|
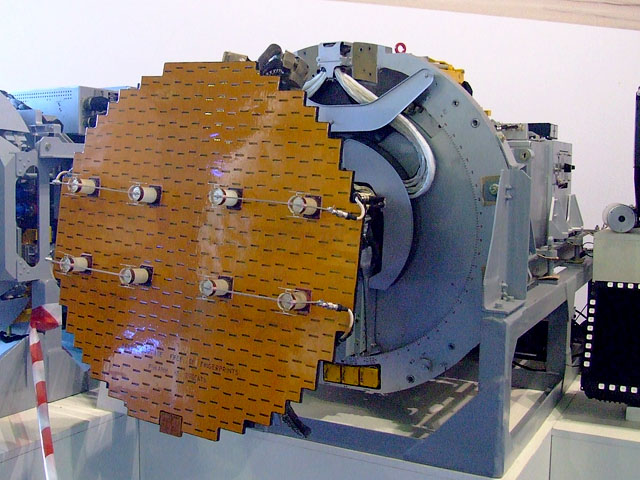
SPG-51
The AN/SPG-51 is an American tracking / illumination fire-control radar for RIM-24 Tartar and RIM-66 Standard missiles. It is used for target tracking and Surface-to-air missile guidance on s, s, and s. The Italian Navy used it aboard their ''Audace'' class, ''Durand de la Penne'' class and s. The French ''Cassard'' class, Royal Netherlands Navy ''Tromp'' class and Spanish ''Baleares'' class frigates also use this system. Older variants were used on s, as well as the related German ''Lütjens'' class and ''Perth'' class used by the Royal Australian Navy. Aircraft tracking is based on monopulse radar utilizing Pulse-Doppler radar signal processing in MK 74 MOD 14 and MK 74 MOD 15. The MK 74 MOD 15 configuration includes continuous-wave radar tracking in addition to pulse-Doppler tracking. It provides illumination for bistatic radar operation associated with missile guidance in all configurations. Older systems rely on conical scanning Conical scanning is a system used i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Perth-class Destroyer
The ''Perth''-class destroyers were three modified guided missile destroyers operated by the Royal Australian Navy (RAN). Ordered from Defoe Shipbuilding Company during 1962 and 1963, HMA Ships , , and were the first guided missiled-armed warships, and the first naval ships of United States design, to enter service with the RAN. All three ships operated during the Vietnam War, while ''Brisbane'' also participated in the Gulf War. The class was decommissioned between 1999 and 2001, with all three vessels later sunk as dive wrecks. Design and construction During the late 1950s, the RAN announced a requirement for guided missile-armed warships; along with plans to install guided missiles aboard currently active escort vessels, plans were made to acquire two purpose-built destroyers.Cooper, in Stevens, ''The Royal Australian Navy'', p. 190 Although traditionally, Australian warships were based on British designs, the RAN chose to study the United States Navy's (USN) along with th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tromp Class Frigate
The ''Tromp'' class were two frigates built for the Royal Netherlands Navy during the 1970s to replace the s as squadron flagships. The ''Tromp''-class frigates entered service in 1975 and 1976 and served until 1999 and 2001. Both ships were built by Royal Schelde Shipyard in Flushing (Vlissingen). The ships served as fleet flagships and area air defence vessels. Their 3D radar under a large polyester radome, gave the ships the nickname "Kojak" in the Netherlands Navy. Originally the ships were to have the British Sea Dart missile system, but this was changed to the more compact American Standard surface-to-air missile. The ships were replaced by the s. A total of four new frigates have been built, including two also named and . Ships See also * * Maarten Tromp Maarten Harpertszoon Tromp (also written as ''Maerten Tromp''; 23 April 1598 – 31 July 1653) was a Dutch army general and admiral in the Dutch navy. Son of a ship's captain, Tromp spent much of his childhoo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Baleares-class Frigate
The ''Baleares'' class are a group of five frigates built for the Spanish navy in the 1970s. The ships are a modified version of the American s. The key differences are the replacement of the Sea Sparrow PDMS and ASW helicopter facilities by Standard SAM and associated radars. They received a SPS-52B 3D search radar and one SPG-51 illuminator for the Standard SM-1 medium range SAM, fired from a Mk22 16-round single arm launcher. The SQS-26 long range LF sonar was replaced by a SQS-23G MF sonar, while two Mk25 tubes for Mk37 torpedoes were mounted in the transom. The SQS-35 variable depth sonar was maintained. The five ships were upgraded several times during their service lives. They received a Spanish TRITAN combat data system and the EW suite was upgraded with Spanish equipment. Mk36 SROC decoy launchers were also added, as well as two quadruple Harpoon launchers amidships. Two Meroka CIWS gun system were also fitted. The old SQS-23G sonar was replaced by a modern DE-1160LF ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lütjens-class Destroyer
The Type 103 ''Lütjens'' class was the last class of destroyers in service with the German Navy. The ships were US guided missile destroyers but with some modifications to meet German requirements. They were replaced by the new ''Sachsen''-class frigates, designated frigate even though they are much larger and more capable in all aspects than the ''Lütjens''-class destroyers. Development The three ''Lütjens'' destroyers were purchased from the US to provide air defence. For German use, they received the following modifications: * Communication systems according to German standards. The ''Lütjens'' class had more aerials and a second mast mounted on the aft funnel. The large air surveillance radar was positioned further aft (above the funnel). In turn, the new antennas and radar location meant that the funnels had to be modified. On the ''Lütjens'' the exhaust gases were emitted sideways with two pipes on the port and starboard side of each funnel. * New location of the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Durand De La Penne-class Destroyer
The ''Durand de la Penne'' class are two guided-missile destroyers operated by the Italian Navy. The design is an enlarged version of the , updated with diesel and gas turbine CODOG machinery and modern sensors. Four ships were planned but the second pair were cancelled when Italy joined the Horizon project. Origins This class is named after a famous naval diver who served in Italy's Royal Navy during World War II, Luigi Durand de la Penne. He, together with other members of X MAS made the most successful human torpedo mission, damaging the British battleships and in Alexandria, December 1941, with SLCs 'Maiale'. These new ships were meant as very advanced destroyers, with an improvement over the previous types in almost every aspect of design. Because the ships in the Italian Navy are seldom built from scratch (especially for economic reasons), it is worth considering the evolution of this project, starting with the first class of missile destroyers made in Italy. With pr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cassard Class Frigate
The ''Cassard'' class (Type F70 AA) was a class of two anti-air warfare destroyers of the French Navy introduced in the latter 1980s/early 1990s. The class was an air defence variant of the . The two classes have a different armament and propulsion system mounted on an identical hull. Their primary role was to provide air cover for a fleet, an aeronaval group, a convoy & a littoral point. Their secondary role was to manage air assets coordination & aircraft control for the force, especially through Link 16.They can also be used for research, identification or presence missions. Both ships were assigned to the '' Force d'Action Navale.''Gardiner and Chumbly, p. 115 The lead ship of the class, ''Cassard'', was retired in 2019 followed by the retirement of ''Jean Bart'' in 2021. The experience gained during the design and construction of the ''Cassard'' type was used for the design of the . Design The ''Cassard''-class frigate was initially designed to replace the four anti-air warf ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pulse-Doppler Radar
A pulse-Doppler radar is a radar system that determines the range to a target using pulse-timing techniques, and uses the Doppler effect of the returned signal to determine the target object's velocity. It combines the features of pulse radars and continuous-wave radars, which were formerly separate due to the complexity of the electronics. The first operational Pulse Doppler radar was in the CIM-10 Bomarc, an American long range supersonic missile powered by ramjet engines, and which was armed with a W40 nuclear weapon to destroy entire formations of attacking enemy aircraft. Pulse-Doppler systems were first widely used on fighter aircraft starting in the 1960s. Earlier radars had used pulse-timing in order to determine range and the angle of the antenna (or similar means) to determine the bearing. However, this only worked when the radar antenna was not pointed down; in that case the reflection off the ground overwhelmed any returns from other objects. As the ground moves at the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Conical Scanning
Conical scanning is a system used in early radar units to improve their accuracy, as well as making it easier to steer the antenna properly to point at a target. Conical scanning is similar in concept to the earlier lobe switching concept used on some of the earliest radars, and many examples of lobe switching sets were modified in the field to conical scanning during World War II, notably the German Würzburg radar. Antenna guidance can be made entirely automatic, as in the American SCR-584. Potential failure modes and susceptibility to deception jamming led to the replacement of conical scan systems with monopulse radar sets. They are still used by the Deep Space Network for maintaining communications links to space probes. The spin-stabilized Pioneer 10 and Pioneer 11 probes used onboard conical scanning maneuvers to track Earth in its orbit. Concept A typical radar antenna commonly has a beam width of a few degrees. While this is adequate for locating the target in an earl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bistatic Radar
Bistatic radar is a radar system comprising a transmitter and receiver that are separated by a distance comparable to the expected target distance. Conversely, a conventional radar in which the transmitter and receiver are co-located is called a monostatic radar. A system containing multiple spatially diverse monostatic or bistatic radar components with a shared area of coverage is called ''multistatic radar''. Many long-range air-to-air and surface-to-air missile systems use semi-active radar homing, which is a form of bistatic radar. Types Pseudo-monostatic radars Some radar systems may have separate transmit and receive antennas, but if the angle subtended between transmitter, target and receiver (the bistatic angle) is close to zero, then they would still be regarded as monostatic or pseudo-monostatic. For example, some very long range HF radar systems may have a transmitter and receiver which are separated by a few tens of kilometres for electrical isolation, but as ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Continuous-wave Radar
Continuous-wave radar (CW radar) is a type of radar system where a known stable frequency continuous wave radio energy is transmitted and then received from any reflecting objects. Individual objects can be detected using the Doppler effect, which causes the received signal to have a different frequency from the transmitted signal, allowing it to be detected by filtering out the transmitted frequency. Doppler-analysis of radar returns can allow the filtering out of slow or non-moving objects, thus offering immunity to interference from large stationary objects and slow-moving clutter. This makes it particularly useful for looking for objects against a background reflector, for instance, allowing a high-flying aircraft to look for aircraft flying at low altitude against the background of the surface. Because the very strong reflection off the surface can be filtered out, the much smaller reflection from a target can still be seen. CW radar systems are used at both ends of the range ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Monopulse Radar
Monopulse radar is a radar system that uses additional encoding of the radio signal to provide accurate directional information. The name refers to its ability to extract range and direction from a single signal pulse. Monopulse radar avoids problems seen in conical scanning radar systems, which can be confused by rapid changes in signal strength. The system also makes electronic warfare, jamming more difficult. Most radars designed since the 1960s are monopulse systems. The monopulse method is also used in passive systems, such as electronic support measures and radio astronomy. Monopulse radar systems can be constructed with reflector (antenna) , reflector antennas, lens antenna , lens antennas or array antennas. Historically, monopulse systems have been classified as either phase-comparison monopulse or amplitude monopulse. Modern systems determine the direction from the monopulse ratio, which contain both amplitude and phase information. The monopulse method does not requir ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Royal Australian Navy
The Royal Australian Navy (RAN) is the principal naval force of the Australian Defence Force (ADF). The professional head of the RAN is Chief of Navy (CN) Vice Admiral Mark Hammond AM, RAN. CN is also jointly responsible to the Minister of Defence (MINDEF) and the Chief of Defence Force (CDF). The Department of Defence as part of the Australian Public Service administers the ADF. Formed in 1901, as the Commonwealth Naval Forces (CNF), through the amalgamation of the colonial navies of Australia following the federation of Australia. Although it was originally intended for local defence, it became increasingly responsible for regional defence as the British Empire started to diminish its influence in the South Pacific. The Royal Australian Navy was initially a green-water navy, and where the Royal Navy provided a blue-water force to the Australian Squadron, which the Australian and New Zealand governments helped to fund, and that was assigned to the Australia Station. Thi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |

_with_spanish_warships.jpg)