|
Synchro
A synchro (also known as selsyn and by other brand names) is, in effect, a transformer whose primary-to-secondary coupling may be varied by physically changing the relative orientation of the two windings. Synchros are often used for measuring the angle of a rotating machine such as an antenna platform or transmitting rotation. In its general physical construction, it is much like an electric motor. The primary winding of the transformer, fixed to the rotor, is excited by an alternating current, which by electromagnetic induction causes voltages to appear between the Y-connected secondary windings fixed at 120 degrees to each other on the stator. The voltages are measured and used to determine the angle of the rotor relative to the stator. Uses Synchro systems were first used in the control system of the Panama Canal in the early 1900s to transmit lock gate and valve stem positions, and water levels, to the control desks. Fire-control system designs developed during Worl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Electrical Generator
In electricity generation, a generator, also called an ''electric generator'', ''electrical generator'', and ''electromagnetic generator'' is an electromechanical device that converts mechanical energy to electrical energy for use in an external circuit. In most generators which are rotating machines, a source of kinetic power rotates the generator's shaft, and the generator produces an electric current at its output terminals which flows through an external circuit, powering electrical loads. Sources of mechanical energy used to drive generators include steam turbines, gas turbines, water turbines, internal combustion engines, wind turbines and even hand cranks. Generators produce nearly all of the electric power for worldwide electric power grids. The first electromagnetic generator, the Faraday disk, was invented in 1831 by British scientist Michael Faraday. The reverse conversion of electrical energy into mechanical energy is done by an electric motor, and motors a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Servomechanism
In mechanical and control engineering, a servomechanism (also called servo system, or simply servo) is a control system for the position and its time derivatives, such as velocity, of a mechanical system. It often includes a servomotor, and uses closed-loop control to reduce steady-state error and improve dynamic response. In closed-loop control, error-sensing negative feedback is used to correct the action of the mechanism. In displacement-controlled applications, it usually includes a built-in encoder or other position feedback mechanism to ensure the output is achieving the desired effect. Following a specified motion trajectory is called servoing, where "servo" is used as a verb. The ''servo'' prefix originates from the Latin word ''servus'' meaning slave. The term correctly applies only to systems where the feedback or error-correction signals help control mechanical position, speed, attitude or any other measurable variables. For example, an automotive power win ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
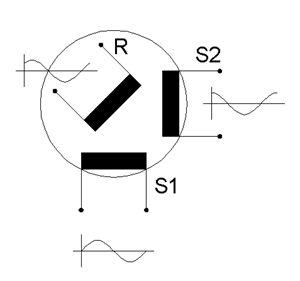
Resolver (electrical)
A resolver is a type of rotary electrical transformer used for measuring degrees of rotation. It is considered an analog device, and has digital counterparts such as the digital resolver, rotary (or pulse) encoder. A rotating coil induces voltage in two stationary coils, and by comparing the phase of the signal in the two secondaries, the angle can be accurately determined. These systems were commonly used in mechanical control systems, for instance, counting the number of revolutions of a screw jack to move an aircraft's flaps to a specific extension. Description The most common type of resolver is the brushless transmitter resolver (other types are described at the end). On the outside, this type of resolver may look like a small electrical motor having a stator and rotor. On the inside, the configuration of the wire windings makes it different. The stator portion of the resolver houses three windings: an exciter winding and two two-phase windings, usually labeled "x" a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Servomotor
A servomotor (or servo motor or simply servo) is a rotary or linear actuator that allows for precise control of angular or linear position, velocity, and acceleration in a mechanical system. It constitutes part of a servomechanism, and consists of a suitable motor coupled to a sensor for position feedback and a controller (often a dedicated module designed specifically for servomotors). Servomotors are not a specific class of motor, although the term ''servomotor'' is often used to refer to a motor suitable for use in a closed-loop control system. Servomotors are used in applications such as robotics, CNC machinery, and automated manufacturing. Mechanism A servomotor is a closed-loop servomechanism that uses position feedback (either linear or rotational position) to control its motion and final position. The input to its control is a signal (either analog or digital) representing the desired position of the output shaft. The motor is paired with some type of positio ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rotary Encoder
A rotary encoder, also called a shaft encoder, is an electro-mechanical device that converts the angle, angular position or motion of a shaft or axle to Analog signal, analog or Digital signal, digital output signals. There are two main types of rotary encoder: absolute and incremental. The output of an absolute encoder indicates the current shaft position, making it an transducer, angle transducer. The output of an incremental encoder provides information about the ''motion'' of the shaft, which typically is processed elsewhere into information such as position, speed and distance. Rotary encoders are used in a wide range of applications that require monitoring or control, or both, of mechanical systems, including industrial controls, robotics, photographic lenses, computer input devices such as optomechanical computer mouse, mice and trackballs, controlled stress rheometers, and rotating radar platforms. Technologies * Mechanical: Also known as conductive encoders. A serie ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rotor (electric)
The rotor is a moving component of an electromagnetic system in the electric motor, electric generator, or alternator. Its rotation is due to the interaction between the windings and magnetic fields which produces a torque around the rotor's axis.Staff. "Understanding Alternators. What Is an Alternator and How Does It Work." N.p., n.d. Web. 24 November 2014 . Early development An early example of electromagnetic rotation was the first rotary machine built by Ányos Jedlik with electromagnets and a commutator, in 1826-27. Other pioneers in the field of electricity include Hippolyte Pixii who built an alternating current generator in 1832, and William Ritchie's construction of an electromagnetic generator with four rotor coils, a commutator and brushes, also in 1832. Development quickly included more useful applications such as Moritz Hermann Jacobi's motor that could lift 10 to 12 pounds with a speed of one foot per second, about 15 watts of mechanical power in 1834. In 18 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Electromagnetic Induction
Electromagnetic or magnetic induction is the production of an electromotive force, electromotive force (emf) across an electrical conductor in a changing magnetic field. Michael Faraday is generally credited with the discovery of induction in 1831, and James Clerk Maxwell mathematically described it as Faraday's law of induction. Lenz's law describes the direction of the induced field. Faraday's law was later generalized to become the Maxwell–Faraday equation, one of the four Maxwell's equations, Maxwell equations in his theory of electromagnetism. Electromagnetic induction has found many applications, including electrical components such as inductors and transformers, and devices such as electric motors and electric generator, generators. History Electromagnetic induction was discovered by Michael Faraday, published in 1831. It was discovered independently by Joseph Henry in 1832. In Faraday's first experimental demonstration, on August 29, 1831, he wrapped two wires aro ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Crystal Oscillators
A crystal oscillator is an electronic oscillator circuit that uses a piezoelectric crystal as a frequency-selective element. The oscillator frequency is often used to keep track of time, as in quartz wristwatches, to provide a stable clock signal for digital integrated circuits, and to stabilize frequencies for radio transmitters and receivers. The most common type of piezoelectric resonator used is a quartz crystal, so oscillator circuits incorporating them became known as crystal oscillators. However, other piezoelectric materials including polycrystalline ceramics are used in similar circuits. A crystal oscillator relies on the slight change in shape of a quartz crystal under an electric field, a property known as inverse piezoelectricity. A voltage applied to the electrodes on the crystal causes it to change shape; when the voltage is removed, the crystal generates a small voltage as it elastically returns to its original shape. The quartz oscillates at a stable resonan ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Transformer
In electrical engineering, a transformer is a passive component that transfers electrical energy from one electrical circuit to another circuit, or multiple Electrical network, circuits. A varying current in any coil of the transformer produces a varying magnetic flux in the transformer's core, which induces a varying electromotive force, electromotive force (EMF) across any other coils wound around the same core. Electrical energy can be transferred between separate coils without a metallic (conductive) connection between the two circuits. Faraday's law of induction, discovered in 1831, describes the induced voltage effect in any coil due to a changing magnetic flux encircled by the coil. Transformers are used to change Alternating current, AC voltage levels, such transformers being termed step-up or step-down type to increase or decrease voltage level, respectively. Transformers can also be used to provide galvanic isolation between circuits as well as to couple stages of signa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rotary Transformer
A rotary (rotatory) transformer is a specialized transformer used to couple electrical signals between two parts that rotate in relation to each other. They may be either cylindrical or 'pancake' shaped. Slip rings can be used for the same purpose, but are subject to friction, wear, intermittent contact, and limitations on the rotational speed that can be accommodated without damage. Wear can be eliminated by using a pool of liquid Mercury (element), mercury or liquid metal alloy instead of a solid ring contact, but the Mercury poisoning, toxicity and slow corrosion of mercury are problematic, and very high rotational speeds are again difficult to achieve. A rotary transformer has none of these limitations. Rotary transformers are constructed by winding the primary and secondary windings into separate halves of a ''cup core''; these concentric halves face each other, with each half mounted to one of the rotating parts. Magnetic flux provides the coupling from one half of th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Antenna (electronics)
In radio-frequency engineering, an antenna (American English) or aerial (British English) is an electronic device that converts an alternating current, alternating electric current into radio waves (transmitting), or radio waves into an electric current (receiving). It is the interface between radio waves Radio propagation, propagating through space and electric currents moving in metal Electrical conductor, conductors, used with a transmitter or receiver (radio), receiver. In transmission (telecommunications), transmission, a radio transmitter supplies an electric current to the antenna's Terminal (electronics), terminals, and the antenna radiates the energy from the current as electromagnetic radiation, electromagnetic waves (radio waves). In receiver (radio), reception, an antenna intercepts some of the power of a radio wave in order to produce an electric current at its terminals, that is applied to a receiver to be amplifier, amplified. Antennas are essential components ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |