|
SS-A
Anti-SSA autoantibodies (anti–Sjögren's-syndrome-related antigen A autoantibodies, also called anti-Ro, or similar names including anti-SSA/Ro, anti-Ro/SSA, anti–SS-A/Ro, and anti-Ro/SS-A) are a type of anti-nuclear autoantibodies that are associated with many autoimmune diseases, such as systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE), SS/SLE overlap syndrome, subacute cutaneous lupus erythematosus (SCLE), neonatal lupus and primary biliary cirrhosis. They are often present in Sjögren's syndrome (SS). Additionally, Anti-Ro/SSA can be found in other autoimmune diseases such as Systemic scleroderma, systemic sclerosis (SSc), polymyositis/dermatomyositis (PM/DM), rheumatoid arthritis (RA), and mixed connective tissue disease (MCTD), and are also associated with heart arrhythmia. Anti-SSA/Ro autoantibodies are classified as extractable nuclear antigens. The Anti-SSA/Ro autoantibody targets Ro proteins, namely Ro52 and Ro60. Ro52 and Ro60 were originally thought to be one protein, however cu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Anti-nuclear Autoantibodies
Antinuclear antibodies (ANAs, also known as antinuclear factor or ANF) are autoantibodies that bind to contents of the cell nucleus. In normal individuals, the immune system produces antibodies to foreign proteins (antigens) but not to human proteins (autoantigens). In some cases, antibodies to human antigens are produced. There are many subtypes of ANAs such as anti-Ro antibodies, anti-La antibodies, anti-Sm antibodies, anti-nRNP antibodies, anti-Scl-70 antibodies, anti-dsDNA antibodies, anti-histone antibodies, antibodies to nuclear pore complexes, anti-centromere antibodies and anti-sp100 antibodies. Each of these antibody subtypes binds to different proteins or protein complexes within the nucleus. They are found in many disorders including autoimmunity, cancer and infection, with different prevalences of antibodies depending on the condition. This allows the use of ANAs in the diagnosis of some autoimmune disorders, including systemic lupus erythematosus, Sjögren synd ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Anti-nuclear Antibody
Antinuclear antibodies (ANAs, also known as antinuclear factor or ANF) are autoantibodies that bind to contents of the cell nucleus. In normal individuals, the immune system produces antibodies to foreign proteins (antigens) but not to human proteins (autoantigens). In some cases, antibodies to human antigens are produced. There are many subtypes of ANAs such as anti-Ro antibodies, anti-La antibodies, anti-Sm antibodies, anti-nRNP antibodies, anti-Scl-70 antibodies, anti-dsDNA antibodies, anti-histone antibodies, antibodies to nuclear pore complexes, anti-centromere antibodies and anti-sp100 antibodies. Each of these antibody subtypes binds to different proteins or protein complexes within the nucleus. They are found in many disorders including autoimmunity, cancer and infection, with different prevalences of antibodies depending on the condition. This allows the use of ANAs in the diagnosis of some autoimmune disorders, including systemic lupus erythematosus, Sjögren synd ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Systemic Lupus Erythematosus
Lupus, technically known as systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE), is an autoimmune disease in which the body's immune system mistakenly attacks healthy tissue in many parts of the body. Symptoms vary among people and may be mild to severe. Common symptoms include painful and swollen joints, fever, chest pain, hair loss, mouth ulcers, swollen lymph nodes, feeling tired, and a red rash which is most commonly on the face. Often there are periods of illness, called flares, and periods of remission during which there are few symptoms. The cause of SLE is not clear. It is thought to involve a mixture of genetics combined with environmental factors. Among identical twins, if one is affected there is a 24% chance the other one will also develop the disease. Female sex hormones, sunlight, smoking, vitamin D deficiency, and certain infections are also believed to increase a person's risk. The mechanism involves an immune response by autoantibodies against a person's own tissues. T ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
TRIM21
Tripartite motif-containing protein 21, also known as E3 ubiquitin-protein ligase TRIM21, is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ''TRIM21'' gene. Alternatively spliced transcript variants for this gene have been described but the full-length nature of only one has been determined. It is expressed in most human tissues. Structure TRIM21 is a member of the tripartite motif (TRIM) family. The TRIM motif includes three zinc-binding domains, a RING finger domain, a B-box type 1 and a B-box type 2 zinc finger, and a coiled coil region. Function TRIM21 is an intracellular antibody effector in the intracellular antibody-mediated proteolysis pathway. It recognizes Fc domain and binds to immunoglobulin G, immunoglobulin A and immunoglobulin M on antibody marked non-enveloped virions which have infected the cell. Either by autoubiquitination or by ubiquitination of a cofactor, it is then responsible for directing the virions to the proteasome. TRIM21 itself is not degraded in the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Human Leukocyte Antigen
The human leukocyte antigen (HLA) system or complex is a complex of genes on chromosome 6 in humans which encode cell-surface proteins responsible for the regulation of the immune system. The HLA system is also known as the human version of the major histocompatibility complex (MHC) found in many animals. Mutations in HLA genes may be linked to autoimmune disease such as type I diabetes, and celiac disease. The HLA gene complex resides on a 3 Mbp stretch within chromosome 6, p-arm at 21.3. HLA genes are highly polymorphic, which means that they have many different alleles, allowing them to fine-tune the adaptive immune system. The proteins encoded by certain genes are also known as ''antigens'', as a result of their historic discovery as factors in organ transplants. HLAs corresponding to MHC class I ( A, B, and C), all of which are the HLA Class1 group, present peptides from inside the cell. For example, if the cell is infected by a virus, the HLA system brings fragme ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tumor Necrosis Factor Alpha
Tumor necrosis factor (TNF, cachexin, or cachectin; formerly known as tumor necrosis factor alpha or TNF-α) is an adipokine and a cytokine. TNF is a member of the TNF superfamily, which consists of various transmembrane proteins with a homologous TNF domain. As an adipokine, TNF promotes insulin resistance, and is associated with obesity-induced type 2 diabetes. As a cytokine, TNF is used by the immune system for cell signaling. If macrophages (certain white blood cells) detect an infection, they release TNF to alert other immune system cells as part of an inflammatory response. TNF signaling occurs through two receptors: TNFR1 and TNFR2. TNFR1 is constituitively expressed on most cell types, whereas TNFR2 is restricted primarily to endothelial, epithelial, and subsets of immune cells. TNFR1 signaling tends to be pro-inflammatory and apoptotic, whereas TNFR2 signaling is anti-inflammatory and promotes cell proliferation. Suppression of TNFR1 signaling has been important for ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Apoptosis
Apoptosis (from grc, ἀπόπτωσις, apóptōsis, 'falling off') is a form of programmed cell death that occurs in multicellular organisms. Biochemical events lead to characteristic cell changes (morphology) and death. These changes include blebbing, cell shrinkage, nuclear fragmentation, chromatin condensation, DNA fragmentation, and mRNA decay. The average adult human loses between 50 and 70 billion cells each day due to apoptosis. For an average human child between eight and fourteen years old, approximately twenty to thirty billion cells die per day. In contrast to necrosis, which is a form of traumatic cell death that results from acute cellular injury, apoptosis is a highly regulated and controlled process that confers advantages during an organism's life cycle. For example, the separation of fingers and toes in a developing human embryo occurs because cells between the digits undergo apoptosis. Unlike necrosis, apoptosis produces cell fragments called apoptotic ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
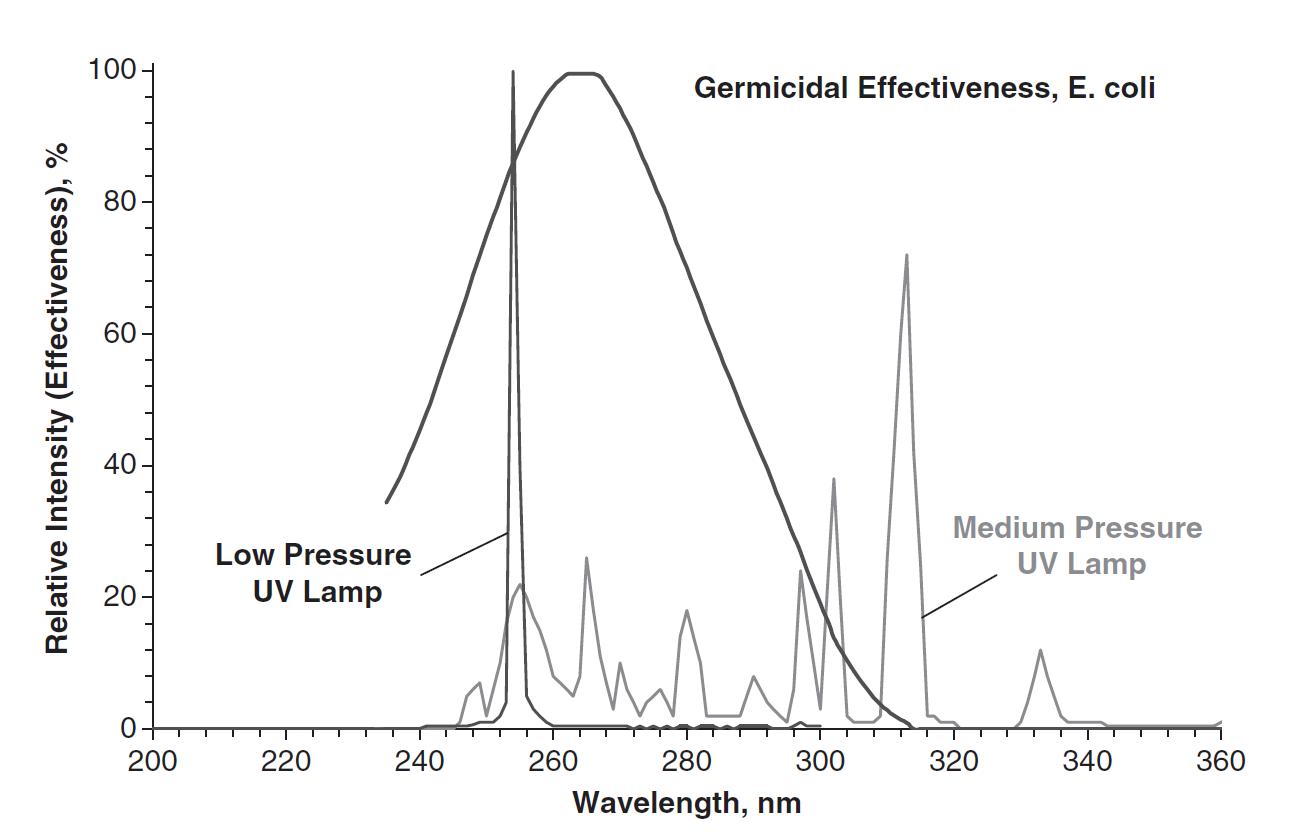
UV Irradiation
Ultraviolet germicidal irradiation (UVGI) is a disinfection method that uses short-wavelength ultraviolet (ultraviolet C or UV-C) light to kill or inactivate microorganisms by destroying nucleic acids and disrupting their DNA, leaving them unable to perform vital cellular functions. UVGI is used in a variety of applications, such as food, surface, air, and water purification. UV-C light is weak at the Earth's surface since the ozone layer of the atmosphere blocks it. UVGI devices can produce strong enough UV-C light in circulating air or water systems to make them inhospitable environments to microorganisms such as bacteria, viruses, molds, and other pathogens. Recent studies have proven the ability of UVC light in inactivating the novel Coronavirus (COVID-19). UVGI can be coupled with a filtration system to sanitize air and water. The application of UVGI to disinfection has been an accepted practice since the mid-20th century. It has been used primarily in medical sanitation a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
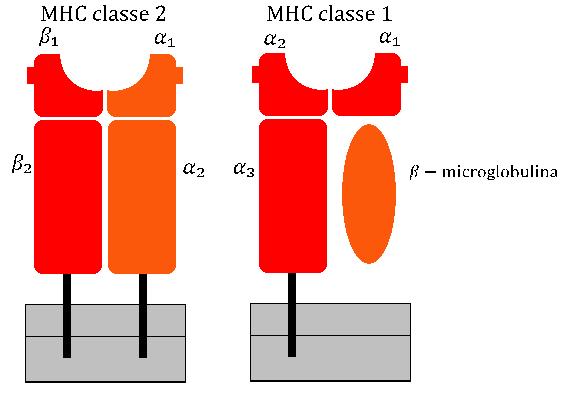
Major Histocompatibility Complex
The major histocompatibility complex (MHC) is a large locus on vertebrate DNA containing a set of closely linked polymorphic genes that code for cell surface proteins essential for the adaptive immune system. These cell surface proteins are called MHC molecules. This locus got its name because it was discovered via the study of transplanted tissue compatibility. Later studies revealed that tissue rejection due to incompatibility is only a facet of the full function of MHC molecules: binding an antigen derived from self-proteins, or from pathogens, and bringing the antigen presentation to the cell surface for recognition by the appropriate T-cells. MHC molecules mediate the interactions of leukocytes, also called white blood cells (WBCs), with other leukocytes or with body cells. The MHC determines donor compatibility for organ transplant, as well as one's susceptibility to autoimmune diseases. In a cell, protein molecules of the host's own phenotype or of other biologic entities ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
SSA SSB ANA
SSA may refer to: Geography * Sub-Saharan Africa Organizations * Safe Schools Alliance, a British advocacy group * SSA Global Technologies, American software company acquired by Infor Global Solutions * Shan State Army, a former insurgent group in Burma * Slovak Society of Actuaries ( sk, Slovenská spoločnosť aktuárov), professional association in Slovakia * Soaring Society of America, American sporting society founded in 1932 * Society of Scottish Artists, artists society founded in 1891 * Swedish Society of Radio Amateurs, an amateur radio organization * Singapore Scout Association, youth movement founded 1910 * Seismological Society of America, international scientific society founded1906 * Scottish Socialist Alliance, a coalition of left-wing bodies, fore-runner to the Scottish Socialist Party * Shipconstructors' and Shipwrights' Association, a former British trade union * Sainsbury's Staff Association, of Sainsbury's, UK * Sudan Studies Association, US professiona ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
HLA-DR3
HLA-DR3 is composed of the HLA-DR17 and HLA-DR18 split 'antigens' serotypes. DR3 is a component gene-allele of the AH8.1 haplotype in Northern and Western Europeans. Genes between B8 and DR3 on this haplotype are frequently associated with autoimmune disease. Type 1 diabetes mellitus is associated with HLA-DR3 or HLA-DR4. Nearly half the US population has either DR3 or DR4 (only 1–3% have both), yet only a small percentage (about 0.5%) of these individuals will develop type 1 diabetes. Serology Some DR3 also react with HLA-DR17 and/or HLA-DR18. The DRB1*0304 primarily reacts with DR3. The serotypes of *0305, *0306, *0308 to *0331 are unknown. Disease associations By serotype HLA-DR3 is associated with early-age onset myasthenia gravis, Hashimoto's thyroiditis (along with DR5), primary sclerosing cholangitis, and opportunistic infections in AIDS, but lowered risk for cancers. It is also associated with membranous glomerulonephritis By allele DRB1*0301 (see HLA-DR17) DRB1* ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
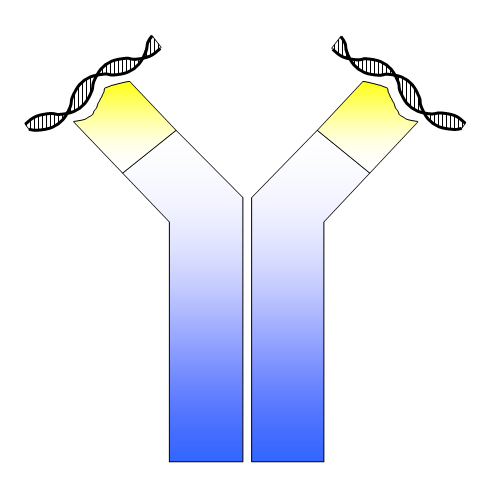
Immunoglobulin M
Immunoglobulin M (IgM) is one of several isotypes of antibody (also known as immunoglobulin) that are produced by vertebrates. IgM is the largest antibody, and it is the first antibody to appear in the response to initial exposure to an antigen. In humans and other mammals that have been studied, plasmablasts residing in the spleen are the main source for specific IgM production. History In 1937, an antibody was observed in horses hyper-immunized with pneumococcus polysaccharide that was much larger in size than the typical rabbit γ-globulin, with a molecular weight of 990,000 daltons. In accordance with its larger size, the new antibody was originally referred to as γ-macroglobulin, and subsequently termed as IgM—M for “macro”. The V domains of normal immunoglobulin are highly heterogeneous, reflecting their role in protecting against the great variety of infectious microbes, and this heterogeneity impeded detailed structural analysis of IgM. Two sources of homogen ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |