa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Scuttled
Scuttling is the deliberate sinking of a ship. Scuttling may be performed to dispose of an abandoned, old, or captured vessel; to prevent the vessel from becoming a navigation hazard; as an act of self-destruction to prevent the ship from being captured by an enemy force (or, in the case of a vessel engaged in illegal activities, by the authorities); as a blockship to restrict navigation through a channel or within a harbor; to provide an artificial reef for divers and marine life; or to alter the flow of rivers. Notable historical examples Skuldelev ships (around 1070) The Skuldelev ships, five Viking ships, were sunk to prevent attacks from the sea on the Danish city of Roskilde. The scuttling blocked a major waterway, redirecting ships to a smaller one that required considerable local knowledge. Cog near Kampen (early 15th century) In 2012, a cog preserved from the keel up to the decks in the silt was discovered alongside two smaller vessels in the river IJssel in t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cape Kennedy
, image = cape canaveral.jpg , image_size = 300 , caption = View of Cape Canaveral from space in 1991 , map = Florida#USA , map_width = 300 , type =Cape , map_caption = Location in Florida , location = Florida, United States , water_bodies = Atlantic Ocean , coordinates = , relief = 1 , elevation = , area = , references = Cape Canaveral ( es, Cabo Cañaveral) is a cape in Brevard County, Florida, in the United States, near the center of the state's Atlantic coast. Officially Cape Kennedy from 1963 to 1973, it lies east of Merritt Island, separated from it by the Banana River. It is part of a region known as the Space Coast, and is the site of the Cape Canaveral Space Force Station. Since many U.S. spacecraft have been launched from both the station and the Kennedy Space Center on adjacent Merritt Island, the two are sometimes conflated with each other. Other features of the cape include Port Canavera ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
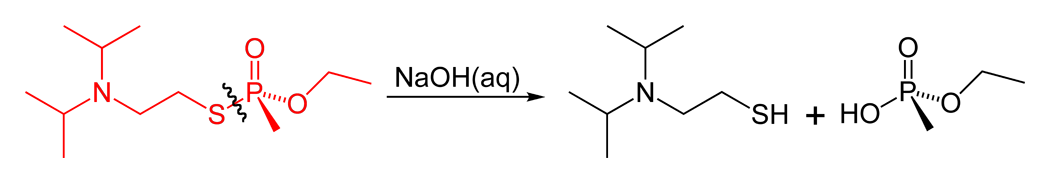
VX Gas
VX is an extremely toxic chemical synthesis, synthetic chemical compound in the organophosphorus compound, organophosphorus class, specifically, a phosphonate, thiophosphonate. In the class of nerve agents, it was developed for military use in chemical warfare after translational science, translation of earlier discoveries of organophosphate toxicity in pesticide research. In recent years, VX was found to be the agent used in the assassination of Kim Jong-nam. In its pure form, VX is an oily, relatively Volatility (chemistry), non-volatile liquid that is amber-like in colour. Because of its low volatility, VX persists in environments where it is dispersed. VX, short for "venomous agent X", is one of the best known of the V nerve agents and was first discovered at Porton Down by Ranajit Ghosh in England during the early 1950s based on research first done by Gerhard Schrader, a chemist working for IG Farben in Germany during the 1930s. It is now one of a broader V-series of agen ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sarin
Sarin (NATO designation GB G-series, "B"">Nerve_agent#G-series.html" ;"title="hort for Nerve agent#G-series">G-series, "B" is an extremely toxic synthetic organophosphorus compound.Sarin (GB) Emergency Response Safety and Health Database. National Institute for Occupational Safety and Health. Accessed April 20, 2009. A colourless, odourless , it is used as a due to its extreme potency as a . Exposure is lethal even at very low concen ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |



.png)