|
Syringohydromyelia
Syringomyelia is a generic term referring to a disorder in which a cyst or cavity forms within the spinal cord. Often, syringomyelia is used as a generic term before an etiology is determined. This cyst, called a syrinx, can expand and elongate over time, destroying the spinal cord. The damage may result in loss of feeling, paralysis, weakness, and stiffness in the back, shoulders, and extremities. Syringomyelia may also cause a loss of the ability to feel extremes of hot or cold, especially in the hands. It may also lead to a cape-like bilateral loss of pain and temperature sensation along the upper chest and arms. The combination of symptoms varies from one patient to another depending on the location of the syrinx within the spinal cord, as well as its extent. Syringomyelia has a prevalence estimated at 8.4 cases per 100,000 people, with symptoms usually beginning in young adulthood. Signs of the disorder tend to develop slowly, although sudden onset may occur with coughing, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Arnold–Chiari Malformation
Chiari malformation (CM) is a structural defect in the cerebellum, characterized by a downward displacement of one or both cerebellar tonsils through the foramen magnum (the opening at the base of the skull). CMs can cause headaches, difficulty swallowing, vomiting, dizziness, neck pain, unsteady gait, poor hand coordination, numbness and tingling of the hands and feet, and speech problems. Less often, people may experience ringing or buzzing in the ears, weakness, slow heart rhythm, or fast heart rhythm, curvature of the spine (scoliosis) related to spinal cord impairment, abnormal breathing, such as central sleep apnea, characterized by periods of breathing cessation during sleep, and, in severe cases, paralysis. This can sometimes lead to non-communicating hydrocephalus as a result of obstruction of cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) outflow. The cerebrospinal fluid outflow is caused by phase difference in outflow and influx of blood in the vasculature of the brain. The malformation ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
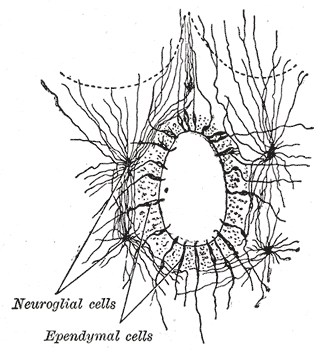
Central Canal
The central canal (also known as spinal foramen or ependymal canal) is the cerebrospinal fluid-filled space that runs through the spinal cord. The central canal lies below and is connected to the ventricular system of the brain, from which it receives cerebrospinal fluid, and shares the same ependymal lining. The central canal helps to transport nutrients to the spinal cord as well as protect it by cushioning the impact of a force when the spine is affected. The central canal represents the adult remainder of the central cavity of the neural tube. It generally occludes (closes off) with age. Structure The central canal below at the ventricular system of the brain, beginning at a region called the obex where the fourth ventricle, a cavity present in the brainstem, narrows. The central canal is located in the third of the spinal cord in the cervical and thoracic regions. In the lumbar spine it enlarges and is located more centrally. At the conus medullaris, where the spinal co ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lexico
Lexico was a dictionary website that provided a collection of English and Spanish dictionaries produced by Oxford University Press (OUP), the publishing house of the University of Oxford. While the dictionary content on Lexico came from OUP, this website was operated by Dictionary.com, whose eponymous website hosts dictionaries by other publishers such as Random House. The website was closed and redirected to Dictionary.com on 26 August 2022. Before the Lexico site was launched, the '' Oxford Dictionary of English'' and ''New Oxford American Dictionary'' were hosted by OUP's own website Oxford Dictionaries Online (ODO), later known as Oxford Living Dictionaries. The dictionaries' definitions have also appeared in Google definition search and the Dictionary application on macOS, among others, licensed through the Oxford Dictionaries API. History In the 2000s, OUP allowed access to content of the ''Compact Oxford English Dictionary of Current English'' on a website called AskOx ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Neuropathic Arthropathy
Neuropathic arthropathy (or neuropathic osteoarthropathy), also known as Charcot joint (often Charcot foot) after the first to describe it, Jean-Martin Charcot, refers to progressive degeneration of a weight-bearing joint, a process marked by bony destruction, bone resorption, and eventual deformity due to loss of sensation. Onset is usually insidious. If this pathological process continues unchecked, it can result in joint deformity, ulceration and/or superinfection, loss of function, and in the worst-case scenario, amputation or death. Early identification of joint changes is the best way to limit morbidity. Symptoms and signs The clinical presentation varies depending on the stage of the disease from mild swelling to severe swelling and moderate deformity. Inflammation, erythema, pain and increased skin temperature (3–7 degrees Celsius) around the joint may be noticeable on examination. X-rays may reveal bone resorption and degenerative changes in the joint. These finding ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Human Brain
The human brain is the central organ of the human nervous system, and with the spinal cord makes up the central nervous system. The brain consists of the cerebrum, the brainstem and the cerebellum. It controls most of the activities of the body, processing, integrating, and coordinating the information it receives from the sense organs, and making decisions as to the instructions sent to the rest of the body. The brain is contained in, and protected by, the skull bones of the head. The cerebrum, the largest part of the human brain, consists of two cerebral hemispheres. Each hemisphere has an inner core composed of white matter, and an outer surface – the cerebral cortex – composed of grey matter. The cortex has an outer layer, the neocortex, and an inner allocortex. The neocortex is made up of six neuronal layers, while the allocortex has three or four. Each hemisphere is conventionally divided into four lobes – the frontal, temporal, parietal, and occipital lo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tumor
A neoplasm () is a type of abnormal and excessive growth of tissue. The process that occurs to form or produce a neoplasm is called neoplasia. The growth of a neoplasm is uncoordinated with that of the normal surrounding tissue, and persists in growing abnormally, even if the original trigger is removed. This abnormal growth usually forms a mass, when it may be called a tumor. ICD-10 classifies neoplasms into four main groups: benign neoplasms, in situ neoplasms, malignant neoplasms, and neoplasms of uncertain or unknown behavior. Malignant neoplasms are also simply known as cancers and are the focus of oncology. Prior to the abnormal growth of tissue, as neoplasia, cells often undergo an abnormal pattern of growth, such as metaplasia or dysplasia. However, metaplasia or dysplasia does not always progress to neoplasia and can occur in other conditions as well. The word is from Ancient Greek 'new' and 'formation, creation'. Types A neoplasm can be benign, potentially m ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hemorrhage
Bleeding, hemorrhage, haemorrhage or blood loss, is blood escaping from the circulatory system from damaged blood vessels. Bleeding can occur internally, or externally either through a natural opening such as the mouth, nose, ear, urethra, vagina or anus, or through a puncture in the skin. Hypovolemia is a massive decrease in blood volume, and death by excessive loss of blood is referred to as exsanguination. Typically, a healthy person can endure a loss of 10–15% of the total blood volume without serious medical difficulties (by comparison, blood donation typically takes 8–10% of the donor's blood volume). The stopping or controlling of bleeding is called hemostasis and is an important part of both first aid and surgery. Types * Upper head ** Intracranial hemorrhage – bleeding in the skull. ** Cerebral hemorrhage – a type of intracranial hemorrhage, bleeding within the brain tissue itself. ** Intracerebral hemorrhage – bleeding in the brain caused by the ruptu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Meningitis
Meningitis is acute or chronic inflammation of the protective membranes covering the brain and spinal cord, collectively called the meninges. The most common symptoms are fever, headache, and neck stiffness. Other symptoms include confusion or altered consciousness, nausea, vomiting, and an inability to tolerate light or loud noises. Young children often exhibit only nonspecific symptoms, such as irritability, drowsiness, or poor feeding. A non-blanching rash (a rash that does not fade when a glass is rolled over it) may also be present. The inflammation may be caused by infection with viruses, bacteria or other microorganisms. Non-infectious causes include malignancy (cancer), subarachnoid haemorrhage, chronic inflammatory disease (sarcoidosis) and certain drugs. Meningitis can be life-threatening because of the inflammation's proximity to the brain and spinal cord; therefore, the condition is classified as a medical emergency. A lumbar puncture, in which a needle is inserte ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Physical Trauma
An injury is any physiological damage to living tissue caused by immediate physical stress. An injury can occur intentionally or unintentionally and may be caused by blunt trauma, penetrating trauma, burning, toxic exposure, asphyxiation, or overexertion. Injuries can occur in any part of the body, and different symptoms are associated with different injuries. Treatment of a major injury is typically carried out by a health professional and varies greatly depending on the nature of the injury. Traffic collisions are the most common cause of accidental injury and injury-related death among humans. Injuries are distinct from chronic conditions, psychological trauma, infections, or medical procedures, though injury can be a contributing factor to any of these. Several major health organizations have established systems for the classification and description of human injuries. Occurrence Injuries may be intentional or unintentional. Intentional injuries may be acts o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
GeneCards
GeneCards is a database of human genes that provides genomic, proteomic, transcriptomic, genetic and functional information on all known and predicted human genes. It is being developed and maintained by the Crown Human Genome Center at the Weizmann Institute of Science. The database aims at providing a quick overview of the current available biomedical information about the searched gene, including the human genes, the encoded proteins, and the relevant diseases. The GeneCards database provides access to free Web resources about more than 7000 all known human genes that integrated from >90 data resources, such as HGNC, Ensembl, and NCBI. The core gene list is based on approved gene symbols published by the HUGO Gene Nomenclature Committee (HGNC). The information is carefully gathered and selected from these databases by its engine. If the search does not return any results, this database will give several suggestions to help users accomplish their search depending on the typ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
WebMD
WebMD is an American corporation known primarily as an online publisher of news and information pertaining to human health and well-being. The site includes information pertaining to drugs. It is one of the top healthcare websites. It was founded in 1998 by internet entrepreneur Jeff Arnold. In early 1999, it was part of a three way merger with Sapient Health Network (SHN) and Direct Medical Knowledge (DMK). SHN began in Portland, Oregon, in 1996 by Jim Kean, Bill Kelly, and Kris Nybakken, who worked together at a CD-ROM publishing firm, Creative Multimedia. Later in 1999, WebMD merged with Healtheon, founded by Netscape Communications founder James H. Clark. Traffic During March 2020, WebMD's network of websites reached more unique visitors each month than any other leading private or government healthcare website, making it the leading health publisher in the United States. In the fourth quarter of 2016, WebMD recorded an average of 179.5 million unique users per month, and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Arachnoiditis
Arachnoiditis is an inflammatory condition of the arachnoid mater or 'arachnoid', one of the membranes known as meninges that surround and protect the nerves of the central nervous system, including the brain and spinal cord. The arachnoid can become inflamed because of adverse reactions to chemicals, infection from bacteria or viruses, as the result of direct injury to the spine, chronic compression of spinal nerves, complications from spinal surgery or other invasive spinal procedures, or the accidental intrathecal injection of steroids intended for the epidural space. Inflammation can sometimes lead to the formation of scar tissue and adhesion that can make the spinal nerves "stick" together,NINDS Arachnoiditis Information Page |