|
Synthetic Seismogram
A synthetic seismogram is the result of forward modelling the seismic response of an input earth model, which is defined in terms of 1D, 2D or 3D variations in physical properties. In hydrocarbon exploration this is used to provide a 'tie' between changes in rock properties in a borehole and seismic reflection data at the same location. It can also be used either to test possible interpretation models for 2D and 3D seismic data or to model the response of the predicted geology as an aid to planning a seismic reflection survey. In the processing of wide-angle reflection and refraction (WARR) data, synthetic seismograms are used to further constrain the results of seismic tomography. In earthquake seismology, synthetic seismograms are used either to match the predicted effects of a particular earthquake source fault model with observed seismometer records or to help constrain the Earth's velocity structure. Synthetic seismograms are generated using specialized geophysical software. 1D ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Reflection Seismology
Reflection seismology (or seismic reflection) is a method of exploration geophysics that uses the principles of seismology to estimate the properties of the Earth's subsurface from reflection (physics), reflected seismic waves. The method requires a controlled seismic source of energy, such as dynamite or Tovex blast, a specialized Seismic source#Air gun, air gun or a seismic vibrator. Reflection seismology is similar to sonar and acoustic location, echolocation. History Reflections and refractions of seismic waves at geologic Interface (matter), interfaces within the Earth were first observed on recordings of earthquake-generated seismic waves. The basic model of the Earth's deep interior is based on observations of earthquake-generated seismic waves transmitted through the Earth's interior (e.g., Mohorovičić, 1910). The use of human-generated seismic waves to map in detail the geology of the upper few kilometers of the Earth's crust followed shortly thereafter and has deve ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hydrocarbon Exploration
Hydrocarbon exploration (or oil and gas exploration) is the search by petroleum geologists and geophysicists for hydrocarbon deposits, particularly petroleum and natural gas, in the Earth's crust using petroleum geology. Exploration methods Visible surface features such as oil seeps, natural gas seeps, pockmarks (underwater craters caused by escaping gas) provide basic evidence of hydrocarbon generation (be it shallow or deep in the Earth). However, most exploration depends on highly sophisticated technology to detect and determine the extent of these deposits using exploration geophysics. Areas thought to contain hydrocarbons are initially subjected to a gravity survey, magnetic survey, passive seismic or regional seismic reflection surveys to detect large-scale features of the sub-surface geology. Features of interest (known as ''leads'') are subjected to more detailed seismic surveys which work on the principle of the time it takes for reflected sound waves to travel ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Seismic Tomography
Seismic tomography or seismotomography is a technique for imaging the subsurface of the Earth using seismic waves. The properties of seismic waves are modified by the material through which they travel. By comparing the differences in seismic waves recorded at different locations, it is possible to create a model of the subsurface structure. Most commonly, these seismic waves are generated by earthquakes or man-made sources such as explosions. Different types of waves, including P, S, Rayleigh, and Love waves can be used for tomographic images, though each comes with their own benefits and downsides and are used depending on the geologic setting, seismometer coverage, distance from nearby earthquakes, and required resolution. The model created by tomographic imaging is almost always a seismic velocity model, and features within this model may be interpreted as structural, thermal, or compositional variations. Geoscientists apply seismic tomography to a wide variety of settings i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Earthquake
An earthquakealso called a quake, tremor, or tembloris the shaking of the Earth's surface resulting from a sudden release of energy in the lithosphere that creates seismic waves. Earthquakes can range in intensity, from those so weak they cannot be felt, to those violent enough to propel objects and people into the air, damage critical infrastructure, and wreak destruction across entire cities. The seismic activity of an area is the frequency, type, and size of earthquakes experienced over a particular time. The seismicity at a particular location in the Earth is the average rate of seismic energy release per unit volume. In its most general sense, the word ''earthquake'' is used to describe any seismic event that generates seismic waves. Earthquakes can occur naturally or be induced by human activities, such as mining, fracking, and nuclear weapons testing. The initial point of rupture is called the hypocenter or focus, while the ground level directly above it is the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Seismology
Seismology (; from Ancient Greek σεισμός (''seismós'') meaning "earthquake" and -λογία (''-logía'') meaning "study of") is the scientific study of earthquakes (or generally, quakes) and the generation and propagation of elastic waves through planetary bodies. It also includes studies of the environmental effects of earthquakes such as tsunamis; other seismic sources such as volcanoes, plate tectonics, glaciers, rivers, oceanic microseisms, and the atmosphere; and artificial processes such as explosions. Paleoseismology is a related field that uses geology to infer information regarding past earthquakes. A recording of Earth's motion as a function of time, created by a seismograph is called a seismogram. A seismologist is a scientist who works in basic or applied seismology. History Scholarly interest in earthquakes can be traced back to antiquity. Early speculations on the natural causes of earthquakes were included in the writings of Thales of Miletu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Focal Mechanism
The focal mechanism of an earthquake describes the Fault (geology)#Slip.2C heave.2C throw, deformation in the Hypocenter, source region that generates the seismic waves. In the case of a Fault (geology), fault-related event, it refers to the orientation of the fault plane that slipped, and the slip Euclidean vector, vector and is also known as a fault-plane solution. Focal mechanisms are derived from a solution of the moment tensor for the earthquake, which itself is estimated by an analysis of observed seismic waveforms. The focal mechanism can be derived from observing the pattern of "first motions", whether the first arriving P waves break up or down. This method was used before waveforms were recorded and analysed digitally, and this method is still used for earthquakes too small for easy moment tensor solution. Focal mechanisms are now mainly derived using semi-automatic analysis of the recorded waveforms. Moment tensor solutions The moment tensor solution is displayed gra ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Seismometer
A seismometer is an instrument that responds to ground displacement and shaking such as caused by quakes, volcanic eruptions, and explosions. They are usually combined with a timing device and a recording device to form a seismograph. The output of such a device—formerly recorded on paper (see picture) or film, now recorded and processed digitally—is a ''seismogram''. Such data is used to locate and characterize earthquakes, and to study the internal structure of Earth. Basic principles A simple seismometer, sensitive to up-down motions of the Earth, is like a weight hanging from a spring, both suspended from a frame that moves along with any motion detected. The relative motion between the weight (called the mass) and the frame provides a measurement of the vertical ground motion. A rotating drum is attached to the frame and a pen is attached to the weight, thus recording any ground motion in a seismogram. Any movement from the ground moves the frame. The mass tends ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Wireline Logging
Well logging, also known as borehole logging is the practice of making a detailed record (a ''well log'') of the geologic formations penetrated by a borehole. The log may be based either on visual inspection of samples brought to the surface (''geological'' logs) or on physical measurements made by instruments lowered into the hole (''geophysical'' logs). Some types of geophysical well logs can be done during any phase of a well's history: drilling, completing, producing, or abandoning. Well logging is performed in boreholes drilled for the oil and gas, groundwater, mineral and geothermal exploration, as well as part of environmental, scientific and geotechnical studies. Wireline logging Different industries, as mining, oil and gas uses wireline logging to obtain a continuous record of a formation's rock properties, also, groundwater consultants. Wireline logging can be defined as being "The acquisition and analysis of geophysical data performed as a function of well bor ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Acoustic Impedance
Acoustic impedance and specific acoustic impedance are measures of the opposition that a system presents to the acoustic flow resulting from an acoustic pressure applied to the system. The International System of Units, SI unit of acoustic impedance is the pascal-second per cubic metre (symbol Pa·s/m3), or in the MKS system of units, MKS system the rayl per square metre (Rayl/m2), while that of specific acoustic impedance is the pascal-second per metre (Pa·s/m), or in the MKS system the rayl (Rayl). There is a Mechanical–electrical analogies#Impedance analogies, close analogy with electrical impedance, which measures the opposition that a system presents to the electric current resulting from a voltage applied to the system. Mathematical definitions Acoustic impedance For a LTI system theory, linear time-invariant system, the relationship between the acoustic pressure applied to the system and the resulting acoustic volume flow rate through a surface perpendicular to the di ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
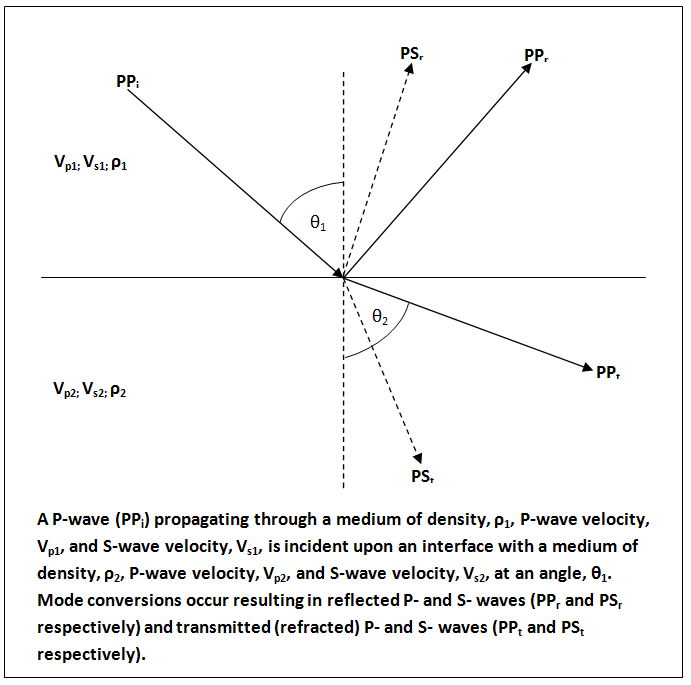
Zoeppritz Equations
In geophysics and reflection seismology, the Zoeppritz equations are a set of equations that describe the partitioning of seismic wave energy at an interface, due to mode conversion. They are named after their author, the German geophysicist Karl Bernhard Zoeppritz, who died before they were published in 1919. The equations are important in geophysics because they relate the amplitude of P-wave, incident upon a plane interface, and the amplitude of reflected and refracted P- and S-waves to the angle of incidence.Sheriff, R. E., Geldart, L. P., (1995), 2nd Edition. Exploration Seismology. Cambridge University Press. They are the basis for investigating the factors affecting the amplitude of a returning seismic wave when the angle of incidence is altered — also known as amplitude versus offset analysis — which is a helpful technique in the detection of petroleum reservoirs. The Zoeppritz equations were not the first to describe the amplitudes of reflected and refracted waves ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Reflection Coefficient
In physics and electrical engineering the reflection coefficient is a parameter that describes how much of a wave is reflected by an impedance discontinuity in the transmission medium. It is equal to the ratio of the amplitude of the reflected wave to the incident wave, with each expressed as phasors. For example, it is used in optics to calculate the amount of light that is reflected from a surface with a different index of refraction, such as a glass surface, or in an electrical transmission line to calculate how much of the electromagnetic wave is reflected by an impedance discontinuity. The reflection coefficient is closely related to the ''transmission coefficient''. The reflectance of a system is also sometimes called a reflection coefficient. Different disciplines have different applications for the term. Transmission lines In telecommunications and transmission line theory, the reflection coefficient is the ratio of the complex amplitude of the reflected wave to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Convolution
In mathematics (in particular, functional analysis), convolution is a operation (mathematics), mathematical operation on two function (mathematics), functions f and g that produces a third function f*g, as the integral of the product of the two functions after one is reflected about the y-axis and shifted. The term ''convolution'' refers to both the resulting function and to the process of computing it. The integral is evaluated for all values of shift, producing the convolution function. The choice of which function is reflected and shifted before the integral does not change the integral result (see #Properties, commutativity). Graphically, it expresses how the 'shape' of one function is modified by the other. Some features of convolution are similar to cross-correlation: for real-valued functions, of a continuous or discrete variable, convolution f*g differs from cross-correlation f \star g only in that either f(x) or g(x) is reflected about the y-axis in convolution; thus i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |