|
Syrian Unity Party
The Syrian Unity party was set up by Syrian emigres in Cairo at the end of 1918. Its founders included signatories to the memorandum that resulted in the Declaration to the Seven and persons previously connected with the Ottoman Party for Administrative Decentralization. In August 1921, the party organized the Syrian–Palestinian Congress in Geneva with a view to influencing the terms of the proposed League of Nations mandate over the region. Members and Platform * Michel Lutfallah; * Rashid Rida; * Rafiq al-Azm; *Haqqi al-Azm; * Abd al-Rahman Shahbandar; * Khaled al-Hakim; *Sheikh Kamal al-Qassab; *Salim Sarkis; *Iskander 'Ammun; * Muhibb al-Din al-Khatib; The party platform stated: Background Before the war, Cairo was a center of activity for the developing Arab independence movement, its permissive atmosphere and community of Syrian emigres was a magnet for political exiles. On 23 October 1918 following the Sinai and Palestine Campaign of World War I, the Occupied En ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Syro-Lebanese In Egypt
The Syro-Lebanese of Egypt ( arz, شوام مصر, transliterated: ''Shawam Masr'') (french: Syro-Libanais d'Egypte), also known as Levantine-Egyptians or Syro-Egyptians, are an ethnic minority group in Egypt. They are Egyptians who have ancestry originating from the Levant, mostly what is now Syria and Lebanon. The majority of Egypt's historic Syro-Lebanese community is Christian, mainly Eastern Catholic ( Melkite and Maronite) and Eastern Orthodox. Since antiquity, there has always been a Levantine presence in Egypt, however, they started becoming a distinctive minority in Egypt around the early 18th century. The majority of Syro-Lebanese migrants who arrived in Egypt during this time were French-speaking and highly influenced by the European Culture. By the dawn of the 20th century, the Syro-Lebanese of Egypt were considered a powerful and cosmopolitan community that played an important role in both Egypt's economy and culture. Due to the rise in nationalism along with t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Occupied Enemy Territory Administration
The Occupied Enemy Territory Administration (OETA) was a joint British, French and Arab military administration over Levantine provinces of the former Ottoman Empire between 1917 and 1920, set up on 23 October 1917 following the Sinai and Palestine Campaign and Arab Revolt of World War I. Although it was declared by the British military, who were in control of the region, it was followed on 30 September 1918 by the 1918 Anglo-French Modus Vivendi in which it was agreed that the British would give the French control in certain areas, and the Hashemites were given joint control of the Eastern area per T.E. Lawrence's November 1918 " Sharifian plan". Following the occupation of the Adana Vilayet (the region of Cilicia) in December 1918, a new territory, OETA North, was set up. The administration ended in OETA West and OETA South in 1920 following the assignment of the Mandate for Syria and the Lebanon and British Mandate for Palestine at the 19–26 April 1920 San Remo conferen ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Arab Nationalist Organizations
The Arabs (singular: Arab; singular ar, عَرَبِيٌّ, DIN 31635: , , plural ar, عَرَب, DIN 31635: , Arabic pronunciation: ), also known as the Arab people, are an ethnic group mainly inhabiting the Arab world in Western Asia, North Africa, the Horn of Africa, and the western Indian Ocean islands (including the Comoros). An Arab diaspora is also present around the world in significant numbers, most notably in the Americas, Western Europe, Turkey, Indonesia, and Iran. In modern usage, the term "Arab" tends to refer to those who both carry that ethnic identity and speak Arabic as their native language. This contrasts with the narrower traditional definition, which refers to the descendants of the tribes of Arabia. The religion of Islam was developed in Arabia, and Classical Arabic serves as the language of Islamic literature. 93 percent of Arabs are Muslims (the remainder consisted mostly of Arab Christians), while Arab Muslims are only 20 percent of th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Arab Nationalism In Syria
The Arabs (singular: Arab; singular ar, عَرَبِيٌّ, DIN 31635: , , plural ar, عَرَب, DIN 31635: , Arabic pronunciation: ), also known as the Arab people, are an ethnic group mainly inhabiting the Arab world in Western Asia, North Africa, the Horn of Africa, and the western Indian Ocean islands (including the Comoros). An Arab diaspora is also present around the world in significant numbers, most notably in the Americas, Western Europe, Turkey, Indonesia, and Iran. In modern usage, the term "Arab" tends to refer to those who both carry that ethnic identity and speak Arabic as their native language. This contrasts with the narrower traditional definition, which refers to the descendants of the tribes of Arabia. The religion of Islam was developed in Arabia, and Classical Arabic serves as the language of Islamic literature. 93 percent of Arabs are Muslims (the remainder consisted mostly of Arab Christians), while Arab Muslims are only 20 percent of the global Musl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Itamar Rabinovich
Itamar Rabinovich ( he, איתמר רבינוביץ; born 1942) is the president of the Israel Institute (Washington and Jerusalem). He was Israel's Ambassador to the United States in the 1990s and former chief negotiator with Syria between 1993 and 1996, and the former president of Tel Aviv University (1999–2007). Currently he is professor emeritus of Middle Eastern History at Tel Aviv University, distinguished global professor at New York University and a distinguished fellow at the Brookings Institution. Biography Itamar Rabinovich received a B.A. degree from the Hebrew University of Jerusalem, an M.A. from Tel Aviv University, and a Ph.D. from the University of California, Los Angeles. Academic career Rabinovich has been a member of Tel Aviv University's faculty since 1971, and served as Ettinger Professor of the Contemporary History of the Middle East, chairman of the Department of Middle Eastern Studies, director of thMoshe Dayan Center for Middle Eastern and African Stu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Greater Syria
Syria (Hieroglyphic Luwian: 𔒂𔒠 ''Sura/i''; gr, Συρία) or Sham ( ar, ٱلشَّام, ash-Shām) is the name of a historical region located east of the Mediterranean Sea in Western Asia, broadly synonymous with the Levant. Other synonyms are Greater Syria or Syria-Palestine. The region boundaries have changed throughout history. In modern times, the term "Syria" alone is used to refer to the Arab Republic of Syria. The term is originally derived from Assyria, an ancient civilization centered in northern Mesopotamia, modern-day Iraq. During the Hellenistic period, the term Syria was applied to the entire Levant as Coele-Syria. Under Roman rule, the term was used to refer to the province of Syria, later divided into Syria Phoenicia and Coele Syria, and to the province of Syria Palaestina. Under the Byzantines, the provinces of Syria Prima and Syria Secunda emerged out of Coele Syria. After the Muslim conquest of the Levant, the term was superseded by the Arabic ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
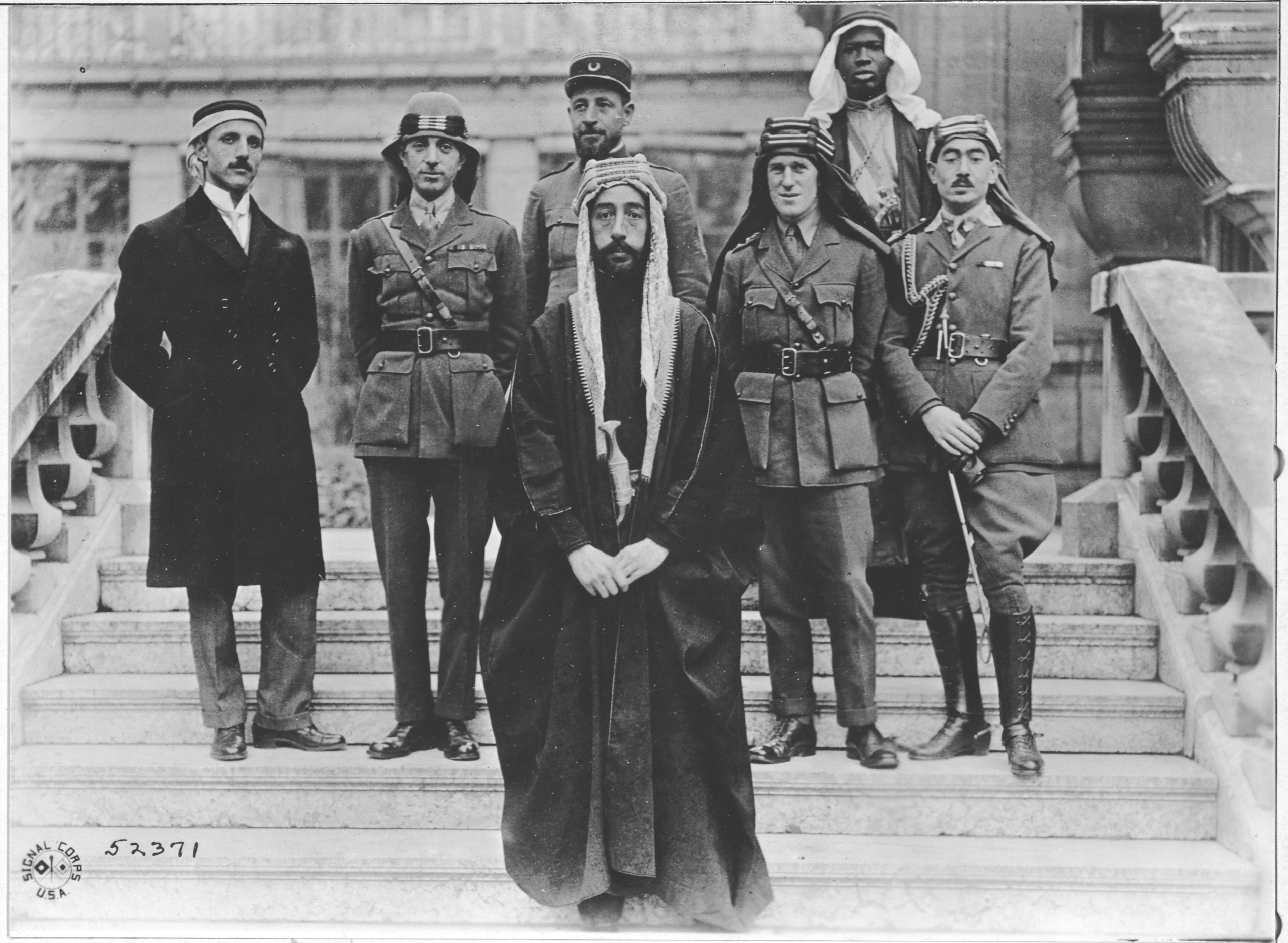
Faisal Bin Hussein
Faisal I bin Al-Hussein bin Ali Al-Hashemi ( ar, فيصل الأول بن الحسين بن علي الهاشمي, ''Faysal el-Evvel bin al-Ḥusayn bin Alī el-Hâşimî''; 20 May 1885 – 8 September 1933) was King of the Arab Kingdom of Syria or Greater Syria in 1920, and was King of Iraq from 23 August 1921 until his death. He was the third son of Hussein bin Ali, the Grand Emir and Sharif of Mecca, who was proclaimed as King of the Arabs in June 1916. He was a 38th-generation direct descendant of Muhammad, as he belonged to the Hashemite family. Faisal fostered unity between Sunni and Shiite Muslims to encourage common loyalty and promote pan-Arabism in the goal of creating an Arab state that would include Iraq, Syria and the rest of the Fertile Crescent. While in power, Faisal tried to diversify his administration by including different ethnic and religious groups in offices. However, Faisal's attempt at pan-Arab nationalism possibly contributed to the isolation of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
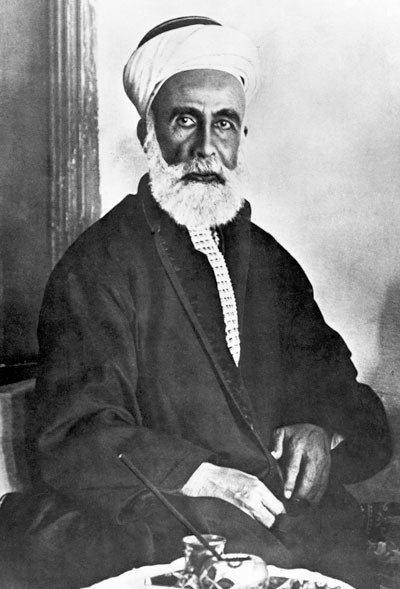
Hussein Bin Ali, Sharif Of Mecca
Hussein bin Ali al-Hashimi ( ar, الحسين بن علي الهاشمي, al-Ḥusayn bin ‘Alī al-Hāshimī; 1 May 18544 June 1931) was an Arab leader from the Banu Hashim clan who was the Sharif and Emir of Mecca from 1908 and, after proclaiming the Great Arab Revolt against the Ottoman Empire, King of the Hejaz from 1916 to 1924 and Caliphate, Caliph from 1924 to 1925. After the Abolition of the Caliphate, abolition of the Ottoman Caliphate he was briefly proclaimed Sharifian Caliph, Caliph until the invasion of the Hejaz by the Saudis the following year. He was a Hashemites#Ancestry, 37th-generation direct descendant of Muhammad, as he belonged to the Hashemite family. A member of the Dhawu Awn clan of the Qatadid emirs of Mecca, he was perceived to have rebellious inclinations and in 1893 was summoned to Istanbul, where he was kept on the Council of State. In 1908, in the aftermath of the Young Turk Revolution, he was appointed Emir of Mecca by the List of sultans of th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Arab Kingdom Of Syria
The Arabs (singular: Arab; singular ar, عَرَبِيٌّ, DIN 31635: , , plural ar, عَرَب, DIN 31635: , Arabic pronunciation: ), also known as the Arab people, are an ethnic group mainly inhabiting the Arab world in Western Asia, North Africa, the Horn of Africa, and the western Indian Ocean islands (including the Comoros). An Arab diaspora is also present around the world in significant numbers, most notably in the Americas, Western Europe, Turkey, Indonesia, and Iran. In modern usage, the term "Arab" tends to refer to those who both carry that ethnic identity and speak Arabic as their native language. This contrasts with the narrower traditional definition, which refers to the descendants of the tribes of Arabia. The religion of Islam was developed in Arabia, and Classical Arabic serves as the language of Islamic literature. 93 percent of Arabs are Muslims (the remainder consisted mostly of Arab Christians), while Arab Muslims are only 20 percent of the global Mus ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Al-Fatat
Al-Fatat or the Young Arab Society ( ar, جمعية العربية الفتاة, Jam’iyat al-’Arabiya al-Fatat) was an underground Arab nationalist organization in the Ottoman Empire. Its aims were to gain independence and unify various Arab territories that were then under Ottoman rule. It found adherents in areas such as Syria. The organization maintained contacts with the reform movement in the Ottoman Empire and included many radicals and revolutionaries, such as Abd al-Mirzai. They were closely linked to the Al-Ahd, or Covenant Society, who had members in positions within the military, most were quickly dismissed after Enver Pasha gained control in Turkey. This organization's parallel in activism were the Young Turks, who had a similar agenda that pertained to Turkish nationalism. History Founding and early years in Paris Al-Fatat was formed in the aftermath of the Young Turk Revolution in 1908. The original founders of the movement were Arab students who felt offended by ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hansard
''Hansard'' is the traditional name of the transcripts of parliamentary debates in Britain and many Commonwealth countries. It is named after Thomas Curson Hansard (1776–1833), a London printer and publisher, who was the first official printer to the Parliament at Westminster. Origins Though the history of the ''Hansard'' began in the British parliament, each of Britain's colonies developed a separate and distinctive history. Before 1771, the British Parliament had long been a highly secretive body. The official record of the actions of the House was publicly available but there was no record of the debates. The publication of remarks made in the House became a breach of parliamentary privilege, punishable by the two Houses of Parliament. As the populace became interested in parliamentary debates, more independent newspapers began publishing unofficial accounts of them. The many penalties implemented by the government, including fines, dismissal, imprisonment, and investigati ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
%2C_Alexandria%2C_Ägypten.jpg)