|
SATA
SATA (Serial AT Attachment) is a computer bus interface that connects host bus adapters to mass storage devices such as hard disk drives, optical drives, and solid-state drives. Serial ATA succeeded the earlier Parallel ATA (PATA) standard to become the predominant interface for storage devices. Serial ATA industry compatibility specifications originate from the Serial ATA International Organization (SATA-IO) which are then promulgated by the INCITS Technical Committee T13, AT Attachment (INCITS T13). History SATA was announced in 2000 in order to provide several advantages over the earlier PATA interface such as reduced cable size and cost (seven conductors instead of 40 or 80), native hot swapping, faster data transfer through higher signaling rates, and more efficient transfer through an (optional) I/O queuing protocol. Revision 1.0 of the specification was released in January 2003. Serial ATA industry compatibility specifications originate from the Serial ATA Internati ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
ESATA
SATA (Serial AT Attachment) is a computer bus interface that connects host bus adapters to mass storage devices such as hard disk drives, optical drives, and solid-state drives. Serial ATA succeeded the earlier Parallel ATA (PATA) standard to become the predominant interface for storage devices. Serial ATA industry compatibility specifications originate from the Serial ATA International Organization (SATA-IO) which are then promulgated by the INCITS Technical Committee T13, AT Attachment (INCITS T13). History SATA was announced in 2000 in order to provide several advantages over the earlier PATA interface such as reduced cable size and cost (seven conductors instead of 40 or 80), native hot swapping, faster data transfer through higher signaling rates, and more efficient transfer through an (optional) I/O queuing protocol. Revision 1.0 of the specification was released in January 2003. Serial ATA industry compatibility specifications originate from the Serial ATA Internatio ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
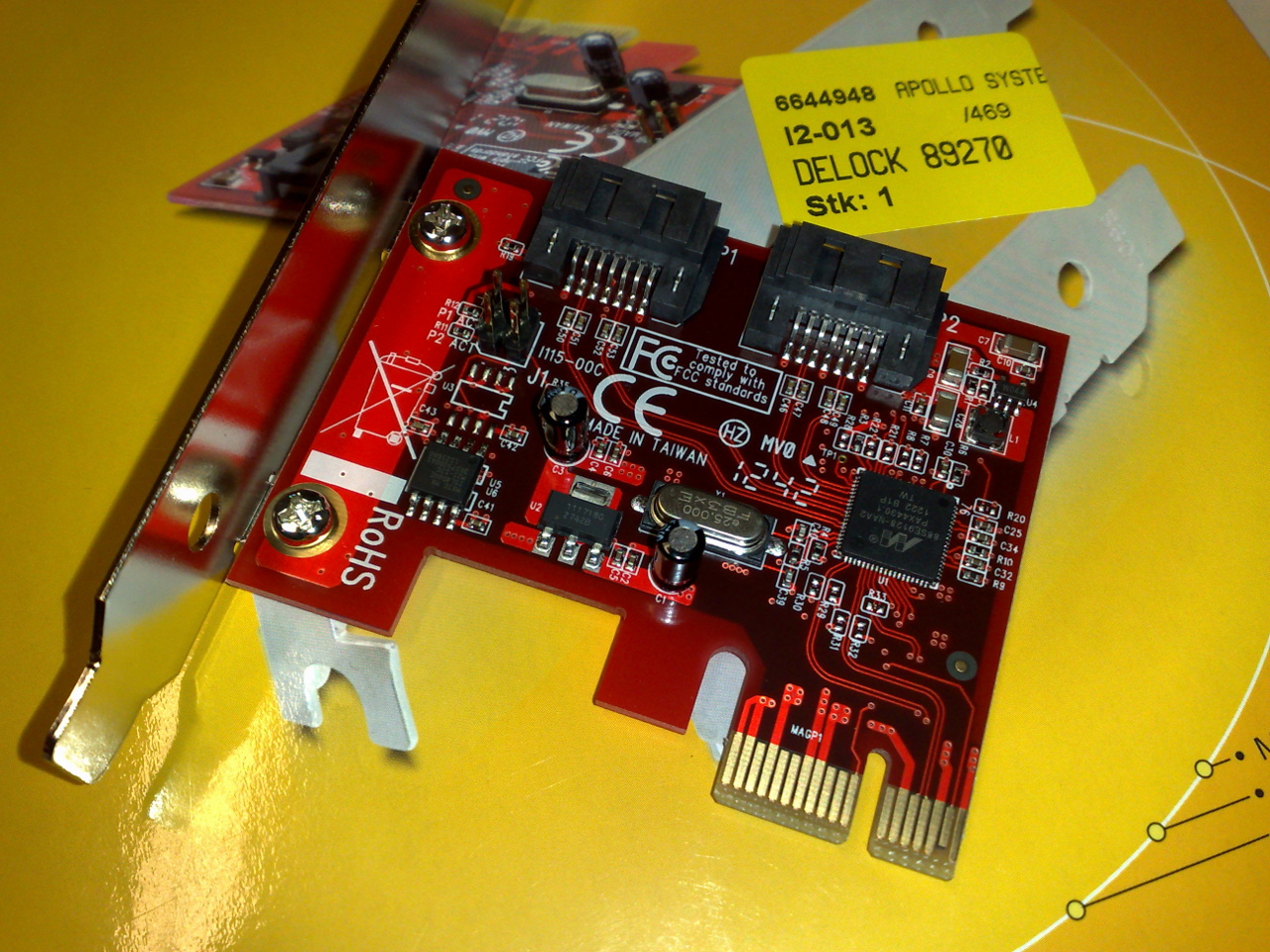
SATA 6 Gbit-s Controller, In Form Of A PCI Express Card
SATA (Serial AT Attachment) is a computer bus interface that connects host adapter, host bus adapters to mass storage devices such as hard disk drives, optical drives, and solid-state drives. Serial ATA succeeded the earlier Parallel ATA (PATA) standard to become the predominant interface for storage devices. Serial ATA industry compatibility specifications originate from the Serial ATA International Organization (SATA-IO) which are then promulgated by the INCITS Technical Committee T13, AT Attachment (INCITS T13). History SATA was announced in 2000 in order to provide several advantages over the earlier PATA interface such as reduced cable size and cost (seven conductors instead of 40 or 80), native hot swapping, faster data transfer through higher signaling rates, and more efficient transfer through an (optional) I/O queuing protocol. #1.0, Revision 1.0 of the specification was released in January 2003. Serial ATA industry compatibility specifications originate from the Seri ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
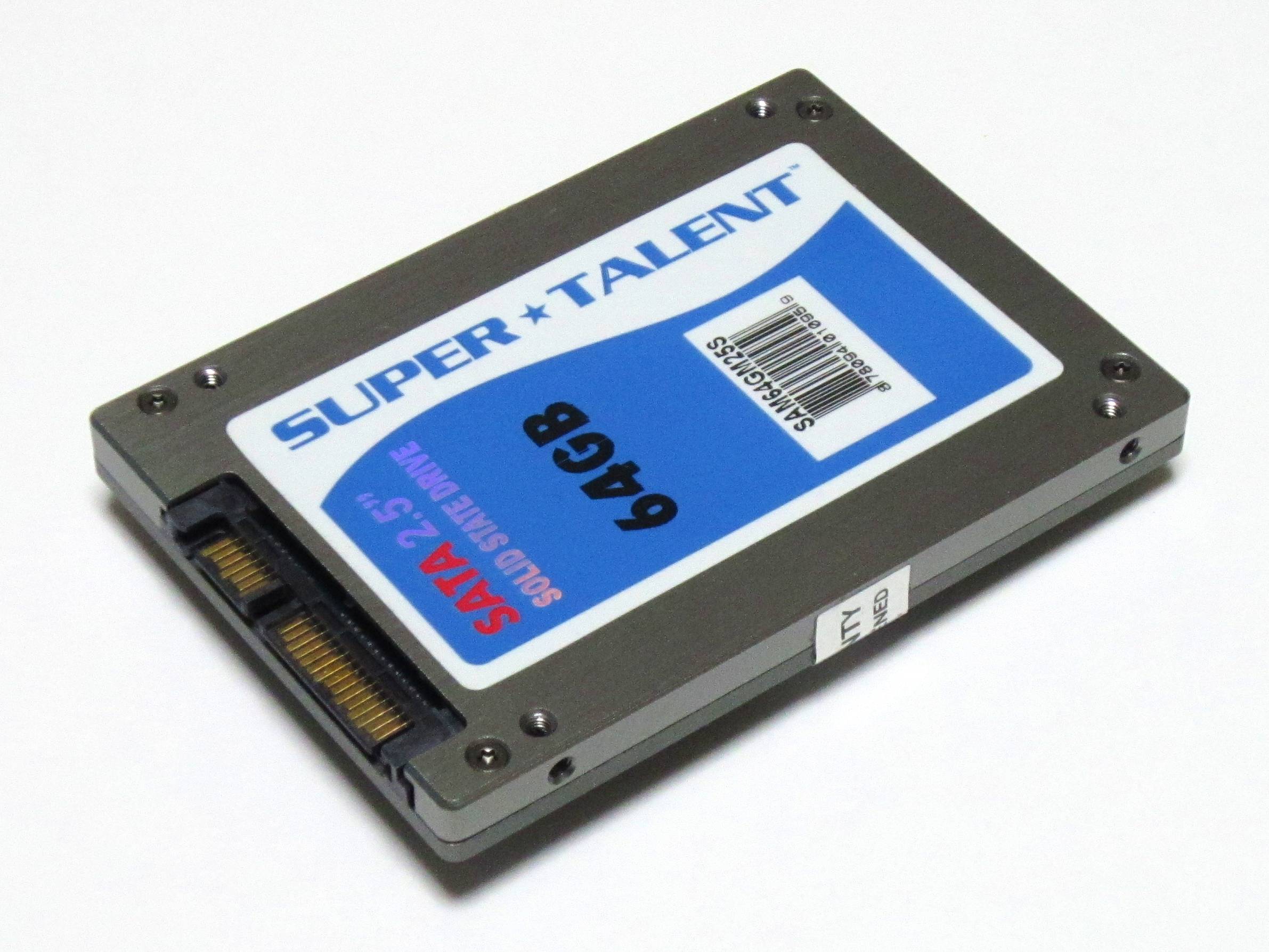
Solid-state Drive
A solid-state drive (SSD) is a solid-state storage device that uses integrated circuit assemblies to store data persistently, typically using flash memory, and functioning as secondary storage in the hierarchy of computer storage. It is also sometimes called a semiconductor storage device, a solid-state device or a solid-state disk, even though SSDs lack the physical spinning disks and movable read–write heads used in hard disk drives (HDDs) and floppy disks. SSD also has rich internal parallelism for data processing. In comparison to hard disk drives and similar electromechanical media which use moving parts, SSDs are typically more resistant to physical shock, run silently, and have higher input/output rates and lower latency. SSDs store data in semiconductor cells. cells can contain between 1 and 4 bits of data. SSD storage devices vary in their properties according to the number of bits stored in each cell, with single-bit cells ("Single Level Cells" or "SLC ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hard Disk Drive
A hard disk drive (HDD), hard disk, hard drive, or fixed disk is an electro-mechanical data storage device that stores and retrieves digital data using magnetic storage with one or more rigid rapidly rotating platters coated with magnetic material. The platters are paired with magnetic heads, usually arranged on a moving actuator arm, which read and write data to the platter surfaces. Data is accessed in a random-access manner, meaning that individual blocks of data can be stored and retrieved in any order. HDDs are a type of non-volatile storage, retaining stored data when powered off. Modern HDDs are typically in the form of a small rectangular box. Introduced by IBM in 1956, HDDs were the dominant secondary storage device for general-purpose computers beginning in the early 1960s. HDDs maintained this position into the modern era of servers and personal computers, though personal computing devices produced in large volume, like cell phones and tablets, rely on ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
CompactFlash
CompactFlash (CF) is a flash memory mass storage device used mainly in portable electronic devices. The format was specified and the devices were first manufactured by SanDisk in 1994. CompactFlash became one of the most successful of the early memory card formats, surpassing Miniature Card and SmartMedia. Subsequent formats, such as MMC/ SD, various Memory Stick formats, and xD-Picture Card offered stiff competition. Most of these cards are smaller than CompactFlash while offering comparable capacity and speed. Proprietary memory card formats for use in professional audio and video, such as P2 and SxS, are faster, but physically larger and more costly. CompactFlash's popularity is declining as CFexpress is taking over. As of 2022, both Canon and Nikon newest high end cameras, e.g. the Canon EOS R5, Canon EOS R3, and Nikon Z 9 use CFexpress cards for the higher performance required to record 8K video. Traditional CompactFlash cards use the Parallel ATA interface, but ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
CFast
CompactFlash (CF) is a flash memory mass storage device used mainly in portable electronic devices. The format was specified and the devices were first manufactured by SanDisk in 1994. CompactFlash became one of the most successful of the early memory card formats, surpassing Miniature Card and SmartMedia. Subsequent formats, such as MMC/ SD, various Memory Stick formats, and xD-Picture Card offered stiff competition. Most of these cards are smaller than CompactFlash while offering comparable capacity and speed. Proprietary memory card formats for use in professional audio and video, such as P2 and SxS, are faster, but physically larger and more costly. CompactFlash's popularity is declining as CFexpress is taking over. As of 2022, both Canon and Nikon newest high end cameras, e.g. the Canon EOS R5, Canon EOS R3, and Nikon Z 9 use CFexpress cards for the higher performance required to record 8K video. Traditional CompactFlash cards use the Parallel ATA interface, but i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Advanced Host Controller Interface
The Advanced Host Controller Interface (AHCI) is a technical standard defined by Intel that specifies the register-level interface of Serial ATA (SATA) host controllers in a non-implementation-specific manner in its motherboard chipsets. The specification describes a system memory structure for computer hardware vendors to exchange data between host system memory and attached storage devices. AHCI gives software developers and hardware designers a standard method for detecting, configuring, and programming SATA/AHCI adapters. AHCI is separate from the SATA 3 Gbit/s standard, although it exposes SATA's advanced capabilities (such as hot swapping and native command queuing) such that host systems can utilize them. For modern solid state drives, the interface has been superseded by NVMe. The current version of the specification is 1.3.1. Operating modes Many SATA controllers offer selectable modes of operation: legacy Parallel ATA emulation (more commonly called IDE Mode) ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Parallel ATA
Parallel ATA (PATA), originally , also known as IDE, is a standard interface designed for IBM PC-compatible computers. It was first developed by Western Digital and Compaq in 1986 for compatible hard drives and CD or DVD drives. The connection is used for storage devices such as hard disk drives, floppy disk drives, and optical disc drives in computers. The standard is maintained by the X3/INCITS committee. It uses the underlying (ATA) and Packet Interface ( ATAPI) standards. The Parallel ATA standard is the result of a long history of incremental technical development, which began with the original AT Attachment interface, developed for use in early PC AT equipment. The ATA interface itself evolved in several stages from Western Digital's original Integrated Drive Electronics (IDE) interface. As a result, many near-synonyms for ATA/ATAPI and its previous incarnations are still in common informal use, in particular Extended IDE (EIDE) and Ultra ATA (UATA). After the introd ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Host Adapter
In computer hardware, a host controller, host adapter, or host bus adapter (HBA), connects a computer system bus, which acts as the host system, to other network and storage devices. The terms are primarily used to refer to devices for connecting SCSI, Fibre Channel and SATA devices. Devices for connecting to IDE, Ethernet, FireWire, USB and other systems may also be called host adapters. Host adapters can be integrated in the motherboard or be on a separate expansion card. The term network interface controller (NIC) is more often used for devices connecting to computer networks, while the term converged network adapter can be applied when protocols such as iSCSI or Fibre Channel over Ethernet allow storage and network functionality over the same physical connection. SCSI A SCSI host adapter connects a host system and a peripheral SCSI device or storage system. These adapters manage service and task communication between the host and target. Typically a device driver, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
SCSI
Small Computer System Interface (SCSI, ) is a set of standards for physically connecting and transferring data between computers and peripheral devices. The SCSI standards define commands, protocols, electrical, optical and logical interfaces. The SCSI standard defines command sets for specific peripheral device types; the presence of "unknown" as one of these types means that in theory it can be used as an interface to almost any device, but the standard is highly pragmatic and addressed toward commercial requirements. The initial Parallel SCSI was most commonly used for hard disk drives and tape drives, but it can connect a wide range of other devices, including scanners and CD drives, although not all controllers can handle all devices. The ancestral SCSI standard, X3.131-1986, generally referred to as SCSI-1, was published by the X3T9 technical committee of the American National Standards Institute (ANSI) in 1986. SCSI-2 was published in August 1990 as X3.T9.2/86-109 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Serial ATA International Organization
Serial ATA International Organization (SATA-IO) is an independent, non-profit organization which provides the computing industry with guidance and support for implementing the SATA specification. SATA-IO was developed by and for leading industry companies. It was officially formed in July 2004 by incorporating the previous Serial ATA Working Group which had been established in February 2000 to specify Serial ATA for desktop applications.SERIAL ATA II WORKING GROUP NAILS KEY TECHNICAL MILESTONES, Serial ATA Working Group Press Release, Sept. 17, 2003 SATA-IO is affiliated directly to INCITS, and indirectly via INCITS to ANSI. Many members form this organization; it is currently led by ATP Electronics, Dell, Hewlett-Packard, HGST, Intel, Marvell, PMC-Sierra, SanDisk, Seagate Technology, and Western Digital. See also * SATA Express * Serial ATA SATA (Serial AT Attachment) is a computer bus interface that connects host bus adapters to mass storage devices such as hard disk ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Computer Bus
In computer architecture, a bus (shortened form of the Latin '' omnibus'', and historically also called data highway or databus) is a communication system that transfers data between components inside a computer, or between computers. This expression covers all related hardware components (wire, optical fiber, etc.) and software, including communication protocols. Early computer buses were parallel electrical wires with multiple hardware connections, but the term is now used for any physical arrangement that provides the same logical function as a parallel electrical busbar. Modern computer buses can use both parallel and bit serial connections, and can be wired in either a multidrop (electrical parallel) or daisy chain topology, or connected by switched hubs, as in the case of Universal Serial Bus (USB). Background and nomenclature Computer systems generally consist of three main parts: * The central processing unit (CPU) that processes data, * The memory that holds the p ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |