|
System Volume Information
System Restore is a feature in Microsoft Windows that allows the user to revert their computer's state (including system files, installed applications, Windows Registry, and system settings) to that of a previous point in time, which can be used to recover from system malfunctions or other problems. First included in Windows Me, it has been included in all following desktop versions of Windows released since, excluding Windows Server. In Windows 10, System Restore is turned off by default and must be enabled by users in order to function. This does not affect personal files such as documents, music, pictures, and videos. In prior Windows versions it was based on a file filter that watched changes for a certain set of file extensions, and then copied files before they were overwritten. An updated version of System Restore introduced by Windows Vista uses the Shadow Copy service as a backend (allowing block-level changes in files located in any directory on the volume to be monit ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Windows 10
Windows 10 is a major release of Microsoft's Windows NT operating system. It is the direct successor to Windows 8.1, which was released nearly two years earlier. It was released to manufacturing on July 15, 2015, and later to retail on July 29, 2015. Windows 10 was made available for download via MSDN and TechNet, as a free upgrade for retail copies of Windows 8 and Windows 8.1 users via the Windows Store, and to Windows 7 users via Windows Update. Windows 10 receives new builds on an ongoing basis, which are available at no additional cost to users, in addition to additional test builds of Windows 10, which are available to Windows Insiders. Devices in enterprise environments can receive these updates at a slower pace, or use long-term support milestones that only receive critical updates, such as security patches, over their ten-year lifespan of extended support. In June 2021, Microsoft announced that support for Windows 10 editions which are not in the Long-Term Se ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
NTFS
New Technology File System (NTFS) is a proprietary journaling file system developed by Microsoft. Starting with Windows NT 3.1, it is the default file system of the Windows NT family. It superseded File Allocation Table (FAT) as the preferred filesystem on Windows and is supported in Linux and BSD as well. NTFS reading and writing support is provided using a free and open-source kernel implementation known as NTFS3 in Linux and the NTFS-3G driver in BSD. By using the convert command, Windows can convert FAT32/16/12 into NTFS without the need to rewrite all files. NTFS uses several files typically hidden from the user to store metadata about other files stored on the drive which can help improve speed and performance when reading data. Unlike FAT and High Performance File System (HPFS), NTFS supports access control lists (ACLs), filesystem encryption, transparent compression, sparse files and file system journaling. NTFS also supports shadow copy to allow backups of a system ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Microsoft Desktop Optimization Pack
Microsoft Desktop Optimization Pack (MDOP) is a suite of utilities for Microsoft Windows customers who have subscribed to Microsoft Software Assurance program. It aims at bringing easier manageability and monitoring of enterprise desktops, emergency recovery, desktop virtualization and application virtualization. Components The MDOP suite is grouped into 3 overall technologies: Virtualize, Manage and Restore Virtualize Microsoft App-V, Microsoft Application Virtualization (App-V) :An application virtualization and application streaming platform that allows clients to run applications locally via on demand streaming from a centralized server. This makes sure that all clients run the application with the same configuration. App-V also allows standalone virtualized applications to run locally on the client. Starting with Windows 10 Anniversary Update, this item became part of Windows 10 and is no longer included in MDOP. Microsoft User Experience Virtualization (UE-V) :A ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
FAT32
File Allocation Table (FAT) is a file system developed for personal computers. Originally developed in 1977 for use on floppy disks, it was adapted for use on hard disks and other devices. It is often supported for compatibility reasons by current operating systems for personal computers and many mobile devices and embedded systems, allowing interchange of data between disparate systems. The increase in disk drives capacity required three major variants: FAT12, FAT16 and FAT32. The FAT standard has also been expanded in other ways while generally preserving backward compatibility with existing software. FAT is no longer the default file system for Microsoft Windows computers. FAT file systems are still commonly found on floppy disks, flash and other solid-state memory cards and modules (including USB flash drives), as well as many portable and embedded devices. FAT is the standard file system for digital cameras per the DCF specification. Overview Concepts ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
My Documents
My Documents is the commonly recognized name of a special folder in Microsoft Windows (starting with Windows Vista, it is called Documents only, and the actual name of the folder might be different when the language of the installed copy of Windows is not English). The folder functions both as an area for the user to store their personal data and as a repository for application data, such as configuration files and saved games. Until Windows XP, it contained other subfolders such as "My Pictures", "My Music" and "My Videos". Starting with Windows Vista, these subfolders are now located alongside "Documents" in each user account's folder. Overview Microsoft first introduced the "My Documents" folder in Windows 95 OEM Service Release 2 as a standard location for storing user-created files. In this version of Windows, the folder is located under the root directory of the boot volume (i.e., if Windows is installed to drive C:, then My Documents will be located at the root of C: ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
E-mail
Electronic mail (email or e-mail) is a method of exchanging messages ("mail") between people using electronic devices. Email was thus conceived as the electronic ( digital) version of, or counterpart to, mail, at a time when "mail" meant only physical mail (hence '' e- + mail''). Email later became a ubiquitous (very widely used) communication medium, to the point that in current use, an email address is often treated as a basic and necessary part of many processes in business, commerce, government, education, entertainment, and other spheres of daily life in most countries. ''Email'' is the medium, and each message sent therewith is also called an ''email.'' The term is a mass noun. Email operates across computer networks, primarily the Internet, and also local area networks. Today's email systems are based on a store-and-forward model. Email servers accept, forward, deliver, and store messages. Neither the users nor their computers are required to be online simult ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
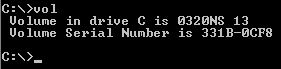
Volume (computing)
In computer data storage, a volume or logical drive is a single accessible storage area with a single file system, typically (though not necessarily) resident on a single partition of a hard disk. Although a volume might be different from a physical disk drive, it can still be accessed with an operating system's logical interface. However, a volume differs from a partition. Differences from partition A volume is not the same thing as a partition. For example, a floppy disk might be accessible as a volume, even though it does not contain a partition, as floppy disks cannot be partitioned with most modern computer software. Also, an OS can recognize a partition without recognizing any volume associated with it, as when the OS cannot interpret the filesystem stored there. This situation occurs, for example, when Windows NT-based OSes encounter disks with non-Microsoft OS partitions, such as the ext3 filesystem commonly used with Linux. Another example occurs in the Intel world wit ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Windows 7
Windows 7 is a major release of the Windows NT operating system developed by Microsoft. It was released to manufacturing on July 22, 2009, and became generally available on October 22, 2009. It is the successor to Windows Vista, released nearly three years earlier. It remained an operating system for use on personal computers, including home and business desktops, laptops, tablet PCs and media center PCs, and itself was replaced in November 2012 by Windows 8, the name spanning more than three years of the product. Until April 9, 2013, Windows 7 original release included updates and technical support, after which installation of Service Pack 1 was required for users to receive support and updates. Windows 7's server counterpart, Windows Server 2008 R2, was released at the same time. The last supported version of Windows based on this operating system was released on July 1, 2011, entitled Windows Embedded POSReady 7. Extended support ended on January 14, 2020, over ten years a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
FIFO (computing And Electronics)
Representation of a FIFO queue In computing and in systems theory, FIFO is an acronym for first in, first out (the first in is the first out), a method for organizing the manipulation of a data structure (often, specifically a data buffer) where the oldest (first) entry, or "head" of the queue, is processed first. Such processing is analogous to servicing people in a queue area on a first-come, first-served (FCFS) basis, i.e. in the same sequence in which they arrive at the queue's tail. FCFS is also the jargon term for the FIFO operating system scheduling algorithm, which gives every process central processing unit (CPU) time in the order in which it is demanded. FIFO's opposite is LIFO, last-in-first-out, where the youngest entry or "top of the stack" is processed first. A priority queue is neither FIFO or LIFO but may adopt similar behaviour temporarily or by default. Queueing theory encompasses these methods for processing data structures, as well as interactions between s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hidden Folder
In computing, a hidden folder (sometimes hidden directory) or hidden file is a folder or file which filesystem utilities do not display by default when showing a directory listing. They are commonly used for storing user preferences or preserving the state of a utility and are frequently created implicitly by using various utilities. They are not a security mechanism because access is not restricted – usually the intent is simply to not "clutter" the display of the contents of a directory listing with files the user did not directly create. Unix and Unix-like environments In Unix-like operating systems, any file or folder that starts with a dot character (for example, ), commonly called a dot file or dotfile, is to be treated as hidden – that is, the ls command does not display them unless the -a or -A flags (ls -a or ls -A) are used. In most command-line shells, wildcards will not match files whose names start with . unless the wildcard itself starts with an explicit . ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |