|
Syriac Orthodox Patriarch Of Antioch And All The East
The Syriac Orthodox Patriarch of Antioch and All the East (Syriac language, Syriac: ܦܛܪܝܪܟܐ ܕܐܢܛܝܘܟܝܐ ܘܕܟܠܗ̇ ܡܕܢܚܐ ''Paṭriarḵo ḏ-Anṭiuḵia waḏ-kuloh madnho'') is the Bishop of Antioch, and head of the Syriac Orthodox Church (Syriac Orthodox Church, Syriac: ܥܺܕܬܳܐ ܣܽܘ̣ܪܝܳܝܬܳܐ ܬܪܺܝܨܰܬ ܫܽܘ̣ܒ̣ܚܳܐ). He presides over the Holy Synod of the Syriac Orthodox Church, which is its highest authority. The current Patriarch of Antioch is Ignatius Aphrem II, who was enthroned on 29 May 2014 as the 122nd Successor to Saint Peter. The position of the Patriarch of Antioch was established and first held by Saint Peter, Peter the Apostle (Syriac language, Syriac: ܫܹܡܥܘܿܢ ܟܹ݁ܐܦ݂ܵܐ ''Šemʿōn Kēp̄ā''). He officially oversees the Church of Antioch, Holy Apostolic See at Antioch (modern-day Antakya, in Turkey), though the Patriarch currently resides in Damascus; the Patriarch fled to Syria during the 1915 Sayfo, Ass ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ignatius Aphrem II
Mor Ignatius Aphrem II (born 3 May 1965 as Sa'id Karim; ) is a Syrian Americans, Syrian-American Christian prelate who is serving as the Syriac Orthodox Patriarch of Antioch and All the East, Patriarch of the Syriac Orthodox Church since 29 May 2014. Born and raised in Qamishli, Qamishili, Syria, Karim took the vows of a monk in 1985 and was later ordained as a deacon and then as a priest. He received a Bachelor of Arts in Divinity (academic discipline), Divinity from the Coptic Theological Seminary in Cairo in 1988. In 1992, he received a Licentiate of Sacred Theology and in 1994, a Doctor of Divinity from St Patrick's College, Maynooth, St Patrick's College, Ireland. In 1996, Aphrem Karim was consecrated as the Vicar, Patriarchal Vicar and Metropolitan bishop, Metropolitan Archbishop of the Archdiocese for the Eastern United States by Ignatius Zakka I, Patriarch Ignatius Zakka I Iwas. As an archbishop, he established 11 new parishes bringing the number of parishes in the arch ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
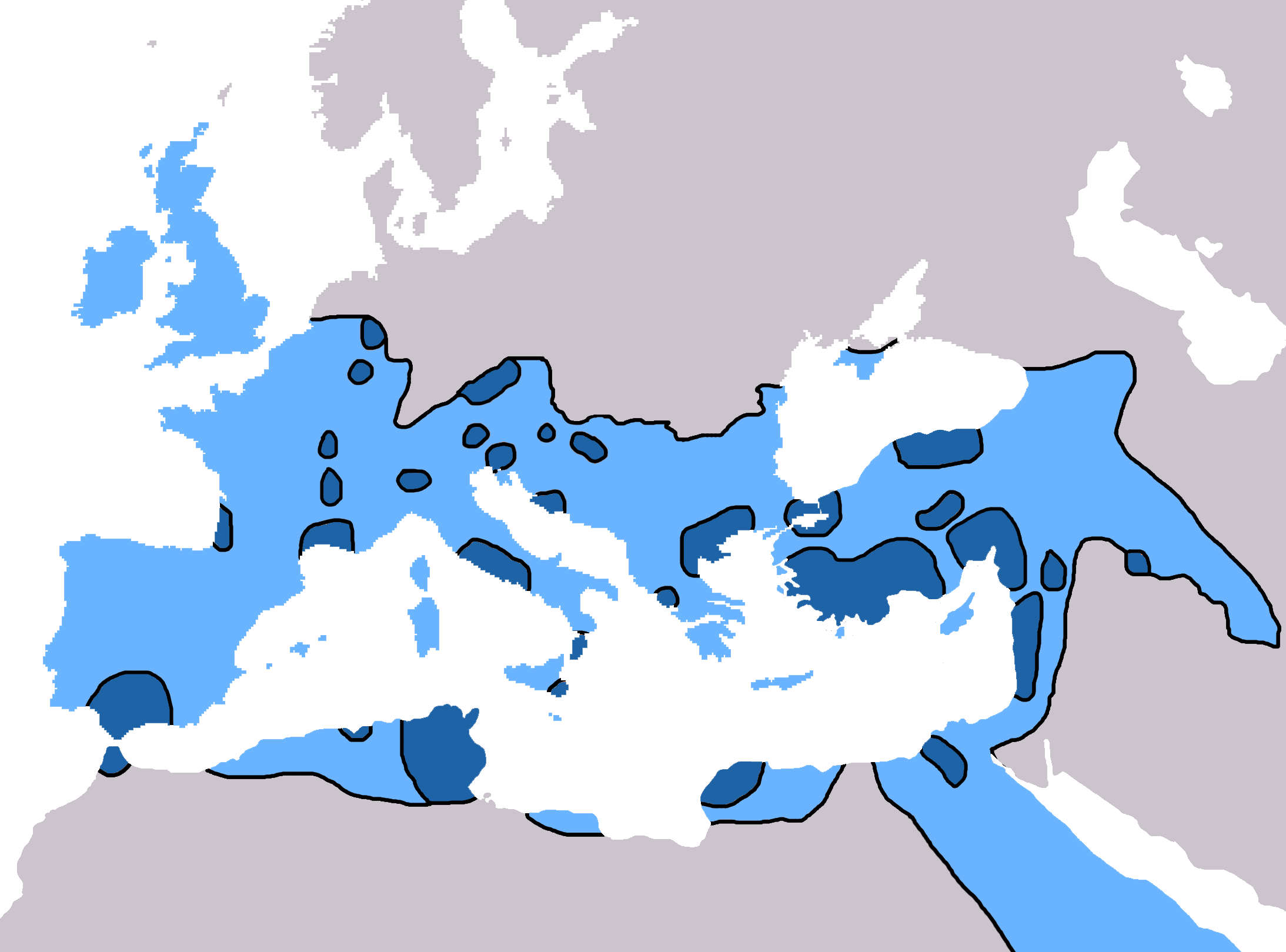
Church Of Antioch
The Church of Antioch (, ; ) was the first of the five major churches of what later became the pentarchy in Christianity, with its primary seat in the ancient Greek city of Antioch (present-day Antakya, Turkey). The earliest record of the church of Antioch is given in Acts 11, stating that some "men of Cyprus and Cyrene, which, when they had come to Antioch, spoke to the Grecians, preaching the Lord Jesus ..and a great number believed, and turned to the Lord." Later, at the start of their missionary journeys, Paul the Apostle (also called Saul) and Barnabas preached in Antioch for a year, and followers of the church were called "Christians" for the first time.Smith's Bible Dictionary History Followers of Jesus as the messiah trace the origin of the term ''Christian'' to the church established at Antioch. The first church was founded by Jesus Christ, before Pentecost on a mountain top with the disciples while Christ was still alive. According to verses 19–26 of Acts 11, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
First Council Of Nicaea
The First Council of Nicaea ( ; ) was a council of Christian bishops convened in the Bithynian city of Nicaea (now İznik, Turkey) by the Roman Emperor Constantine I. The Council of Nicaea met from May until the end of July 325. This ecumenical council was the first of many efforts to attain consensus in the church through an assembly representing all Christendom. Hosius of Corduba may have presided over its deliberations. Attended by at least 200 bishops, its main accomplishments were the settlement of the Christological issue of the divine nature of God the Son and his relationship to God the Father, the construction of the first part of the Nicene Creed, the mandating of uniform observance of the date of Easter, and the promulgation of early canon law. Background Alexandrian controversies The major impetus for the calling of the Council of Nicaea arose in a theological dispute among the Christian clergy of Alexandria concerning the nature of Jesus, his origin, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Diocese Of The East
The Diocese of the East, also called the Diocese of Oriens, (; ) was a diocese of the later Roman Empire, incorporating the provinces of the western Middle East, between the Mediterranean Sea and Mesopotamia. During late Antiquity, it was one of the major commercial, agricultural, religious and intellectual areas of the empire, and its strategic location facing the Sassanid Empire and the nomadic tribes gave it exceptional military importance. History The capital of the diocese was at Antioch, and its governor had the special title of '' comes Orientis'' ("Count of the East", of the rank ''vir spectabilis'' and later '' vir gloriosus'') instead of the ordinary "'' vicarius''". The diocese was established after the reforms of Diocletian (r. 284–305), and was subordinate to the praetorian prefecture of the East. The diocese included originally all Middle Eastern provinces of the Empire: Isauria, Cilicia, Cyprus, Euphratensis, Mesopotamia, Osroene, Syria Coele, Phoenice, Syri ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Primus Inter Pares
is a Latin phrase meaning first among equals. It is typically used as an honorary title for someone who is formally equal to other members of their group but is accorded unofficial respect, traditionally owing to their seniority in office. Historically, the '' princeps senatus'' of the Roman Senate was such a figure and initially bore only the distinction that he was allowed to speak first during debate. After the fall of the Republic, Roman emperors initially referred to themselves only as ''princeps'' despite having enormous power. Various modern figures such as the prime minister in parliamentary systems, the president of the Swiss Confederation, the chief justice of the United States, the chief justice of the Philippines, the archbishop of Canterbury of the Anglican Communion, the chair of the Federal Reserve in the United States and the ecumenical patriarch of Constantinople of the Eastern Orthodox Church fall under both senses: Bearing higher status and various addi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bishop Of Antioch
The Patriarch of Antioch is a traditional title held by the bishop of Antioch (modern-day Antakya, Turkey). As the traditional "overseer" (, , from which the word ''bishop'' is derived) of the first gentile Christian community, the position has been of prime importance in Pauline Christianity from its earliest period. This diocese is one of the few for which the names of its bishops from the apostolic beginnings have been preserved. Today five churches use the title of patriarch of Antioch: one Eastern Orthodox (the Greek Orthodox Church of Antioch); one Oriental Orthodox (the Syriac Orthodox Church); and three Eastern Catholic (the Maronite, Syriac Catholic, and Melkite Greek Catholic Churches). According to the pre-congregation church tradition, this ancient patriarchate was founded by the Apostle Saint Peter. The patriarchal succession was disputed at the time of the Meletian schism in 362 and again after the Council of Chalcedon in 451, when there were rival Melkite and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pope Of The Coptic Orthodox Church
The pope (; ), officially the pope of Alexandria and the patriarch of the see of St. Mark, also known as the bishop of Alexandria, or the patriarch of Alexandria, is the leader of the Coptic Orthodox Church, with ancient Christian roots in Egypt. The primacy of the Patriarch of Alexandria is rooted in his role as successor to Saint Mark, who was consecrated by Saint Peter, as affirmed by the Council of Nicaea. It is one of three Petrine Sees affirmed by the council alongside the Patriarch of Antioch and the Pope of Rome. The current holder of this position is Pope Tawadros II, who was selected as the 118th pope on November 18, 2012. Following the traditions of the church, the Pope is chairman and head of the Holy Synod of the Coptic Orthodox Patriarchate of Alexandria. The Holy Synod is the highest authority in the Church of Alexandria, which has between 12 and 18 million members worldwide, 10 to 14 million of whom are in Egypt. The pope is also the chairman of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
First Council Of Nicaea
The First Council of Nicaea ( ; ) was a council of Christian bishops convened in the Bithynian city of Nicaea (now İznik, Turkey) by the Roman Emperor Constantine I. The Council of Nicaea met from May until the end of July 325. This ecumenical council was the first of many efforts to attain consensus in the church through an assembly representing all Christendom. Hosius of Corduba may have presided over its deliberations. Attended by at least 200 bishops, its main accomplishments were the settlement of the Christological issue of the divine nature of God the Son and his relationship to God the Father, the construction of the first part of the Nicene Creed, the mandating of uniform observance of the date of Easter, and the promulgation of early canon law. Background Alexandrian controversies The major impetus for the calling of the Council of Nicaea arose in a theological dispute among the Christian clergy of Alexandria concerning the nature of Jesus, hi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Christian Church
In ecclesiology, the Christian Church is what different Christian denominations conceive of as being the true body of Christians or the original institution established by Jesus Christ. "Christian Church" has also been used in academia as a synonym for Christianity, despite the fact that it is composed of multiple churches or denominations, many of which hold a doctrinal claim of being the one true church to the exclusion of the others. For many Protestantism, Protestant Christians, the Christian Church has two components: the church visible, institutions in which "the Bible, Word of God purely preached and listened to, and the sacraments administered according to Christ's institution", as well as the church invisible—all "who are truly Salvation in Christianity, saved" (with these beings members of the visible church). In this understanding of the invisible church, "Christian Church" (or Catholic (term), catholic Church) does not refer to a particular Christian denomination, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Patriarchate
Patriarchate (, ; , ''patriarcheîon'') is an ecclesiological term in Christianity, referring to the office and jurisdiction of a patriarch. According to Christian tradition, three patriarchates—Rome, Antioch, and Alexandria—were established by the apostles as apostolic sees in the 1st century. These were officially recognized by the First Council of Nicaea. The Patriarchate of Constantinople was added in the 4th century, and the Patriarchate of Jerusalem followed in the 5th century. These five sees were later recognized collectively as the pentarchy by the Council of Chalcedon in 451. Over the course of Christian history, additional patriarchates were gradually recognized by the original ancient episcopal sees. However, several of these later lost jurisdiction—primarily due to the Islamic conquests in the Middle East and North Africa—and became titular or honorary patriarchates without real institutional authority over their historical territories. Histo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
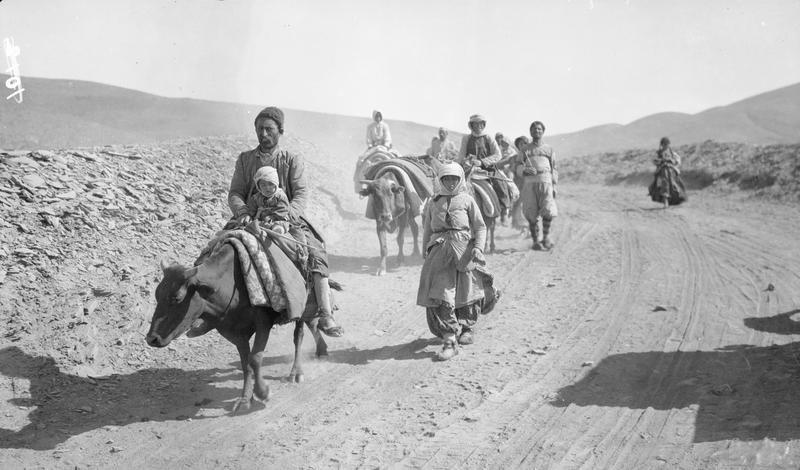
Sayfo
The Sayfo (, ), also known as the Seyfo or the Assyrian genocide, was the mass murder and deportation of Assyrian people, Assyrian/Syriac Christians in southeastern Anatolia and Persia's Azerbaijan (Iran), Azerbaijan province by Ottoman Army (1861–1922), Ottoman forces and some Kurdish tribes during World War I. The Assyrians were divided into mutually antagonistic churches, including the Syriac Orthodox Church, the Assyrian Church of the East, and the Chaldean Catholic Church. Before World War I, they largely lived in mountainous and remote areas of the Ottoman Empire and Persia, some of which were effectively Stateless society, stateless. The Ottoman Empire's nineteenth-century centralization efforts led to increased violence and danger for the Assyrians. Mass killing of Assyrian civilians began during the Persian campaign (World War I), Ottoman occupation of Azerbaijan from January to May 1915, during which massacres were committed by Ottoman forces and pro-Ottoman Kur ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Syria
Syria, officially the Syrian Arab Republic, is a country in West Asia located in the Eastern Mediterranean and the Levant. It borders the Mediterranean Sea to the west, Turkey to Syria–Turkey border, the north, Iraq to Iraq–Syria border, the east and southeast, Jordan to Jordan–Syria border, the south, and Israel and Lebanon to Lebanon–Syria border, the southwest. It is a republic under Syrian transitional government, a transitional government and comprises Governorates of Syria, 14 governorates. Damascus is the capital and largest city. With a population of 25 million across an area of , it is the List of countries and dependencies by population, 57th-most populous and List of countries and dependencies by area, 87th-largest country. The name "Syria" historically referred to a Syria (region), wider region. The modern state encompasses the sites of several ancient kingdoms and empires, including the Eblan civilization. Damascus was the seat of the Umayyad Caliphate and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |