|
Syndesmosis
In anatomy, fibrous joints are joints connected by fibrous tissue, consisting mainly of collagen. These are fixed joints where bones are united by a layer of white fibrous tissue of varying thickness. In the skull the joints between the bones are called sutures. Such immovable joints are also referred to as synarthroses. Types Most fibrous joints are also called "fixed" or "immovable". These joints have no joint cavity and are connected via fibrous connective tissue. The skull bones are connected by fibrous joints called '' sutures''. In fetal skulls the sutures are wide to allow slight movement during birth. They later become rigid ( synarthrodial). Some of the long bones in the body such as the radius and ulna in the forearm are joined by a ''syndesmosis'' (along the interosseous membrane). Syndemoses are slightly moveable ( amphiarthrodial). The distal tibiofibular joint is another example. A ''gomphosis'' is a joint between the root of a tooth and the socket in the maxil ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gomphosis
In anatomy, fibrous joints are joints connected by fibrous tissue, consisting mainly of collagen. These are fixed joints where bones are united by a layer of white fibrous tissue of varying thickness. In the skull the joints between the bones are called sutures. Such immovable joints are also referred to as synarthroses. Types Most fibrous joints are also called "fixed" or "immovable". These joints have no joint cavity and are connected via fibrous connective tissue. The skull bones are connected by fibrous joints called '' sutures''. In fetal skulls the sutures are wide to allow slight movement during birth. They later become rigid ( synarthrodial). Some of the long bones in the body such as the radius and ulna in the forearm are joined by a ''syndesmosis'' (along the interosseous membrane). Syndemoses are slightly moveable ( amphiarthrodial). The distal tibiofibular joint is another example. A ''gomphosis'' is a joint between the root of a tooth and the socket in the maxil ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Syndesmosis
In anatomy, fibrous joints are joints connected by fibrous tissue, consisting mainly of collagen. These are fixed joints where bones are united by a layer of white fibrous tissue of varying thickness. In the skull the joints between the bones are called sutures. Such immovable joints are also referred to as synarthroses. Types Most fibrous joints are also called "fixed" or "immovable". These joints have no joint cavity and are connected via fibrous connective tissue. The skull bones are connected by fibrous joints called '' sutures''. In fetal skulls the sutures are wide to allow slight movement during birth. They later become rigid ( synarthrodial). Some of the long bones in the body such as the radius and ulna in the forearm are joined by a ''syndesmosis'' (along the interosseous membrane). Syndemoses are slightly moveable ( amphiarthrodial). The distal tibiofibular joint is another example. A ''gomphosis'' is a joint between the root of a tooth and the socket in the maxil ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Inferior Tibiofibular Joint
The distal tibiofibular joint (tibiofibular syndesmosis) is formed by the rough, convex surface of the medial side of the distal end of the fibula, and a rough concave surface on the lateral side of the tibia. Below, to the extent of about 4 mm, these surfaces are smooth and covered with cartilage, which is continuous with that of the ankle joint. The ligaments are: * Anterior ligament of the lateral malleolus * Posterior ligament of the lateral malleolus * Interosseous membrane of leg The inferior transverse ligament of the tibiofibular syndesmosis is included in older versions of '' Gray's Anatomy'', but not in ''Terminologia Anatomica''. However, it still appears in some anatomy textbooks. It should not be confused with the superior tibiofibular joint The proximal tibiofibular articulation (also called superior tibiofibular joint) is an arthrodial joint between the lateral condyle of the tibia and the head of the fibula. The contiguous surfaces of the bones p ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Interosseous Membrane Of Forearm
The interosseous membrane of the forearm (rarely middle or intermediate radioulnar joint) is a fibrous sheet that connects the interosseous margins of the radius and the ulna. It is the main part of the radio-ulnar syndesmosis, a fibrous joint between the two bones. Function The interosseous membrane divides the forearm into anterior and posterior compartments, serves as a site of attachment for muscles of the forearm, and transfers loads placed on the forearm. The interosseous membrane is designed to shift compressive loads (as in doing a hand-stand) from the distal radius to the proximal ulna. The fibers within the interosseous membrane are oriented obliquely so that when force is applied the fibers are drawn taut, shifting more of the load to the ulna. This reduces the wear and tear of placing the whole load on a single joint. The role of the membrane in load shifting is illustrated when the interosseous membrane is cut; the forces on each bone equalize from their natural pro ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ulna
The ulna (''pl''. ulnae or ulnas) is a long bone found in the forearm that stretches from the elbow to the smallest finger, and when in anatomical position, is found on the medial side of the forearm. That is, the ulna is on the same side of the forearm as the little finger. It runs parallel to the radius, the other long bone in the forearm. The ulna is usually slightly longer than the radius, but the radius is thicker. Therefore, the radius is considered to be the larger of the two. Structure The ulna is a long bone found in the forearm that stretches from the elbow to the smallest finger, and when in anatomical position, is found on the medial side of the forearm. It is broader close to the elbow, and narrows as it approaches the wrist. Close to the elbow, the ulna has a bony process, the olecranon process, a hook-like structure that fits into the olecranon fossa of the humerus. This prevents hyperextension and forms a hinge joint with the trochlea of the humerus. There is ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Radius (bone)
The radius or radial bone is one of the two large bones of the forearm, the other being the ulna. It extends from the lateral side of the elbow to the thumb side of the wrist and runs parallel to the ulna. The ulna is usually slightly longer than the radius, but the radius is thicker. Therefore the radius is considered to be the larger of the two. It is a long bone, prism-shaped and slightly curved longitudinally. The radius is part of two joints: the elbow and the wrist. At the elbow, it joins with the capitulum of the humerus, and in a separate region, with the ulna at the radial notch. At the wrist, the radius forms a joint with the ulna bone. The corresponding bone in the lower leg is the fibula. Structure The long narrow medullary cavity is enclosed in a strong wall of compact bone. It is thickest along the interosseous border and thinnest at the extremities, same over the cup-shaped articular surface (fovea) of the head. The trabeculae of the spongy tissue are some ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dental Alveolus
Dental alveoli (singular ''alveolus'') are sockets in the jaws in which the roots of teeth are held in the alveolar process with the periodontal ligament. The lay term for dental alveoli is tooth sockets. A joint that connects the roots of the teeth and the alveolus is called ''gomphosis'' (plural ''gomphoses''). Alveolar bone is the bone that surrounds the roots of the teeth forming bone sockets. In mammals, tooth sockets are found in the maxilla, the premaxilla, and the mandible. Etymology 1706, "a hollow," especially "the socket of a tooth," from Latin alveolus "a tray, trough, basin; bed of a small river; small hollow or cavity," diminutive of alvus "belly, stomach, paunch, bowels; hold of a ship," from PIE root *aulo- "hole, cavity" (source also of Greek aulos "flute, tube, pipe;" Serbo-Croatian, Polish, Russian ulica "street," originally "narrow opening;" Old Church Slavonic uliji, Lithuanian aulys "beehive" (hollow trunk), Armenian yli "pregnant"). The word was extended in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
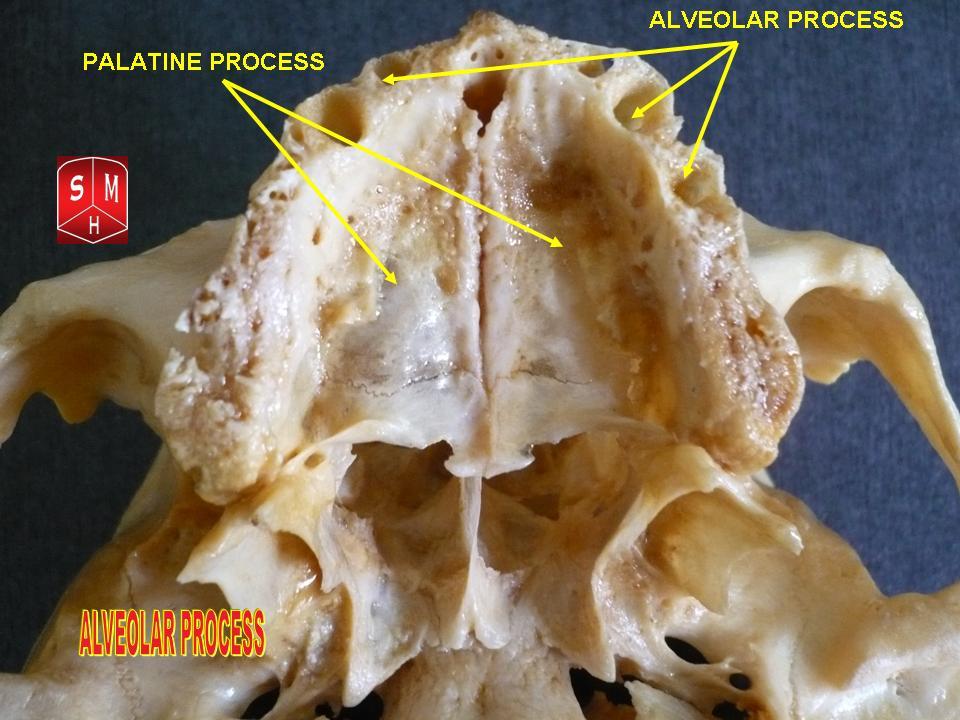
Maxilla
The maxilla (plural: ''maxillae'' ) in vertebrates is the upper fixed (not fixed in Neopterygii) bone of the jaw formed from the fusion of two maxillary bones. In humans, the upper jaw includes the hard palate in the front of the mouth. The two maxillary bones are fused at the intermaxillary suture, forming the anterior nasal spine. This is similar to the mandible (lower jaw), which is also a fusion of two mandibular bones at the mandibular symphysis. The mandible is the movable part of the jaw. Structure In humans, the maxilla consists of: * The body of the maxilla * Four processes ** the zygomatic process ** the frontal process of maxilla ** the alveolar process ** the palatine process * three surfaces – anterior, posterior, medial * the Infraorbital foramen * the maxillary sinus * the incisive foramen Articulations Each maxilla articulates with nine bones: * two of the cranium: the frontal and ethmoid * seven of the face: the nasal, zygomatic, lacrimal, inferior n ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Human Mandible
In anatomy, the mandible, lower jaw or jawbone is the largest, strongest and lowest bone in the human facial skeleton. It forms the lower jaw and holds the lower tooth, teeth in place. The mandible sits beneath the maxilla. It is the only movable bone of the skull (discounting the ossicles of the middle ear). It is connected to the temporal bones by the temporomandibular joints. The bone is formed prenatal development, in the fetus from a fusion of the left and right mandibular prominences, and the point where these sides join, the mandibular symphysis, is still visible as a faint ridge in the midline. Like other symphyses in the body, this is a midline articulation where the bones are joined by fibrocartilage, but this articulation fuses together in early childhood.Illustrated Anatomy of the Head and Neck, Fehrenbach and Herring, Elsevier, 2012, p. 59 The word "mandible" derives from the Latin word ''mandibula'', "jawbone" (literally "one used for chewing"), from ''wikt:mandere ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Anatomy
Anatomy () is the branch of biology concerned with the study of the structure of organisms and their parts. Anatomy is a branch of natural science that deals with the structural organization of living things. It is an old science, having its beginnings in prehistoric times. Anatomy is inherently tied to developmental biology, embryology, comparative anatomy, evolutionary biology, and phylogeny, as these are the processes by which anatomy is generated, both over immediate and long-term timescales. Anatomy and physiology, which study the structure and function (biology), function of organisms and their parts respectively, make a natural pair of related disciplines, and are often studied together. Human anatomy is one of the essential basic research, basic sciences that are applied in medicine. The discipline of anatomy is divided into macroscopic scale, macroscopic and microscopic scale, microscopic. Gross anatomy, Macroscopic anatomy, or gross anatomy, is the examination of an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Human Skull Side Suturas Right
Humans (''Homo sapiens'') are the most abundant and widespread species of primate, characterized by bipedalism and exceptional cognitive skills due to a large and complex brain. This has enabled the development of advanced tools, culture, and language. Humans are highly social and tend to live in complex social structures composed of many cooperating and competing groups, from families and kinship networks to political states. Social interactions between humans have established a wide variety of values, social norms, and rituals, which bolster human society. Its intelligence and its desire to understand and influence the environment and to explain and manipulate phenomena have motivated humanity's development of science, philosophy, mythology, religion, and other fields of study. Although some scientists equate the term ''humans'' with all members of the genus ''Homo'', in common usage, it generally refers to ''Homo sapiens'', the only extant member. Anatomically mode ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sharpey's Fibres
Sharpey's fibres (bone fibres, or perforating fibres) are a Matrix (biology), matrix of connective tissue consisting of bundles of strong predominantly type I Collagen, collagen fibres connecting periosteum to bone. They are part of the outer fibrous layer of periosteum, entering into the outer circumferential and interstitial Lamellae (zoology), lamellae of bone tissue. Sharpey's fibres are also used to attach muscle to the periosteum of bone by merging with the fibrous periosteum and underlying bone as well. A good example is the attachment of the rotator cuff muscles to the blade of the scapula. In the Tooth, teeth, Sharpey's fibres are the terminal ends of principal fibres (of the periodontal ligament) that insert into the cementum and into the periosteum of the alveolar bone. A study on rats suggests that the three-dimensional structure of Sharpey's fibres intensifies the continuity between the periodontal ligament fibre and the Dental alveolus, alveolar bone (tooth socket), ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |