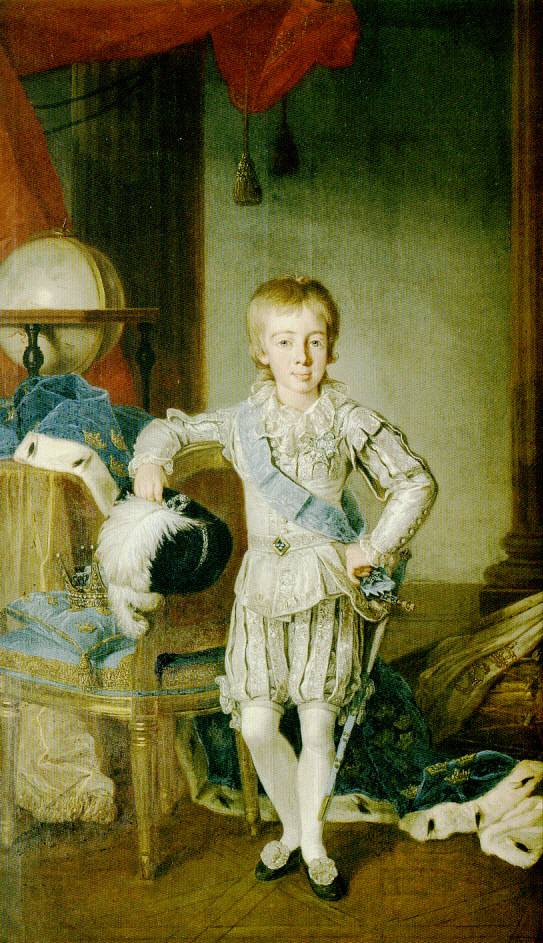|
Swiss Bourgeoisie
In some cantons of Switzerland, the bourgeoisie is both a form of local community right and a personal right. The system of bourgeoisie stems from medieval urban law which was common to all the cities of Western Europe (see: Bourgeois of Brussels). The bourgeoisie, or bourgeois ''commune'' (i.e. municipality), is a local "community" that still exists in certain cantons, in which inhabitants originating from that specific ''commune'', called "old bourgeois", as opposed to the new inhabitants, participate. This current bourgeoisie system, which can be traced back to the law on the communes of 1866, has gradually lost importance. However, these institutions still manage some hospitals and, in some cantons, confer a "right to bourgeoisie", sometimes prior to Swiss naturalization. This system is linked to the place of origin. There is a "Swiss Federation of Bourgeoisies and Corporations" whose roles include the defence of "maintenance of bourgeois institutions". In Switzerland, there ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cantons Of Switzerland
The 26 cantons of Switzerland (german: Kanton; french: canton ; it, cantone; Sursilvan and Surmiran: ; Vallader and Puter: ; Sutsilvan: ; Rumantsch Grischun: ) are the member states of the Swiss Confederation. The nucleus of the Swiss Confederacy in the form of the first three confederate allies used to be referred to as the . Two important periods in the development of the Old Swiss Confederacy are summarized by the terms ('Eight Cantons'; from 1353–1481) and ('Thirteen Cantons', from 1513–1798).rendered "the 'confederacy of eight'" and "the 'Thirteen-Canton Confederation'", respectively, in: Each canton of the Old Swiss Confederacy, formerly also ('lieu/locality', from before 1450), or ('estate', from ), was a fully sovereign state with its own border controls, army, and currency from at least the Treaty of Westphalia (1648) until the establishment of the Swiss federal state in 1848, with a brief period of centralised government during the Helvetic Republic ( ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Salenstein
Salenstein is a Municipalities of Switzerland, municipality in Kreuzlingen District in the Cantons of Switzerland, canton of Thurgau in Switzerland. Salenstein was the home village of Napoleon III, who lived at Castle Arenenberg in his youth. History In the ''Eichholz'' area near Salenstein, burial mounds from the late Hallstatt culture, Hallstatt period (750-450 BC) have been discovered. The modern village of Salenstein is first mentioned in 1092 as ''Salestein''. In the 11th Century, Salenstein Castle was built as a seat for the Ministerialis (unfree knights in the service of a feudal overlord) officials of Reichenau Abbey. The smaller castles of Sandegg and Riederen were added to provide further housing for the officials. The land rights, ''Herrschaft (territory), Herrschaft'' rights and the High, middle and low justice, low court rights were all held by the Abbey. In 1401, the noble Clare of Breitenstein, founded a Béguinage house in the ''Götschen'' woods, which was ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
History Of Switzerland
Since 1848 the Swiss Confederation has been a federal republic of relatively autonomous cantons, some of which have a history of federation that goes back more than 700 years, putting them among the world's oldest surviving republics. The early history of the region is tied to that of Alpine culture. Switzerland was inhabited by the Helvetii, and it came under Roman rule in the 1st century BC. Gallo-Roman culture was amalgamated with Germanic influence during Late Antiquity, with the eastern part of Switzerland becoming Alemannic territory. The area of Switzerland was incorporated in the Frankish Empire in the 6th century. In the High Middle Ages, the eastern part became part of the Duchy of Swabia within the Holy Roman Empire, while the western part was part of Burgundy. The Old Swiss Confederacy in the Late Middle Ages (the ''Eight Cantons'') established its independence from the House of Habsburg and the Duchy of Burgundy, and in the Italian Wars gained territory south of t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bourgeois Of Paris
A bourgeois of Paris was traditionally a member of one of the corporations or guilds that existed under the Ancien Régime. According to Article 173 of the Custom of Paris, a bourgeois had to possess a domicile in Paris as a tenant or owner for at least a year and a day. This qualification was also required for public offices such as provost of the merchants, alderman or consul, but unlike the bourgeois or citizens of other free cities, Parisians did not need letters of bourgeoisie to prove their status. A bourgeois of Paris had privileges as well as duties. While they were exempt from paying the taille, they were required to pay the city taxes, contribute to a public charity, arm themselves at their own expense, and join the urban militia. Definition According to article 173 (previously 129) of the Custom of Paris, the "right of the Bourgeoisie" can be attained in Paris by any person "living and residing there for a year and a day." "Living and residing" meant having a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Place Of Origin
In Switzerland, the place of origin (german: Heimatort or Bürgerort, literally "home place" or "citizen place"; french: Lieu d'origine; it, Luogo d'origine) denotes where a Swiss citizen has their municipal citizenship, usually inherited from previous generations. It is not to be confused with the place of birth or place of residence, although two or all three of these locations may be identical depending on the person's circumstances. Acquisition of municipal citizenship Swiss citizenship has three tiers. For a person applying to naturalise as a Swiss citizen, these tiers are as follows: *Municipal citizenship, granted by the place of residence after fulfilling several preconditions, such as sufficient knowledge of the local language, integration into local society, and a minimum number of years lived in said municipality. *Cantonal (state) citizenship, for which a Swiss municipal citizenship is required. This requires a certain number of years lived in said canton. *Country ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bourgeoisie Of Geneva
The inhabitants of the ''seigneurie'' and the Republic of Geneva were divided into four orders of people:Jean-Jacques Rousseau, Collection complète des œuvres de J.J. Rousseau : Œuvres mêlées, 1776, p. 451 the Citoyens, the Bourgeois, the Habitants, and the Natifs. The Citoyens and the Bourgeois formed the bourgeoisie and, thus the patrician class of the Republic. Status *The Citoyens (citizens) were offspring of bourgeois and born in the city. Only their males could reach the status of magistrate. *The Bourgeois were offspring of bourgeois or citizens who were born in a foreign country, or foreigners who had acquired the right of the bourgeoisie from the Magistrate. To gain access to the bourgeoisie, they had to buy it. In addition to the sum of money, it was customary to pay for a "seillot" and often a firearm. The bourgeoisie acquired services for free or at a reduced price. The bourgeois could be on the General Council and the Council of Two Hundred. *The Habitants (inh ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
In Der Maur
In der Maur (also written as In der Mauer, Indermaur, Indermauer) is an ancient Swiss family. Throughout the Middle Ages and Renaissance, the family held positions of political and economic power as members of the Swiss bourgeoisie, bourgeoisie in Berneck, St. Gallen and as members of the Gentry, lower nobility in Kurtatsch an der Weinstraße. The In der Maur von Berneck family were first granted a Achievement (heraldry), coat of arms in 1478, when Hermann In der Maur was appointed as the Amtmann, Ammann of the Abbot of St. Gallen of Berneck— a position the family continued to hold throughout the reigns of the Prince-Abbots of the Abbey of Saint Gall within the Holy Roman Empire. Members of the family also served as Imperial tax collectors and as clerks of the Court of Berneck. The first member of the family to hold the position of Ammann in Berneck was Ulrich In der Maur in 1435. After Hans Indermaur von Berneck settled in Rheineck in 1590, the family were granted fiefdoms as v ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Federer Family
The Federer family is an old Swiss family that is part of the bourgeoisie of Berneck, St. Gallen. The family originated in the 5th century and rose to prominence in the Middle Ages, with members holding local government offices under the Prince-Abbots of the Abbey of St. Gallen. Notable members of the family include the tennis player Roger Federer, the Catholic priest and writer Heinrich Federer, and the politician Barbara Schmid-Federer. History The Federer family originates in the 5th century from the village of Berneck, St. Gallen in northeastern Switzerland, near the Austrian border. As part of the Swiss bourgeoisie, members of the family were entitled to positions in the local government. The name Federer translates from the Swiss German word for "feather" or "quill", referencing the family's role as scribes in Berneck. In 1544, Ulrich Federer served as the Ammann of Berneck for the Prince-Abbots of St. Gallen. Sebastian Federer served as Ammann in 1665. The Federer famil ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ferdinand Hoefer
Jean Chrétien Ferdinand Hoefer (German: ''Ferdinand Höfer'', 21 April 1811, Döschnitz – 4 May 1878) was a German-French physician and lexicographer. He is now known for his many works on the history of science. Selected works *''Éléments de chimie générale'' (1841) *''Histoire de la chimie''Volume 1 (1842–43) * Dictionnaire de chimie et de physique ' (1846) *''Dictionnaire de médecine pratique'' (1847) * Afrique australe ... Afrique orientale ... Afrique centrale ... Empire de Maroc ' (Pa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nouvelle Biographie Générale
The ''Nouvelle Biographie Générale''Its full title was ''Nouvelle Biographie Générale, depuis les temps les plus reculés jusqu'a nos jours, avec les renseignements bibliographiques et l'indication des sources a consulter'' ("New General Biography, from earliest times to the present, with bibliographic information and details of sources to consult"). ("New General Biography"), was a 46-volume, French-language, biographical reference work, compiled between 1852 and 1866 by Ferdinand Hoefer, French physician and lexicographer. The first nine volumes were entitled ''Nouvelle Biographie Universelle'' ("New Universal Biography"). Notes External links The volumes of the ''Nouvelle Biographie Générale'' (pub. Firmin Didot fréres etc.) in various file formats in the Internet Archive The Internet Archive is an American digital library with the stated mission of "universal access to all knowledge". It provides free public access to collections of digitized materials, incl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Basel
, french: link=no, Bâlois(e), it, Basilese , neighboring_municipalities= Allschwil (BL), Hégenheim (FR-68), Binningen (BL), Birsfelden (BL), Bottmingen (BL), Huningue (FR-68), Münchenstein (BL), Muttenz (BL), Reinach (BL), Riehen (BS), Saint-Louis (FR-68), Weil am Rhein (DE-BW) , twintowns = Shanghai, Miami Beach , website = www.bs.ch Basel ( , ), also known as Basle ( ),french: Bâle ; it, Basilea ; rm, label= Sutsilvan, Basileia; other rm, Basilea . is a city in northwestern Switzerland on the river Rhine. Basel is Switzerland's third-most-populous city (after Zürich and Geneva) with about 175,000 inhabitants. The official language of Basel is (the Swiss variety of Standard) German, but the main spoken language is the local Basel German dialect. Basel is commonly considered to be the cultural capital of Switzerland and the city is famous for its many museums, including the Kunstmuseum, which is the first collection of art accessibl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gustav IV Adolf Of Sweden
Gustav IV Adolf or Gustav IV Adolph (1 November 1778 – 7 February 1837) was King of Sweden from 1792 until he was deposed in a coup in 1809. He was also the last Swedish monarch to be the ruler of Finland. The occupation of Finland in 1808–09 by Russian forces was the immediate cause of Gustav's violent overthrow by officers of his own army. Following his abdication on 29 March 1809, an Instrument of Government was hastily written, which severely circumscribed the powers of the monarchy. The "Instrument" was adopted in 1809 on 6 June, the National Day of Sweden now as well as in his time. It remained in force until replaced in 1974. The crown, now with strictly limited powers, passed to Gustav's uncle Charles XIII, who had no legitimate children; this want of heirs set into motion the quest for a successor, who was found the following year in the person of Jean-Baptiste Jules Bernadotte, the first monarch of the present royal family. ch 37 pp 203-19 Early life Gustav Adolf w ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |