|
Sydney Marow Eardley-Wilmot
Rear Admiral Sir Sydney Marow Eardley-Wilmot (3 October 1847 – 27 February 1929) was a Royal Navy officer who took an active part in the Suakin Expedition and who lost a hand as the result of an explosion at the torpedo school . He had a specialism in naval gunnery and was Superintendent of Ordnance Stores at the Admiralty during the period of the Anglo-German naval arms race when the Dreadnought Fleet was developed. He advocated for the construction of the largest guns possible. He wrote a number of works of naval history as well as two novels that feature near-future naval warfare. Early life and family Sydney Eardley-Wilmot was born at Mortlake, Surrey, on 3 October 1847, the fifth son of Sir John Eardley-Wilmot, 2nd Baronet,"Wills and Bequests", '' The Times'', 10 June 1929, p. 18. member of Parliament, judge, and author. He was educated at the academy of the Reverend W. Foster at Stubbington, Fareham. Eardley-Wilmot married Grace Hoare, daughter of Thomas R. H ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Admiral Sydney Eardley-Wilmot
Admiral is one of the highest ranks in some navies. In the Commonwealth nations and the United States, a "full" admiral is equivalent to a "full" general in the army or the air force, and is above vice admiral and below admiral of the fleet, or fleet admiral. Etymology The word in Middle English comes from Anglo-French , "commander", from Medieval Latin , . These evolved from the Arabic () – (), “king, prince, chief, leader, Nobility, nobleman, lord, a governor, commander, or person who rules over a number of people,” and (), the Arabic article answering to “the.” In Arabic, admiral is also represented as (), where () means the sea. The 1818 edition of Samuel Johnson's ''A Dictionary of the English Language'', edited and revised by the Rev. Henry Todd (priest), Henry John Todd, states that the term “has been traced to the Arab. emir or amir, lord or commander, and the Greek language, Gr. , the sea, q. d. ''prince of the sea''. The word is written both with a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
William Assheton Eardley-Wilmot, 3rd Baronet
Sir William Assheton Eardley-Wilmot, 3rd Baronet (16 May 1841, London - 12 April 1896) was a British Army officer, most notable for his time as Deputy Assistant Adjutant General in Ireland from 1879 to 1882. His regiment was the Northumberland Fusiliers. He was the second child and eldest son of Sir John Eardley-Wilmot, 2nd Baronet and succeeded him in the baronetcy on his death in 1892. William was educated at Charterhouse School from 1853 to 1859 and then at Balliol College, Oxford. He married Mary Russell, daughter of David Watts Russell, on 12 December 1876. They had five children, including his successor John and the Royal Navy officer Frederick Neville Eardley-Wilmot Frederick may refer to: People * Frederick (given name), the name Nobility Anhalt-Harzgerode *Frederick, Prince of Anhalt-Harzgerode (1613–1670) Austria * Frederick I, Duke of Austria (Babenberg), Duke of Austria from 1195 to 1198 * Frederi .... References {{DEFAULTSORT:Eardley-Wilmot, Willia ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
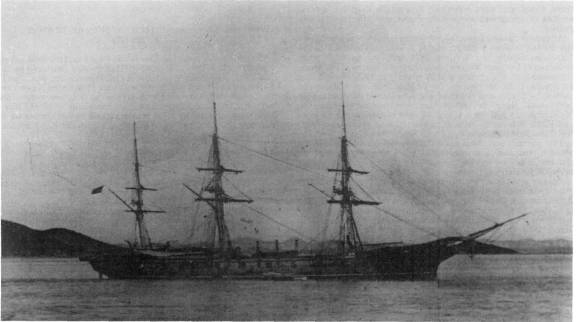
Composite Sloop
A screw sloop is a propeller-driven sloop-of-war. In the 19th century, during the introduction of the steam engine, ships driven by propellers were differentiated from those driven by paddle-wheels by referring to the ship's ''screws'' (propellers). Other propeller-driven warships included screw frigates and screw corvette A corvette is a small warship. It is traditionally the smallest class of vessel considered to be a proper (or " rated") warship. The warship class above the corvette is that of the frigate, while the class below was historically that of the slo ...s. See also * CSS ''Alabama'' * USS ''Alaska'' * USS ''Contoocook'' * HMS ''Gannet'', now a museum ship. * USS ''Housatonic'', sunk by the first successful submarine attack. * USS ''Wyoming'' * * Ship types {{navy-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
British Admiralty
The Admiralty was a department of the Government of the United Kingdom responsible for the command of the Royal Navy until 1964, historically under its titular head, the Lord High Admiral – one of the Great Officers of State. For much of its history, from the early 18th century until its abolition, the role of the Lord High Admiral was almost invariably put "in commission" and exercised by the Lords Commissioner of the Admiralty, who sat on the governing Board of Admiralty, rather than by a single person. The Admiralty was replaced by the Admiralty Board in 1964, as part of the reforms that created the Ministry of Defence and its Navy Department (later Navy Command). Before the Acts of Union 1707, the Office of the Admiralty and Marine Affairs administered the Royal Navy of the Kingdom of England, which merged with the Royal Scots Navy and the absorbed the responsibilities of the Lord High Admiral of the Kingdom of Scotland with the unification of the Kingdom of Great ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Commander (Royal Navy)
Commander (Cdr) is a senior officer rank of the Royal Navy of the United Kingdom. It is immediately junior to captain and immediately senior to the rank of lieutenant commander. Officers holding the junior rank of lieutenant commander are not considered to be commanders. History The title (originally 'master and commander') originated in around 1670 to describe Royal Navy officers who commanded ships of war too large to be commanded by a lieutenant, but too small to warrant the assignment of a post-captain, or (before about 1770) a sailing-master who was in charge of a ship's navigation. These ships were usually unrated sloops-of-war of no more than 20 guns, fireships, hospital ships and store ships. The commanding officer of this type of ship was responsible for both sailing and fighting the ship and was thus its 'master and commander'. Before 1750, the rank was broadly considered as the limit of advancement for those without patronage, especially those who had been promot ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Corvette
A corvette is a small warship. It is traditionally the smallest class of vessel considered to be a proper (or " rated") warship. The warship class above the corvette is that of the frigate, while the class below was historically that of the sloop-of-war. The modern roles that a corvette fulfills include coastal patrol craft, missile boat and fast attack craft. These corvettes are typically between 500 tons and 2,000 .although recent designs may approach 3,000 tons, having size and capabilities that overlap with smaller frigates. However unlike contemporary frigates, a modern corvette does not have sufficient endurance and seaworthiness for long voyages. The word "corvette" is first found in Middle French, a diminutive of the Dutch word ''corf'', meaning a "basket", from the Latin ''corbis''. The rank "corvette captain", equivalent in many navies to "lieutenant commander", derives from the name of this type of ship. The rank is the most junior of three "captain" ranks in sev ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
John Fisher, 1st Baron Fisher
John Arbuthnot Fisher, 1st Baron Fisher, (25 January 1841 – 10 July 1920), commonly known as Jacky or Jackie Fisher, was a British Admiral of the Fleet. With more than sixty years in the Royal Navy, his efforts to reform the service helped to usher in an era of modernisation which saw the supersession of wooden sailing ships armed with muzzleloader, muzzle-loading cannon by steel-hulled battlecruisers, submarines and the first aircraft carriers. Fisher has a reputation as an innovator, strategist and developer of the navy rather than as a seagoing admiral involved in major battles, although in his career he experienced all these things. When appointed First Sea Lord in 1904 he removed 150 ships then on active service which were no longer useful and set about constructing modern replacements, developing a modern fleet prepared to meet German Empire, Germany during the First World War. Fisher saw the need to improve the range, accuracy and rate-of-fire of naval gunnery, and be ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
HMS Queen Charlotte (1810)
HMS ''Queen Charlotte'' was a 104-gun first-rate ship of the line of the Royal Navy, launched on 17 July 1810 at Deptford. She replaced the first sunk in 1800. Career A Black sailor from Grenada named William Brown was discharged from ''Queen Charlotte'' in 1815 for being a woman. She was Lord Exmouth's flagship during the Bombardment of Algiers in 1816. On 17 September 1817, ''Linnet'', a tender to ''Queen Charlotte'', seized a smuggled cargo of tobacco. The officers and crew of ''Queen Charlotte'' shared in the prize money. On 17 December 1823, ''Queen Charlotte'' was driven into the British ship ''Brothers'' at Portsmouth, Hampshire, England. ''Brothers'' suffered severe damage in the collision. Fate ''Queen Charlotte'' was converted to serve as a training ship A training ship is a ship used to train students as sailors. The term is mostly used to describe ships employed by navies to train future officers. Essentially there are two types: those used for traini ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Oxford University Press
Oxford University Press (OUP) is the university press of the University of Oxford. It is the largest university press in the world, and its printing history dates back to the 1480s. Having been officially granted the legal right to print books by decree in 1586, it is the second oldest university press after Cambridge University Press. It is a department of the University of Oxford and is governed by a group of 15 academics known as the Delegates of the Press, who are appointed by the vice-chancellor of the University of Oxford. The Delegates of the Press are led by the Secretary to the Delegates, who serves as OUP's chief executive and as its major representative on other university bodies. Oxford University Press has had a similar governance structure since the 17th century. The press is located on Walton Street, Oxford, opposite Somerville College, in the inner suburb of Jericho. For the last 500 years, OUP has primarily focused on the publication of pedagogical texts and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Who Was Who
''Who's Who'' is a reference work. It is a book, and also a CD-ROM and a website, giving information on influential people from around the world. Published annually as a book since 1849, it lists people who influence British life, according to its editors. Entries include notable figures from government, politics, academia, business, sport and the arts. ''Who's Who 2022'' is the 174th edition and includes more than 33,000 people. The book is the original ''Who's Who'' book and "the pioneer work of its type". The book is an origin of the expression "who's who" used in a wider sense. History ''Who's Who'' has been published since 1849."More about Who's Who" OUP. It was originally published by . ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Canadian General Service Medal
The Canada General Service Medal was a campaign medal awarded by the Canadian Government to both Imperial and Canadian forces for duties related to the Fenian raids between 1866 and 1871. The medal was initially issued in 1899 and had to be applied for. The application period was later extended to 1907, then to 1928. With late applications, 17,623 medals were awarded, including 15,300 to members of Canadian units. The medal, in diameter, is silver and has a plain straight swivel suspender. The obverse bears the head of Queen Victoria with the legend VICTORIA REGINA ET IMPERATRIX, while the reverse depicts the ensign of Canada surrounded by a wreath of maple leaves with the word CANADA above.The recipient's name, rank and unit appear on the rim of the medal. A number of different impressed and engraved styles were used, reflecting that the medal was awarded over a long period of time.The wide ribbon consists of three equal stripes of red, white and red. In 1943 the same ribb ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |




.jpg)