|
Syrian Wars
The Syrian Wars were a series of six wars between the Seleucid Empire and the Ptolemaic Kingdom of Egypt, successor states to Alexander the Great's empire, during the 3rd and 2nd centuries BC over the region then called Coele-Syria, one of the few avenues into Egypt. These conflicts drained the material and manpower of both parties and led to their eventual destruction and conquest by Rome and Parthia. They are briefly mentioned in the biblical Books of the Maccabees. Background In the Wars of the Diadochi following Alexander's death, Coele-Syria initially came under the rule of Antigonus I Monophthalmus. In 301 BC Ptolemy I Soter, who four years earlier had crowned himself King of Egypt, exploited events surrounding the Battle of Ipsus to take control of the region. The victors at Ipsus, however, had allocated Coele-Syria to Ptolemy's former ally Seleucus I Nicator, founder of the Seleucid Empire. Seleucus, who had been aided by Ptolemy during his ascent to power, did ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Antiochus IV Epiphanes
Antiochus IV Epiphanes ( 215 BC–November/December 164 BC) was king of the Seleucid Empire from 175 BC until his death in 164 BC. Notable events during Antiochus' reign include his near-conquest of Ptolemaic Egypt, his persecution of the Jews of Judea and Samaria, and the Maccabean Revolt, rebellion of the Jewish Maccabees. The son of List of Seleucid rulers, King Antiochus III the Great, Antiochus IV accession to the throne was controversial, as he was seen as a usurper by some. After the death of his brother Seleucus IV Philopator in 175 BC, the "true" heir should have been Seleucus's son Demetrius I Soter, Demetrius I. However, Demetrius I was very young and a hostage in Rome at the time, and Antiochus seized the opportunity to declare himself king instead, successfully rallying enough of the Greek ruling class in Antioch to support his claim. This helped set a destabilizing trend in the Seleucid Empire in subsequent generations, as an increasing number of claimants tried to u ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
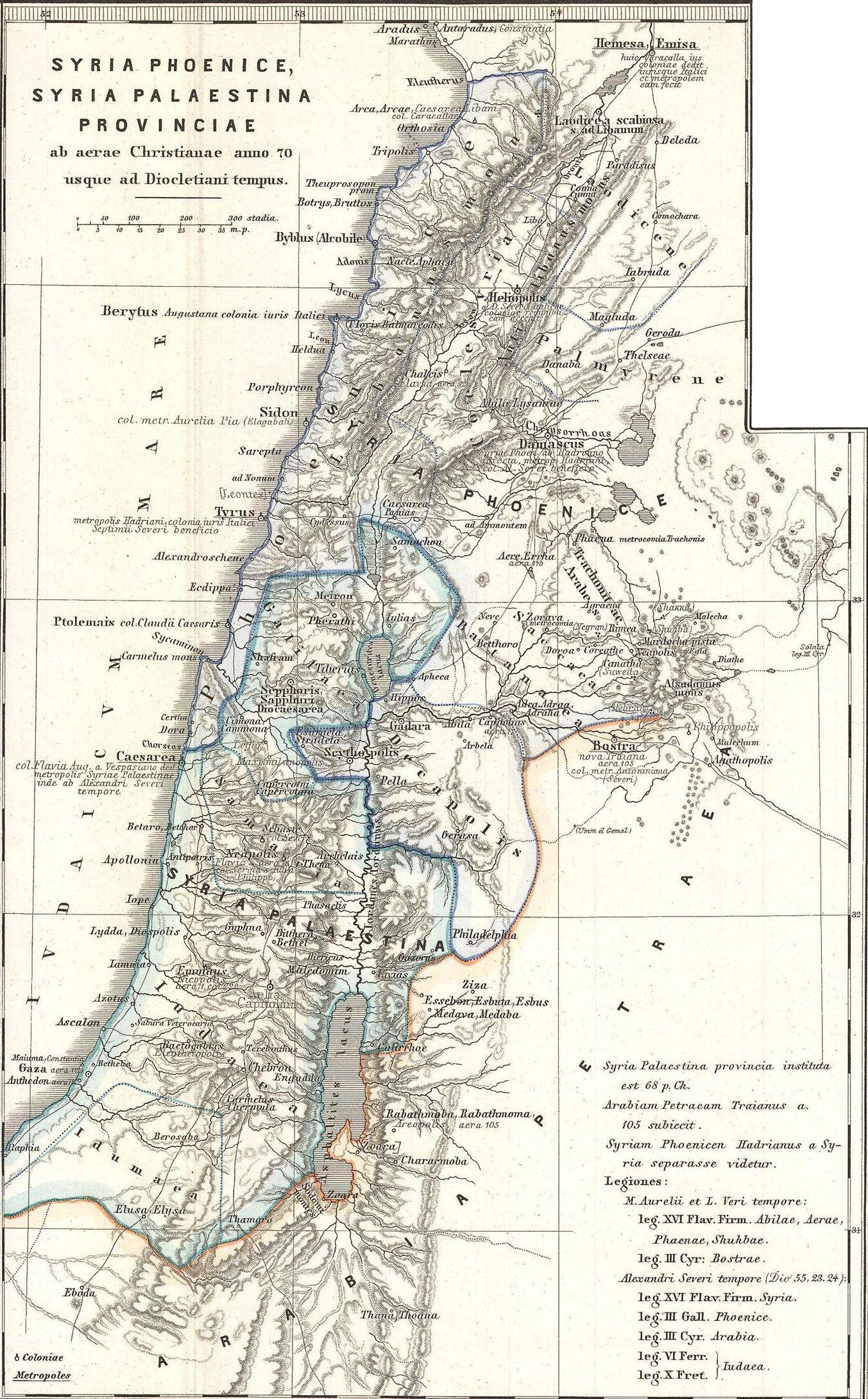
Coele-Syria
Coele-Syria () was a region of Syria in classical antiquity. The term originally referred to the "hollow" Beqaa Valley between the Lebanon and the Anti-Lebanon mountain ranges, but sometimes it was applied to a broader area of the region of Syria. The area is now part of modern-day Syria and Lebanon. Name It is widely accepted that the term Coele is a transcription of Aramaic ܟܠ ''kul'' , such that the term originally identified ''all'' of Syria.A History of the Jews and Judaism in the Second Temple Period, Volume 2, Lester L. Grabbe, p173 "Yet the suggestion is widely accepted that the name actually derives from Aramaic for "all Syria", which was then assimilated by the Greeks to a more usual pattern for place names" The word "Coele", with ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cleopatra II
Cleopatra II Philometor Soteira (Greek: Κλεοπάτρα Φιλομήτωρ Σώτειρα, ''Kleopatra Philomētōr Sōteira''; c. 185 BC – 116/115 BC) was Queen consort of Ptolemaic Egypt from 175 to 170 BC as wife of Ptolemy VI Philometor, and then Queen regnant since 170 BC as co-ruler with her two successive brother-husbands, her daughter, and her grandson. She co-ruled during her first reign since 170 until 164 BC, with Ptolemy VI Philometor, her first husband and the older of her brothers, and Ptolemy VIII Euergetes II, her younger brother. During her second reign she co-ruled again with Ptolemy VI from 163 BC until his death in 145 BC. She then ruled with her younger brother, Ptolemy VIII, whom she married, and her daughter Cleopatra III. She was sole ruler of Egypt from 131 BC to 127 BC. Her final reign from 124 BC to 116/5 BC was also spent in coregency with Ptolemy VIII and Cleopatra III. She was the first Ptolemaic queen known for certain to rule in he ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Seleucus I Nicator
Seleucus I Nicator (; Ancient Greek, Greek: Σέλευκος Νικάτωρ, ''Séleukos Nikátōr'', "Seleucus the Victorious"; ) was a Ancient Macedonians, Macedonian Greek general, officer and successor of Alexander the Great who went on to found the eponymous Seleucid Empire, led by the Seleucid dynasty. Initially a secondary player in the power struggles following Alexander's death, Seleucus rose to become the total ruler of Asia Minor, Syria (region), Syria, Mesopotamia, and the Iranian plateau, assuming the title of ''basileus'' (king). The Seleucid Empire was one of the major powers of the Hellenistic period, Hellenistic world, until it was overcome by the Roman Republic and Parthian Empire in the late second and early first centuries BC. While serving under Alexander, Seleucus was commander of the ''Hypaspists, Hypaspistai,'' an elite Macedonian infantry unit. After the death of Alexander in June 323 BC, Seleucus initially supported Perdiccas, the regent of Alexander's em ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Battle Of Ipsus
The Battle of Ipsus () was fought between some of the Diadochi (the successors of Alexander the Great) in 301 BC near the town of Ipsus in Phrygia. Antigonus I Monophthalmus, the Macedonian ruler of large parts of Asia, and his son Demetrius were pitted against the coalition of three other successors of Alexander: Cassander, ruler of Macedon; Lysimachus, ruler of Thrace; and Seleucus I Nicator, ruler of Babylonia and Persia. Sources Diodorus Siculus is the principal source for the history of the Diadochi, in his 'Library of history' (''Bibliotheca historica''). Diodorus is often derided by modern historians for his style and inaccuracies, but he preserves many details of the ancient period found nowhere else. Diodorus worked primarily by epitomizing the works of other historians, omitting many details where they did not suit his purpose, which was to illustrate moral lessons from history.Buckler, p. ''xiv''. However, since Diodorus provides the only continuous narrative for the h ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ptolemy I Soter
Ptolemy I Soter (; , ''Ptolemaîos Sōtḗr'', "Ptolemy the Savior"; 367 BC – January 282 BC) was a Macedonian Greek general, historian, and successor of Alexander the Great who went on to found the Ptolemaic Kingdom centered on Egypt. Ptolemy was ''basileus'' and pharaoh of Ptolemaic Egypt from 305/304 BC to his death in 282 BC, and his descendants continued to rule Egypt until 30 BC. During their rule, Egypt became a thriving bastion of Hellenistic civilization and Alexandria a great seat of Greek culture. Ptolemy I was the son of Arsinoe of Macedon by either her husband Lagus or Philip II of Macedon, the father of Alexander. However, the latter is unlikely and may be a myth fabricated to glorify the Ptolemaic Dynasty. Ptolemy was one of Alexander's most trusted companions and military officers. After the death of Alexander in 323 BC, Ptolemy retrieved his body as it was en route to be buried in Macedon, placing it in Memphis instead, where it was later moved to Al ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Antigonus I Monophthalmus
Antigonus I Monophthalmus ( , "Antigonus the One-Eyed"; 382 – 301 BC) was a Ancient Macedonians, Macedonian Greek general and Diadochi, successor of Alexander the Great. A prominent military leader in Alexander's army, he went on to control large parts of Empire of Alexander the Great, Alexander's former empire. He assumed the title of ''basileus'' (king) in 306 BC and reigned until his death. He was the founder of the Antigonid dynasty, which ruled over Macedonia until its conquest by the Roman Republic in 168 BC. Antigonus likely served under Philip II of Macedon. He took part in Alexander's Wars of Alexander the Great, invasion of Achaemenid Persia and was named satrap of Phrygia. After Alexander's death in 323 BC, he also received Pamphylia and Lycia in accordance with the Partition of Babylon. However, he later incurred the enmity of Perdiccas, the regent of Alexander's empire, and was driven from Phrygia. He fled to Greece and formed an alliance with Antipater, later joine ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Books Of The Maccabees
The Books of the Maccabees or the Sefer HaMakabim (the ''Book of the Maccabees'') recount the history of the Maccabees, the leaders of the Jewish rebellion against the Seleucid dynasty. List of books The Books of the Maccabees refers to canonical and deutero canonical books of the Bible: * 1 Maccabees, originally written in Hebrew and only surviving in a Greek translation, it contains an account of the history of the Maccabees from 175 BC until 134 BC. * 2 Maccabees, Jason of Cyrene's Greek abridgment of an earlier history which was written in Hebrew, recounts the history of the Maccabees from 176 BC until 161 BC. It focuses on Judas Maccabeus, and it also describes prayers for the dead and offerings. * 3 Maccabees, a Greek narrative that contains an account of Egyptian Jews being delivered from their impending martyrdom at the hands of Ptolemy IV Philopator in the 3rd century BC. * 4 Maccabees, a Greek philosophic discourse that praises the supremacy of reason over passion, usi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Parthia
Parthia ( ''Parθava''; ''Parθaw''; ''Pahlaw'') is a historical region located in northeastern Greater Iran. It was conquered and subjugated by the empire of the Medes during the 7th century BC, was incorporated into the subsequent Achaemenid Empire under Cyrus the Great in the 6th century BC, and formed part of the Hellenistic Seleucid Empire after the Wars of Alexander the Great, 4th-century BC conquests of Alexander the Great. The region later served as the political and cultural base of the Eastern Iranian languages, Eastern Iranian Parni people and Arsacid dynasty, rulers of the Parthian Empire (247 BC – 224 AD). The Sasanian Empire, the last state of History of Iran, pre-Islamic Iran, also held the region and maintained the Seven Great Houses of Iran, seven Parthian clans as part of their feudal aristocracy. Name The name "Parthia" is a continuation from Latin language, Latin ', from Old Persian ', which was the Parthian language self-designator signifying "of the Pa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Alexander The Great
Alexander III of Macedon (; 20/21 July 356 BC – 10/11 June 323 BC), most commonly known as Alexander the Great, was a king of the Ancient Greece, ancient Greek kingdom of Macedonia (ancient kingdom), Macedon. He succeeded his father Philip II of Macedon, Philip II to the throne in 336 BC at the age of 20 and spent most of his ruling years conducting Wars of Alexander the Great, a lengthy military campaign throughout West Asia, Western Asia, Central Asia, parts of South Asia, and ancient Egypt, Egypt. By the age of 30, he had created one of the List of largest empires, largest empires in history, stretching from History of Greece, Greece to northwestern History of India, India. He was undefeated in battle and is widely considered to be one of history's greatest and most successful military commanders. Until the age of 16, Alexander was tutored by Aristotle. In 335 BC, shortly after his assumption of kingship over Macedon, he Alexander's Balkan campaign, campaigned in the Bal ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Diadochi
The Diadochi were the rival generals, families, and friends of Alexander the Great who fought for control over his empire after his death in 323 BC. The Wars of the Diadochi mark the beginning of the Hellenistic period from the Mediterranean Sea to the Indus River Valley. The most notable Diadochi include Ptolemy I Soter, Ptolemy, Antigonus I Monophthalmus, Antigonus, Cassander, and Seleucus I Nicator, Seleucus as the last remaining at the end of the Wars of the Diadochi, Wars of the Successors, ruling in Egypt, Anatolia, Asia-Minor, Macedonia (ancient kingdom), Macedon and Achaemenid Empire, Persia respectively, all forging dynasties lasting several centuries. Background Ancient role In ancient Greek, is a noun (substantive or adjective) formed from the verb, ''diadechesthai'', "succeed to," a compound of ''dia-'' and ''dechesthai'', "receive." The word-set descends straightforwardly from Proto-Indo-European language, Indo-European *dek-, "receive", the substantive ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Roman Republic
The Roman Republic ( ) was the era of Ancient Rome, classical Roman civilisation beginning with Overthrow of the Roman monarchy, the overthrow of the Roman Kingdom (traditionally dated to 509 BC) and ending in 27 BC with the establishment of the Roman Empire following the War of Actium. During this period, Rome's control expanded from the city's immediate surroundings to hegemony over the entire Mediterranean Sea, Mediterranean world. Roman society at the time was primarily a cultural mix of Latins (Italic tribe), Latin and Etruscan civilization, Etruscan societies, as well as of Sabine, Oscan, and Greek cultural elements, which is especially visible in the Ancient Roman religion and List of Roman deities, its pantheon. Its political organisation developed at around the same time as direct democracy in Ancient Greece, with collective and annual magistracies, overseen by Roman Senate, a senate. There were annual elections, but the republican system was an elective olig ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |