|
Syzygites
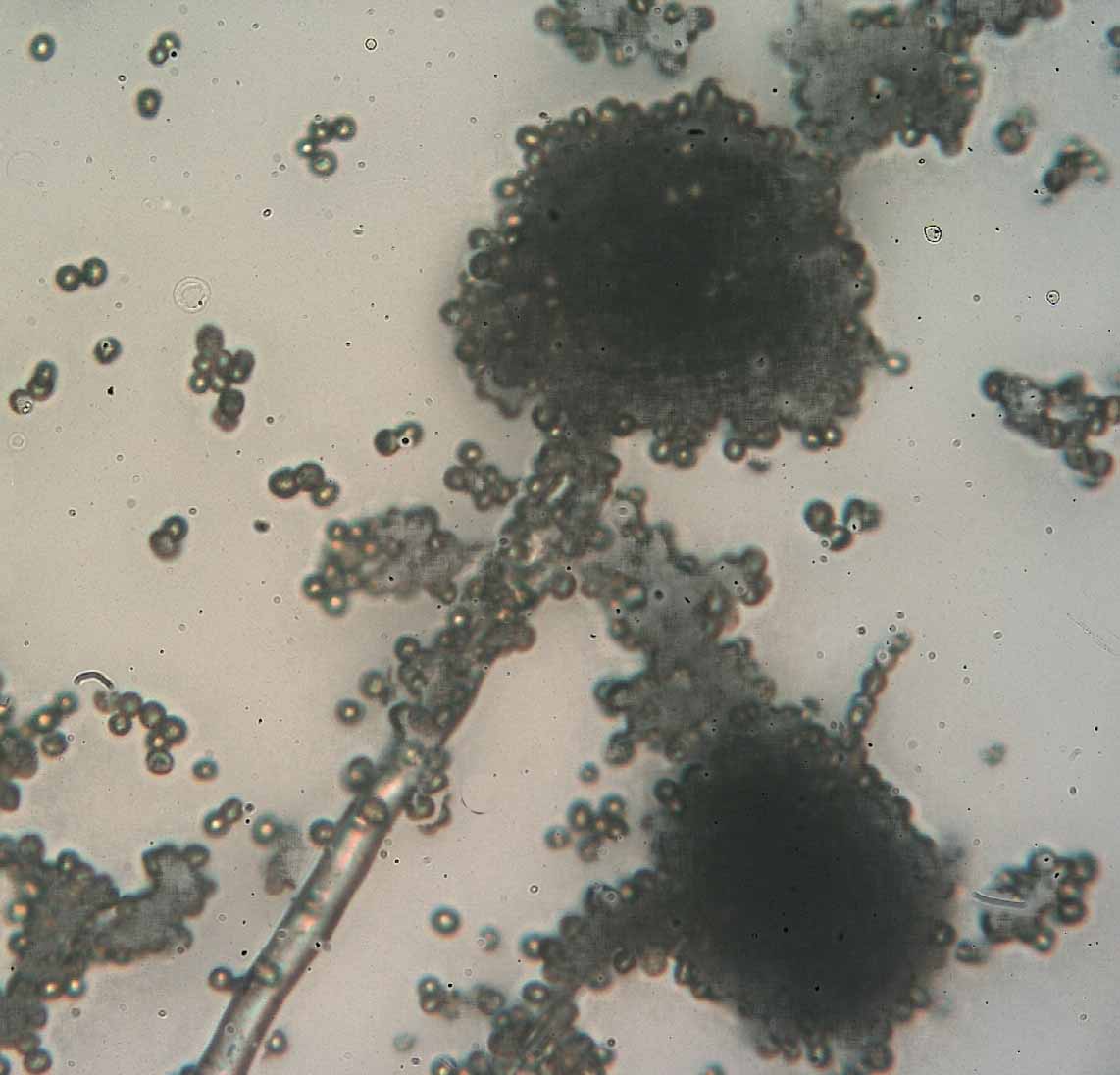
''Syzygites'' is a monotypic genus in Zygomycota. The sole described species is ''Syzygites megalocarpus'', which was the first fungus for which sex was reported and the main homothallic representative in the research that allowed for the classification of fungi as homothallic or heterothallic. It is also the fungus from which the term " zygospore" was coined. Morphology ''Syzygites megalocarpus'' produces phototropic, repeatedly dichotomously branched sporangiophores that terminate in globose, apophysate sporangia. Sporangiospores have a spinose wall, which is rare in Mucorales. Zygospores are pigmented, ornamented, and produced on equally sized suspensors. Due to the presence of carotenoids, the myceliuem can appear yellowish, though mature sporangia darken giving it a brownish appearance. Ecology ''S. megalocarpus'' is a necrotrophic parasite of mushrooms in temperate regions, though there are reports of it from ascomycetes. It can parasitize at least 98 different ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Syzygites Megalocarpus Sporangiole
''Syzygites'' is a monotypic genus in Zygomycota. The sole described species is ''Syzygites megalocarpus'', which was the first fungus for which sex was reported and the main homothallic representative in the research that allowed for the classification of fungi as homothallic or heterothallic. It is also the fungus from which the term " zygospore" was coined. Morphology ''Syzygites megalocarpus'' produces phototropic, repeatedly dichotomously branched sporangiophores that terminate in globose, apophysate sporangia. Sporangiospores have a spinose wall, which is rare in Mucorales. Zygospores are pigmented, ornamented, and produced on equally sized suspensors. Due to the presence of carotenoids, the myceliuem can appear yellowish, though mature sporangia darken giving it a brownish appearance. Ecology ''S. megalocarpus'' is a necrotrophic parasite of mushrooms in temperate regions, though there are reports of it from ascomycetes. It can parasitize at least 98 different ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Syzygites Megalocarpus 400x Dichotomous Sporangiophores
''Syzygites'' is a monotypic genus in Zygomycota. The sole described species is ''Syzygites megalocarpus'', which was the first fungus for which sex was reported and the main homothallic representative in the research that allowed for the classification of fungi as homothallic or heterothallic. It is also the fungus from which the term " zygospore" was coined. Morphology ''Syzygites megalocarpus'' produces phototropic, repeatedly dichotomously branched sporangiophores that terminate in globose, apophysate sporangia. Sporangiospores have a spinose wall, which is rare in Mucorales. Zygospores are pigmented, ornamented, and produced on equally sized suspensors. Due to the presence of carotenoids, the myceliuem can appear yellowish, though mature sporangia darken giving it a brownish appearance. Ecology ''S. megalocarpus'' is a necrotrophic parasite of mushrooms in temperate regions, though there are reports of it from ascomycetes. It can parasitize at least 98 different ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Carotenoid
Carotenoids (), also called tetraterpenoids, are yellow, orange, and red organic compound, organic pigments that are produced by plants and algae, as well as several bacteria, and Fungus, fungi. Carotenoids give the characteristic color to pumpkins, carrots, parsnips, maize, corn, tomatoes, Domestic Canary, canaries, flamingos, salmon, lobster, shrimp, and daffodils. Carotenoids can be produced from Lipid, fats and other basic organic metabolic building blocks by all these organisms. It is also produced by Endosymbiont, endosymbiotic bacteria in Whitefly, whiteflies. Carotenoids from the diet are stored in the fatty tissues of animals, and exclusively Carnivore, carnivorous animals obtain the compounds from animal fat. In the human diet, Small intestine#Absorption, absorption of carotenoids is improved when consumed with fat in a meal. Cooking carotenoid-containing vegetables in oil and shredding the vegetable both increase carotenoid bioavailability. There are over 1,100 known c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rhizopus
''Rhizopus'' is a genus of common saprophytic fungi on plants and specialized parasites on animals. They are found in a wide variety of organic substances, including "mature fruits and vegetables", jellies, syrups, leather, bread, peanuts, and tobacco. They are multicellular. Some ''Rhizopus'' species are opportunistic human pathogens that often cause fatal disease called mucormycosis. This widespread genus includes at least eight species. ''Rhizopus'' species grow as filamentous, branching hyphae that generally lack cross-walls (i.e., they are coenocytic). They reproduce by forming asexual and sexual spores. In asexual reproduction, sporangiospores are produced inside a spherical structure, the sporangium. Sporangia are supported by a large apophysate columella atop a long stalk, the sporangiophore. Sporangiophores arise among distinctive, root-like rhizoids. In sexual reproduction, a dark zygospore is produced at the point where two compatible mycelia fuse. Upon germination, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
High-mobility Group
High-Mobility Group or HMG is a group of chromosomal proteins that are involved in the regulation of DNA-dependent processes such as transcription, replication, recombination, and DNA repair. Families The HMG proteins are subdivided into 3 superfamilies each containing a characteristic functional domain: * HMGA – contains an AT-hook domain ** HMGA1 ** HMGA2 * HMGB – contains a HMG-box domain ** HMGB1 ** HMGB2 ** HMGB3 ** HMGB4 * HMGN – contains a nucleosomal binding domain ** HMGN1 ** HMGN2 ** HMGN3 ** HMGN4 ** HMGN5 Proteins containing any of these embedded in their sequence are known as HMG motif proteins. HMG-box proteins are found in a variety of eukaryotic organisms. They were originally isolated from mammalian cells, and named according to their electrophoretic mobility in polyacrylamide gels. Other families with HMG-box domain * SOX gene family ** Sex-Determining Region Y Protein ** SOX1, SOX2, etc. * TCF/LEF family (T cell factor/lymphoid enhancer factor fa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ascomycota
Ascomycota is a phylum of the kingdom Fungi that, together with the Basidiomycota, forms the subkingdom Dikarya. Its members are commonly known as the sac fungi or ascomycetes. It is the largest phylum of Fungi, with over 64,000 species. The defining feature of this fungal group is the " ascus" (), a microscopic sexual structure in which nonmotile spores, called ascospores, are formed. However, some species of the Ascomycota are asexual, meaning that they do not have a sexual cycle and thus do not form asci or ascospores. Familiar examples of sac fungi include morels, truffles, brewers' and bakers' yeast, dead man's fingers, and cup fungi. The fungal symbionts in the majority of lichens (loosely termed "ascolichens") such as ''Cladonia'' belong to the Ascomycota. Ascomycota is a monophyletic group (it contains all descendants of one common ancestor). Previously placed in the Deuteromycota along with asexual species from other fungal taxa, asexual (or anamorphic) ascomyce ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mushroom
A mushroom or toadstool is the fleshy, spore-bearing fruiting body of a fungus, typically produced above ground, on soil, or on its food source. ''Toadstool'' generally denotes one poisonous to humans. The standard for the name "mushroom" is the cultivated white button mushroom, ''Agaricus bisporus''; hence the word "mushroom" is most often applied to those fungi ( Basidiomycota, Agaricomycetes) that have a stem ( stipe), a cap ( pileus), and gills (lamellae, sing. lamella) on the underside of the cap. "Mushroom" also describes a variety of other gilled fungi, with or without stems, therefore the term is used to describe the fleshy fruiting bodies of some Ascomycota. These gills produce microscopic spores that help the fungus spread across the ground or its occupant surface. Forms deviating from the standard morphology usually have more specific names, such as "bolete", "puffball", "stinkhorn", and " morel", and gilled mushrooms themselves are often called "agarics" in refere ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Necrotroph
A fungus ( : fungi or funguses) is any member of the group of eukaryotic organisms that includes microorganisms such as yeasts and molds, as well as the more familiar mushrooms. These organisms are classified as a kingdom, separately from the other eukaryotic kingdoms, which by one traditional classification include Plantae, Animalia, Protozoa, and Chromista. A characteristic that places fungi in a different kingdom from plants, bacteria, and some protists is chitin in their cell walls. Fungi, like animals, are heterotrophs; they acquire their food by absorbing dissolved molecules, typically by secreting digestive enzymes into their environment. Fungi do not photosynthesize. Growth is their means of mobility, except for spores (a few of which are flagellated), which may travel through the air or water. Fungi are the principal decomposers in ecological systems. These and other differences place fungi in a single group of related organisms, named the ''Eumycota'' (''true fun ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Christian Gottfried Ehrenberg
Christian Gottfried Ehrenberg (19 April 1795 – 27 June 1876) was a German naturalist, zoologist, comparative anatomist, geologist, and microscopist. Ehrenberg was an evangelist and was considered to be of the most famous and productive scientists of his time. Early collections The son of a judge, Christian Gottfried Ehrenberg was born in Delitzsch, near Leipzig. He first studied theology at the University of Leipzig, then medicine and natural sciences in Berlin and became a friend of the famous explorer Alexander von Humboldt. In 1818, he completed his doctoral dissertation on fungi, ''Sylvae mycologicae Berolinenses.'' In 1820–1825, on a scientific expedition to the Middle East with his friend Wilhelm Hemprich, he collected thousands of specimens of plants and animals. He investigated parts of Egypt, the Libyan Desert, the Nile valley and the northern coasts of the Red Sea, where he made a special study of the corals. Subsequently, parts of Syria, Arabia and Abyss ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Phototropism
Phototropism is the growth of an organism in response to a light stimulus. Phototropism is most often observed in plants, but can also occur in other organisms such as fungi. The cells on the plant that are farthest from the light contain a hormone called auxin that reacts when phototropism occurs. This causes the plant to have elongated cells on the furthest side from the light. Phototropism is one of the many plant tropisms or movements which respond to external stimuli. Growth towards a light source is called positive phototropism, while growth away from light is called negative phototropism. Negative phototropism is not to be confused with skototropism which is defined as the growth towards darkness, whereas negative phototropism can refer to either the growth away from a light source or towards the darkness. Most plant shoots exhibit positive phototropism, and rearrange their chloroplasts in the leaves to maximize photosynthetic energy and promote growth.Goyal, A., Szarzyns ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Monotypic Taxon
In biology, a monotypic taxon is a taxonomic group (taxon) that contains only one immediately subordinate taxon. A monotypic species is one that does not include subspecies or smaller, infraspecific taxa. In the case of genera, the term "unispecific" or "monospecific" is sometimes preferred. In botanical nomenclature, a monotypic genus is a genus in the special case where a genus and a single species are simultaneously described. In contrast, an oligotypic taxon contains more than one but only a very few subordinate taxa. Examples Just as the term ''monotypic'' is used to describe a taxon including only one subdivision, the contained taxon can also be referred to as monotypic within the higher-level taxon, e.g. a genus monotypic within a family. Some examples of monotypic groups are: Plants * In the order Amborellales, there is only one family, Amborellaceae and there is only one genus, '' Amborella'', and in this genus there is only one species, namely ''Amborella trichopoda ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Zygospore
A zygospore is a diploid reproductive stage in the life cycle of many fungi and protists. Zygospores are created by the nuclear fusion of haploid cells. In fungi, zygospores are formed in zygosporangia after the fusion of specialized budding structures, from mycelia of the same (in homothallic fungi) or different mating types (in heterothallic fungi), and may be chlamydospores. In many eukaryotic algae, including many species of the Chlorophyta, zygospores are formed by the fusion of unicellular gametes of different mating types. A zygospore remains dormant while it waits for environmental cues, such as light, moisture, heat, or chemicals secreted by plants. When the environment is favorable, the zygospore germinates, meiosis occurs, and haploid vegetative cells are released. In fungi, a sporangium is produced at the end of a sporangiophore that sheds spores. A fungus that forms zygospores is called a zygomycete, indicating that the class Class or The Class may refer to: Com ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |


.jpg)