|
SOXS
Solar X-Ray Spectrometer, or SOXS, was an experimental payload launched onboard Indian geostationary satellite GSAT-2 by the Indian Space Research Organisation, ISRO. SOXS collected data about X-ray emissions from solar flares with high energy and temporal resolutions. Features * X-Ray Spectrometer (SOXS) was flown onboard GSAT-2 on 8-May-2003. * SOXS employs Si and CZT semiconductor devices, which are extremely high resolution and low noise detectors. * Detector package is mounted on a Sun Pointing Mechanism with tracking accuracy better than 0.1 degree. * Pulse Height (PHA) measurements in 256 channels. * System Dead Time- 16 microseconds for Si Pin and 13 microseconds for CZT. * Energy window counters. * On board calibration using Cd109 Radio isotope. * System Health Parameters Monitoring. * Onboard selection for Background Rejection (LLD/Threshold). * In view of Temperature Temperature is a physical quantity that expresses quantitatively the perceptions of hotness and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
GSAT-2
GSAT-2 was an experimental communication satellite built by the Indian Space Research Organisation (ISRO) and launched on one of the first GSLVs. The satellite was positioned at 48 deg east longitude in the geo-stationary orbit. Payloads GSAT-2 carried four C-band transponders, two Ku band transponders and a Mobile Satellite Service (MSS) payload operating in S-band forward link and C-band return link. Besides the communication payloads, GSAT-2 carried the following four piggyback experimental payloads: *Total Radiation Dose Monitor (TRDM) to compare the estimated radiation doses inside the satellite with the directly measured radiation doses using a Radiation Sensitive Field Effect Transistor (RADFET) *Surface Charge Monitor (SCM) to indicate the state of the charging environment in the vicinity of the spacecraft * Solar X-ray Spectrometer (SOXS) to study the solar flare emission in 4 keV - 60 keV energy range using state of the art semiconductor devices and Phoswich Scintill ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Geostationary Satellite
A geostationary orbit, also referred to as a geosynchronous equatorial orbit''Geostationary orbit'' and ''Geosynchronous (equatorial) orbit'' are used somewhat interchangeably in sources. (GEO), is a circular geosynchronous orbit in altitude above Earth's equator ( in radius from Earth's center) and following the direction of Earth's rotation. An object in such an orbit has an orbital period equal to Earth's rotational period, one sidereal day, and so to ground observers it appears motionless, in a fixed position in the sky. The concept of a geostationary orbit was popularised by the science fiction writer Arthur C. Clarke in the 1940s as a way to revolutionise telecommunications, and the first satellite to be placed in this kind of orbit was launched in 1963. Communications satellites are often placed in a geostationary orbit so that Earth-based satellite antennas do not have to rotate to track them but can be pointed permanently at the position in the sky where the sate ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Indian Space Research Organisation
The Indian Space Research Organisation (ISRO; ) is the national space agency of India, headquartered in Bengaluru. It operates under the Department of Space (DOS) which is directly overseen by the Prime Minister of India, while the Chairman of ISRO acts as the executive of DOS as well. ISRO is India's primary agency for performing tasks related to space-based applications, space exploration and the development of related technologies. It is one of six government space agencies in the world which possess full launch capabilities, deploy cryogenic engines, launch extraterrestrial missions and operate large fleets of artificial satellites. The Indian National Committee for Space Research (INCOSPAR) was established by Jawaharlal Nehru under the Department of Atomic Energy (DAE) in 1962, on the urging of scientist Vikram Sarabhai, recognising the need in space research. INCOSPAR grew and became ISRO in 1969, within DAE. In 1972, the government of India set up a Space Commissi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
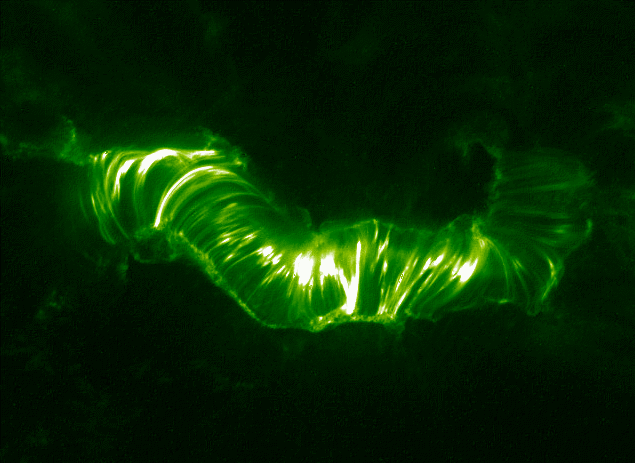
Solar Flare
A solar flare is an intense localized eruption of electromagnetic radiation in the Sun's atmosphere. Flares occur in active regions and are often, but not always, accompanied by coronal mass ejections, solar particle events, and other solar phenomena. The occurrence of solar flares varies with the 11-year solar cycle. Solar flares are thought to occur when stored magnetic energy in the Sun's atmosphere accelerates charged particles in the surrounding plasma. This results in the emission of electromagnetic radiation across the electromagnetic spectrum. High-energy electromagnetic radiation from solar flares is absorbed by the daylight side of Earth's upper atmosphere, in particular the ionosphere, and does not reach the surface. This absorption can temporarily increase the ionization of the ionosphere which may interfere with short-wave radio communication. The prediction of solar flares is an active area of research. Flares also occur on other stars, where the term ''stellar ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Shodhganga
Shodhganga: a reservoir of Indian theses (Sanskrit:, ; ''Ganga'', the river) is a digital repository of theses and dissertations submitted to universities in India. About It is maintained by INFLIBNET Centre which is an autonomous Inter-University Centre of the University Grants Commission (UGC) of India. It was initially located in the campus of Gujarat University, Ahmedabad. As of January 2013, INFLIBNET Centre has moved to its new institutional building at infocity, Gandhinagar, capital of Gujarat. By 2022, as many as 544 universities in India have signed MoUs with the INFLIBNET Centre to participate in the Shodhganga project. The full text of all the documents submitted to Shodhganga are available to read and to download in open access to the academic community worldwide. The repository has a collection of over 3 lakh theses and 8000 synopses. The Shodhganga repository was created consequent on the University Grants Commission making it mandatory through regulations issued ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cadmium Zinc Telluride
Cadmium zinc telluride, (CdZnTe) or CZT, is a compound of cadmium, zinc and tellurium or, more strictly speaking, an alloy of cadmium telluride and zinc telluride. A direct bandgap semiconductor, it is used in a variety of applications, including semiconductor radiation detectors, photorefractive gratings, electro-optic modulators, solar cells, and terahertz generation and detection. The band gap varies from approximately 1.4 to 2.2 eV, depending on composition. Radiation detectors using CZT can operate in direct-conversion (or photoconductive) mode at room temperature, unlike some other materials (particularly germanium) which require cooling. Their relative advantages include high sensitivity for X-rays and gamma rays, due to the high atomic numbers of Cd and Te, and better energy resolution than scintillator detectors. CZT can be formed into different shapes for different radiation-detecting applications, and a variety of electrode geometries, such as coplanar grids and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Semiconductor
A semiconductor is a material which has an electrical resistivity and conductivity, electrical conductivity value falling between that of a electrical conductor, conductor, such as copper, and an insulator (electricity), insulator, such as glass. Its electrical resistivity and conductivity, resistivity falls as its temperature rises; metals behave in the opposite way. Its conducting properties may be altered in useful ways by introducing impurities ("doping (semiconductor), doping") into the crystal structure. When two differently doped regions exist in the same crystal, a semiconductor junction is created. The behavior of charge carriers, which include electrons, ions, and electron holes, at these junctions is the basis of diodes, transistors, and most modern electronics. Some examples of semiconductors are silicon, germanium, gallium arsenide, and elements near the so-called "metalloid staircase" on the periodic table. After silicon, gallium arsenide is the second-most common s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pulse Height Analyzer
A pulse-height analyzer (PHA) is an instrument that accepts electronic pulses of varying heights from particle and event detectors, digitizes the pulse heights, and saves the number of pulses of each height in registers or channels, thus recording a pulse-height spectrum or pulse-height distribution used for later pulse-height analysis. PHAs are used in nuclear- and elementary-particle physics research. A PHA is a specific modification to multichannel analyzers. A pulse-height analyzer is also integrated into particle counters or used as a discrete module to calibrate particle counters. See also * Nuclear electronics Nuclear electronics is a subfield of electronics concerned with the design and use of high-speed electronic systems for nuclear physics and elementary particle physics research, and for industrial and medical use. Essential elements of such systems ... Experimental particle physics {{nuclear-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Microsecond
A microsecond is a unit of time in the International System of Units (SI) equal to one millionth (0.000001 or 10−6 or ) of a second. Its symbol is μs, sometimes simplified to us when Unicode is not available. A microsecond is equal to 1000 nanoseconds or of a millisecond. Because the next SI prefix is 1000 times larger, measurements of 10−5 and 10−4 seconds are typically expressed as tens or hundreds of microseconds. Examples * 1 microsecond (1 μs) – cycle time for frequency (1 MHz), the inverse unit. This corresponds to radio wavelength 300 m (AM medium wave band), as can be calculated by multiplying 1 μs by the speed of light (approximately ). * 1 microsecond – the length of time of a high-speed, commercial strobe light flash (see air-gap flash). * 1 microsecond – protein folding takes place on the order of microseconds. * 1.8 microseconds – the amount of time subtracted from the Earth's day as a result of the 2011 Japanese earthquake. * 2 m ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cadmium
Cadmium is a chemical element with the symbol Cd and atomic number 48. This soft, silvery-white metal is chemically similar to the two other stable metals in group 12, zinc and mercury. Like zinc, it demonstrates oxidation state +2 in most of its compounds, and like mercury, it has a lower melting point than the transition metals in groups 3 through 11. Cadmium and its congeners in group 12 are often not considered transition metals, in that they do not have partly filled ''d'' or ''f'' electron shells in the elemental or common oxidation states. The average concentration of cadmium in Earth's crust is between 0.1 and 0.5 parts per million (ppm). It was discovered in 1817 simultaneously by Stromeyer and Hermann, both in Germany, as an impurity in zinc carbonate. Cadmium occurs as a minor component in most zinc ores and is a byproduct of zinc production. Cadmium was used for a long time as a corrosion-resistant plating on steel, and cadmium compounds are used as red, orang ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Radio Isotope
A radionuclide (radioactive nuclide, radioisotope or radioactive isotope) is a nuclide that has excess nuclear energy, making it unstable. This excess energy can be used in one of three ways: emitted from the nucleus as gamma radiation; transferred to one of its electrons to release it as a conversion electron; or used to create and emit a new particle (alpha particle or beta particle) from the nucleus. During those processes, the radionuclide is said to undergo radioactive decay. These emissions are considered ionizing radiation because they are energetic enough to liberate an electron from another atom. The radioactive decay can produce a stable nuclide or will sometimes produce a new unstable radionuclide which may undergo further decay. Radioactive decay is a random process at the level of single atoms: it is impossible to predict when one particular atom will decay. However, for a collection of atoms of a single nuclide the decay rate, and thus the half-life (''t''1/2) f ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Temperature
Temperature is a physical quantity that expresses quantitatively the perceptions of hotness and coldness. Temperature is measured with a thermometer. Thermometers are calibrated in various temperature scales that historically have relied on various reference points and thermometric substances for definition. The most common scales are the Celsius scale with the unit symbol °C (formerly called ''centigrade''), the Fahrenheit scale (°F), and the Kelvin scale (K), the latter being used predominantly for scientific purposes. The kelvin is one of the seven base units in the International System of Units (SI). Absolute zero, i.e., zero kelvin or −273.15 °C, is the lowest point in the thermodynamic temperature scale. Experimentally, it can be approached very closely but not actually reached, as recognized in the third law of thermodynamics. It would be impossible to extract energy as heat from a body at that temperature. Temperature is important in all fields of natur ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |