|
Synthetic Genomics
In September 2021, Synthetic Genomics Inc. (SGI), a private company located in La Jolla, California, changed its name to Viridos. The company is focused on the field of synthetic biology, especially harnessing photosynthesis with micro algae to create alternatives to fossil fuels. Viridos designs and builds biological systems to address global sustainability problems. Synthetic biology is an interdisciplinary branch of biology and engineering, combining fields such as biotechnology, evolutionary biology, molecular biology, systems biology, biophysics, computer engineering, and genetic engineering. Synthetic Genomics uses techniques such as software engineering, bioprocessing, bioinformatics, biodiscovery, analytical chemistry, fermentation, cell optimization, and DNA synthesis to design and build biological systems. The company produces or performs research in the fields of sustainable bio-fuels, insect resistant crops, transplantable organs, targeted medicines, DNA synthesis i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Synthetic Biology
Synthetic biology (SynBio) is a multidisciplinary area of research that seeks to create new biological parts, devices, and systems, or to redesign systems that are already found in nature. It is a branch of science that encompasses a broad range of methodologies from various disciplines, such as biotechnology, biomaterials, material science/engineering, genetic engineering, molecular biology, molecular engineering, systems biology, membrane science, biophysics, chemical and biological engineering, electrical and computer engineering, control engineering and evolutionary biology. Due to more powerful genetic engineering capabilities and decreased DNA synthesis and sequencing costs, the field of synthetic biology is rapidly growing. In 2016, more than 350 companies across 40 countries were actively engaged in synthetic biology applications; all these companies had an estimated net worth of $3.9 billion in the global market. Definition Synthetic biology currently has no ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sustainability
Specific definitions of sustainability are difficult to agree on and have varied in the literature and over time. The concept of sustainability can be used to guide decisions at the global, national, and individual levels (e.g. sustainable living). Sustainability is commonly described as having three dimensions (also called pillars): environmental, economic, and social. Many publications state that the environmental dimension (also called " planetary integrity" or "ecological integrity") is the most important, and, in everyday usage, "sustainability" is often focused on countering major environmental problems, such as climate change, loss of biodiversity, loss of ecosystem services, land degradation, and air and water pollution. Humanity is now exceeding several " planetary boundaries". A closely related concept is that of sustainable development, and the terms are often used synonymously. However, UNESCO distinguishes the two thus: "''Sustainability'' is often thought of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fermentation
Fermentation is a metabolic process that produces chemical changes in organic substrates through the action of enzymes. In biochemistry, it is narrowly defined as the extraction of energy from carbohydrates in the absence of oxygen. In food production, it may more broadly refer to any process in which the activity of microorganisms brings about a desirable change to a foodstuff or beverage. The science of fermentation is known as zymology. In microorganisms, fermentation is the primary means of producing adenosine triphosphate (ATP) by the degradation of organic nutrients anaerobically. Humans have used fermentation to produce foodstuffs and beverages since the Neolithic age. For example, fermentation is used for preservation in a process that produces lactic acid found in such sour foods as pickled cucumbers, kombucha, kimchi, and yogurt, as well as for producing alcoholic beverages such as wine and beer. Fermentation also occurs within the gastrointestinal tra ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Analytical Chemistry
Analytical chemistry studies and uses instruments and methods to separate, identify, and quantify matter. In practice, separation, identification or quantification may constitute the entire analysis or be combined with another method. Separation isolates analytes. Qualitative analysis identifies analytes, while quantitative analysis determines the numerical amount or concentration. Analytical chemistry consists of classical, wet chemical methods and modern, instrumental methods. Classical qualitative methods use separations such as precipitation, extraction, and distillation. Identification may be based on differences in color, odor, melting point, boiling point, solubility, radioactivity or reactivity. Classical quantitative analysis uses mass or volume changes to quantify amount. Instrumental methods may be used to separate samples using chromatography, electrophoresis or field flow fractionation. Then qualitative and quantitative analysis can be performed, often with ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bioinformatics
Bioinformatics () is an interdisciplinary field that develops methods and software tools for understanding biological data, in particular when the data sets are large and complex. As an interdisciplinary field of science, bioinformatics combines biology, chemistry, physics, computer science, information engineering, mathematics and statistics to analyze and interpret the biological data. Bioinformatics has been used for '' in silico'' analyses of biological queries using computational and statistical techniques. Bioinformatics includes biological studies that use computer programming as part of their methodology, as well as specific analysis "pipelines" that are repeatedly used, particularly in the field of genomics. Common uses of bioinformatics include the identification of candidates genes and single nucleotide polymorphisms ( SNPs). Often, such identification is made with the aim to better understand the genetic basis of disease, unique adaptations, desirable propertie ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bioprocess Engineering
Bioprocess engineering, also biochemical engineering, is a specialization of chemical engineering or biological engineering. It deals with the design and development of equipment and processes for the manufacturing of products such as agriculture, food, feed, pharmaceuticals, nutraceuticals, chemicals, and polymers and paper from biological materials & treatment of waste water. Bioprocess engineering is a conglomerate of mathematics, biology and industrial design, and consists of various spectrums like the design and study of bioreactors (operational mode, instrumentation, and physical layout) to the creation of kinetic models. It also deals with studying various biotechnological processes used in industries for large scale production of biological product for optimization of yield in the end product and the quality of end product. Bioprocess engineering may include the work of mechanical, electrical, and industrial engineers to apply principles of their disciplines to processes ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Software Engineering
Software engineering is a systematic engineering approach to software development. A software engineer is a person who applies the principles of software engineering to design, develop, maintain, test, and evaluate computer software. The term '' programmer'' is sometimes used as a synonym, but may also lack connotations of engineering education or skills. Engineering techniques are used to inform the software development process which involves the definition, implementation, assessment, measurement, management, change, and improvement of the software life cycle process itself. It heavily uses software configuration management which is about systematically controlling changes to the configuration, and maintaining the integrity and traceability of the configuration and code throughout the system life cycle. Modern processes use software versioning. History Beginning in the 1960s, software engineering was seen as its own type of engineering. Additionally, the development of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Genetic Engineering
Genetic engineering, also called genetic modification or genetic manipulation, is the modification and manipulation of an organism's genes using technology. It is a set of technologies used to change the genetic makeup of cells, including the transfer of genes within and across species boundaries to produce improved or novel organisms. New DNA is obtained by either isolating and copying the genetic material of interest using recombinant DNA methods or by artificially synthesising the DNA. A construct is usually created and used to insert this DNA into the host organism. The first recombinant DNA molecule was made by Paul Berg in 1972 by combining DNA from the monkey virus SV40 with the lambda virus. As well as inserting genes, the process can be used to remove, or " knock out", genes. The new DNA can be inserted randomly, or targeted to a specific part of the genome. An organism that is generated through genetic engineering is considered to be genetically modified ( ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Computer Engineering
Computer engineering (CoE or CpE) is a branch of electrical engineering and computer science that integrates several fields of computer science and electronic engineering required to develop computer hardware and software. Computer engineers not only require training in electronic engineering, software design, and hardware-software integration, but also in software engineering. It uses the techniques and principles of electrical engineering and computer science, but also covers areas such as artificial intelligence (AI), robotics, computer networks, computer architecture and operating systems. Computer engineers are involved in many hardware and software aspects of computing, from the design of individual microcontrollers, microprocessors, personal computers, and supercomputers, to circuit design. This field of engineering not only focuses on how computer systems themselves work, yet it also demands them to integrate into the larger picture. Robots are one of the appl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Biophysics
Biophysics is an interdisciplinary science that applies approaches and methods traditionally used in physics to study biological phenomena. Biophysics covers all scales of biological organization, from molecular to organismic and populations. Biophysical research shares significant overlap with biochemistry, molecular biology, physical chemistry, physiology, nanotechnology, bioengineering, computational biology, biomechanics, developmental biology and systems biology. The term ''biophysics'' was originally introduced by Karl Pearson in 1892. Roland Glaser. Biophysics: An Introduction'. Springer; 23 April 2012. . The term ''biophysics'' is also regularly used in academia to indicate the study of the physical quantities (e.g. electric current, temperature, stress, entropy) in biological systems. Other biological sciences also perform research on the biophysical properties of living organisms including molecular biology, cell biology, chemical biology, and biochemistry. O ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Molecular Biology
Molecular biology is the branch of biology that seeks to understand the molecular basis of biological activity in and between cells, including biomolecular synthesis, modification, mechanisms, and interactions. The study of chemical and physical structure of biological macromolecules is known as molecular biology. Molecular biology was first described as an approach focused on the underpinnings of biological phenomena - uncovering the structures of biological molecules as well as their interactions, and how these interactions explain observations of classical biology. In 1945 the term molecular biology was used by physicist William Astbury. In 1953 Francis Crick, James Watson, Rosalind Franklin, and colleagues, working at Medical Research Council unit, Cavendish laboratory, Cambridge (now the MRC Laboratory of Molecular Biology), made a double helix model of DNA which changed the entire research scenario. They proposed the DNA structure based on previous research done by ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
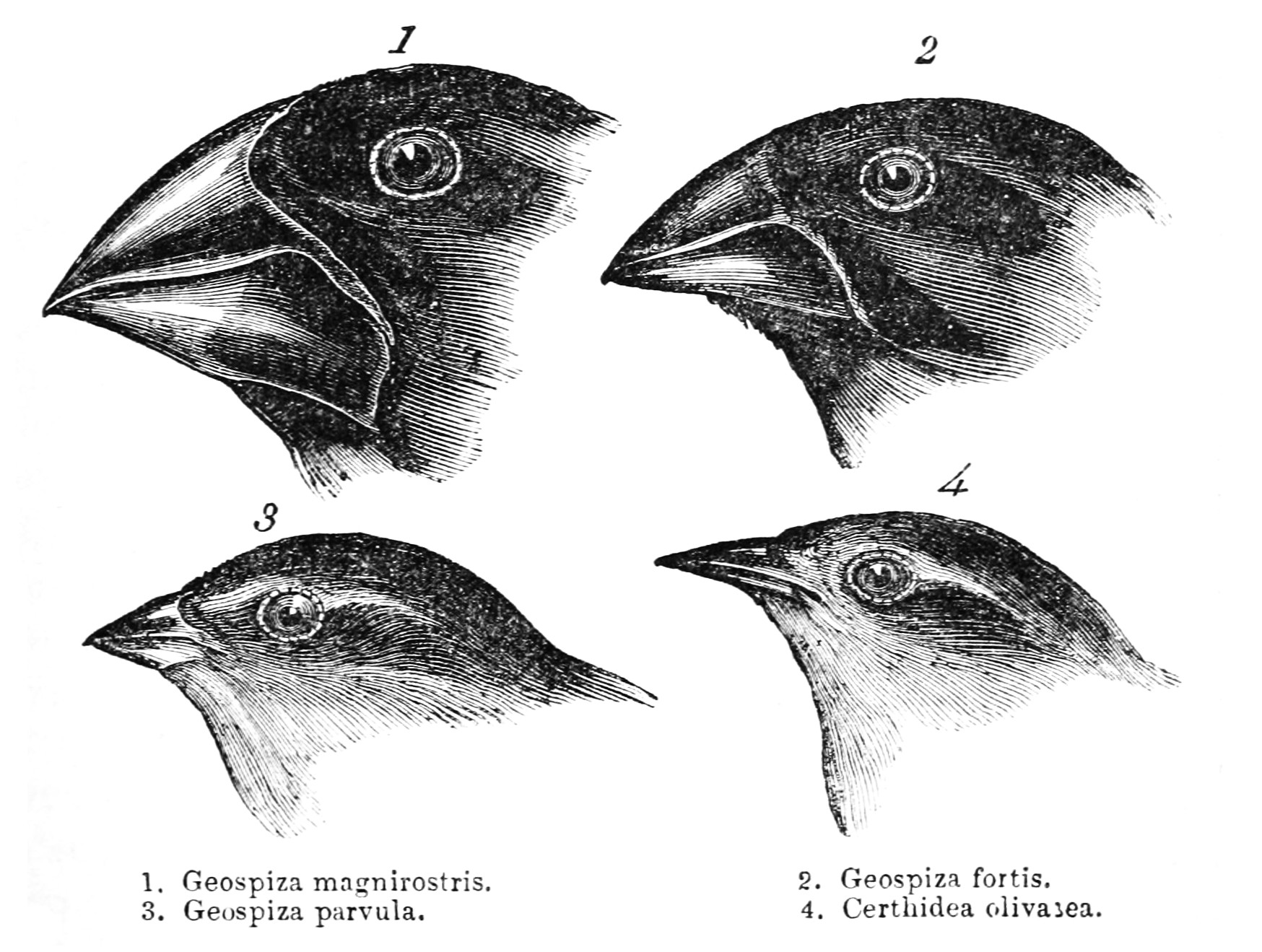
Evolutionary Biology
Evolutionary biology is the subfield of biology that studies the evolutionary processes (natural selection, common descent, speciation) that produced the diversity of life on Earth. It is also defined as the study of the history of life forms on Earth. Evolution is based on the theory that all species are related and they gradually change over time. In a population, the genetic variations affect the physical characteristics i.e. phenotypes of an organism. These changes in the phenotypes will be an advantage to some organisms, which will then be passed onto their offspring. Some examples of evolution in species over many generations are the Peppered Moth and Flightless birds. In the 1930s, the discipline of evolutionary biology emerged through what Julian Huxley called the modern synthesis of understanding, from previously unrelated fields of biological research, such as genetics and ecology, systematics, and paleontology. The importance of studying Evolutionary biology ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |