|
Sycosis
Sycosis is an inflammation of hair follicles, especially of the beard area,thefreedictionary.com > sycosisciting: Dorland's Medical Dictionary for Health Consumers. 2007thefreedictionary.com > sycosisciting: The American Heritage® Medical Dictionary Copyright © 2007thefreedictionary.com > sycosisciting: Miller-Keane Encyclopedia & Dictionary of Medicine, Nursing, and Allied Health, Seventh Edition. © 2003 and generally classified as papulopustular and chronic. Types Types include: * Sycosis barbae * Lupoid sycosis * Tinea sycosis * Herpetic sycosis Herpes simplex is a viral infection caused by the herpes simplex virus. Infections are categorized based on the part of the body infected. Oral herpes involves the face or mouth. It may result in small blisters in groups often called cold ... References Bacterium-related cutaneous conditions {{dermatology-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sycosis Barbae
Sycosis is an inflammation of hair follicles, especially of the beard area,thefreedictionary.com > sycosisciting: Dorland's Medical Dictionary for Health Consumers. 2007thefreedictionary.com > sycosisciting: The American Heritage® Medical Dictionary Copyright © 2007thefreedictionary.com > sycosisciting: Miller-Keane Encyclopedia & Dictionary of Medicine, Nursing, and Allied Health, Seventh Edition. © 2003 and generally classified as papulopustular and chronic. Types Types include: * Sycosis barbae * Lupoid sycosis * Tinea sycosis Dermatophytosis, also known as ringworm, is a fungal infection of the skin. Typically it results in a red, itchy, scaly, circular rash. Hair loss may occur in the area affected. Symptoms begin four to fourteen days after exposure. Multiple ar ... * Herpetic sycosis References Bacterium-related cutaneous conditions {{dermatology-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
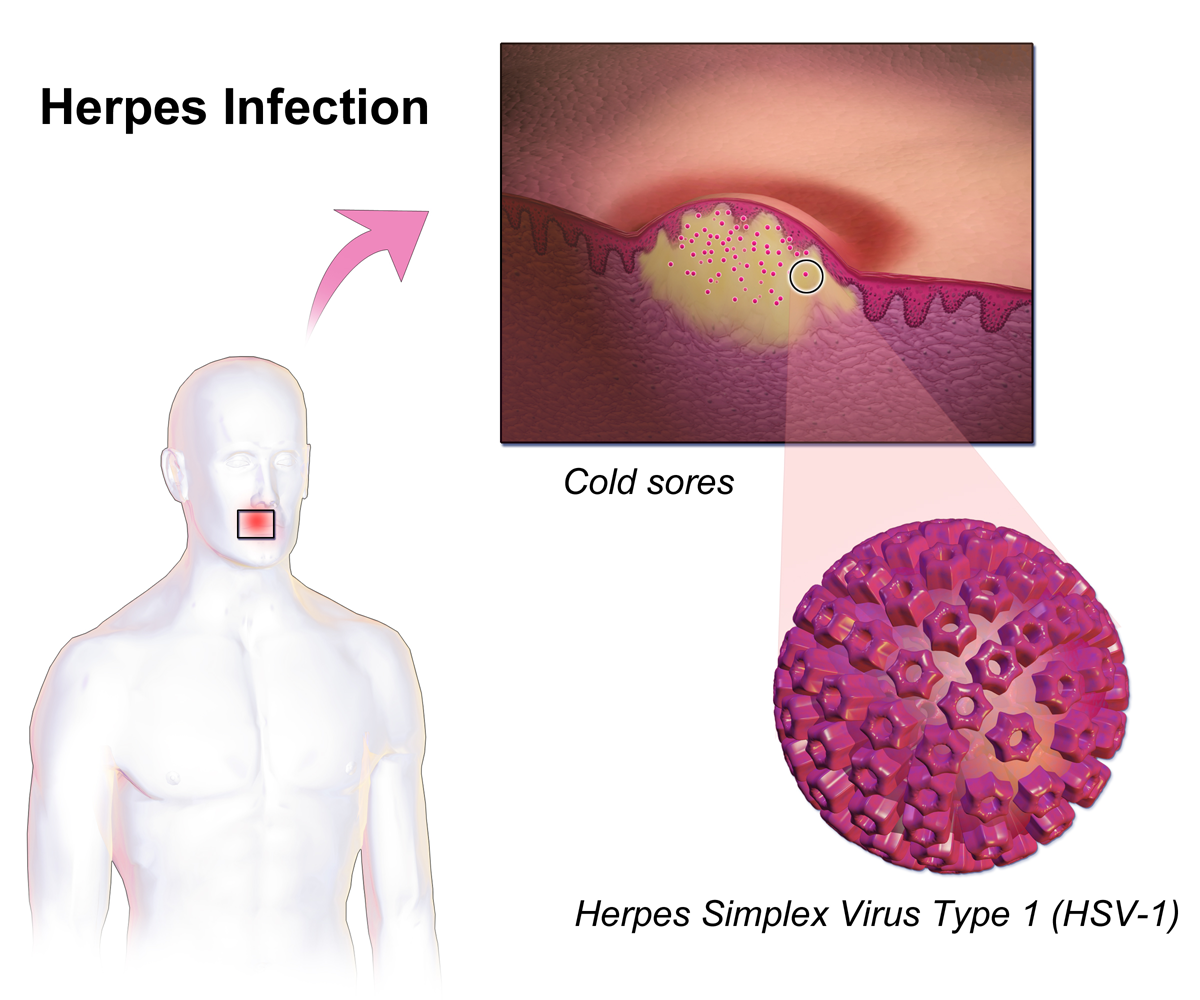
Herpetic Sycosis
Herpes simplex is a viral infection caused by the herpes simplex virus. Infections are categorized based on the part of the body infected. Oral herpes involves the face or mouth. It may result in small blisters in groups often called cold sores or fever blisters or may just cause a sore throat. Genital herpes, often simply known as herpes, involves the genitalia. It may have minimal symptoms or form blisters that break open and result in small ulcers. These typically heal over two to four weeks. Tingling or shooting pains may occur before the blisters appear. Herpes cycles between periods of active disease followed by periods without symptoms. The first episode is often more severe and may be associated with fever, muscle pains, swollen lymph nodes and headaches. Over time, episodes of active disease decrease in frequency and severity. Herpetic whitlow typically involves the fingers or thumb. Herpes simplex keratitis involves the eye. Herpesviral encephalitis involves ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lupoid Sycosis
Lupoid sycosis is a cutaneous condition that is characterized by a scarring form of deep folliculitis, typically affecting the beard area. See also * Sycosis barbae * List of cutaneous conditions References Bacterium-related cutaneous conditions {{Dermatology-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hair Follicle
The hair follicle is an organ found in mammalian skin. It resides in the dermal layer of the skin and is made up of 20 different cell types, each with distinct functions. The hair follicle regulates hair growth via a complex interaction between hormones, neuropeptides, and immune cells. This complex interaction induces the hair follicle to produce different types of hair as seen on different parts of the body. For example, terminal hairs grow on the scalp and lanugo hairs are seen covering the bodies of fetuses in the uterus and in some newborn babies. The process of hair growth occurs in distinct sequential stages. The first stage is called ''anagen'' and is the active growth phase, ''telogen'' is the resting stage, ''catagen'' is the regression of the hair follicle phase, ''exogen'' is the active shedding of hair phase and lastly ''kenogen'' is the phase between the empty hair follicle and the growth of new hair. The function of hair in humans has long been a subject of int ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Beard
A beard is the hair that grows on the jaw, chin, upper lip, lower lip, cheeks, and neck of humans and some non-human animals. In humans, usually pubescent or adult males are able to grow beards. Throughout the course of history, societal attitudes toward male beards have varied widely depending on factors such as prevailing cultural-religious traditions and the current era's fashion trends. Some religions (such as some sects of Islam, and Sikhism) have considered a full beard to be essential and mandate it as part of their observance. Other cultures, even while not officially mandating it, view a beard as central to a man's virility, exemplifying such virtues as wisdom, strength, sexual prowess and high social status. In cultures where facial hair is uncommon (or currently out of fashion), beards may be associated with poor hygiene or an unconventional demeanor. In countries with colder climates, beards help protect the wearer's face from the elements. Beards also provide sun ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Miller-Keane Encyclopedia & Dictionary Of Medicine, Nursing, And Allied Health
The ''Miller-Keane Encyclopedia & Dictionary of Medicine, Nursing, and Allied Health'' is written for use by students and health care providers including medics, nurses, and paramedics. The entries are alphabetical and compiled with multidisciplinary collaboration. Illustrations and tables were included from the sixth edition. The latest edition is the seventh, which lists over 40,000 terms and was published in 2005. The book has been reviewed by publications including the ''American Journal of Occupational Therapy The ''American Journal of Occupational Therapy'' is a bimonthly peer-reviewed medical journal that is published by the American Occupational Therapy Association. It covers research practice and health care issues in the field of occupational thera ...'', '' Gastroenterology Nursing'', '' Annals of the Rheumatic Diseases'', '' Hospitals & Health Networks'', and '' Hospital Topics''. References Medical dictionaries {{med-book-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Papulopustular
A papulopustular condition is a condition composed of both papule and pustules.thefreedictionary.com > papulopustularciting: *The American Heritage® Medical Dictionary Copyright © 2007 *Mosby's Medical Dictionary, 8th edition. © 2009 * Miller-Keane Encyclopedia & Dictionary of Medicine, Nursing, and Allied Health, Seventh Edition. 2003 Examples of papulopustular conditions include: *Papulopustular rosacea *Papulopustular acne *Sycosis Sycosis is an inflammation of hair follicles, especially of the beard area,thefreedictionary.com > sycosisciting: Dorland's Medical Dictionary for Health Consumers. 2007thefreedictionary.com > sycosisciting: The American Heritage® Medical Diction ... References Dermatologic terminology {{dermatology-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tinea Sycosis
Dermatophytosis, also known as ringworm, is a fungal infection of the skin. Typically it results in a red, itchy, scaly, circular rash. Hair loss may occur in the area affected. Symptoms begin four to fourteen days after exposure. Multiple areas can be affected at a given time. About 40 types of fungus can cause ringworm. They are typically of the ''Trichophyton'', ''Microsporum'', or '' Epidermophyton'' type. Risk factors include using public showers, contact sports such as wrestling, excessive sweating, contact with animals, obesity, and poor immune function. Ringworm can spread from other animals or between people. Diagnosis is often based on the appearance and symptoms. It may be confirmed by either culturing or looking at a skin scraping under a microscope. Prevention is by keeping the skin dry, not walking barefoot in public, and not sharing personal items. Treatment is typically with antifungal creams such as clotrimazole or miconazole. If the scalp is involved, a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |