|
Swish Function
The swish function is a family of mathematical function defined as follows: : \operatorname_\beta(x) = x \operatorname(\beta x) = \frac. where \beta can be constant (usually set to 1) or trainable and "sigmoid" refers to the logistic function. The swish family was designed to smoothly interpolate between a linear function and the ReLU function. When considering positive values, Swish is a particular case of doubly parameterized sigmoid shrinkage function defined in . Variants of the swish function include Mish. Special values For β = 0, the function is linear: f(''x'') = ''x''/2. For β = 1, the function is the Sigmoid Linear Unit (SiLU). With β → ∞, the function converges to ReLU. Thus, the swish family smoothly interpolates between a linear function and the ReLU function. Since \operatorname_\beta(x) = \operatorname_1(\beta x) / \beta, all instances of swish have the same shape as the default \operatorname_1 , zoomed by \beta . ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Function (mathematics)
In mathematics, a function from a set (mathematics), set to a set assigns to each element of exactly one element of .; the words ''map'', ''mapping'', ''transformation'', ''correspondence'', and ''operator'' are sometimes used synonymously. The set is called the Domain of a function, domain of the function and the set is called the codomain of the function. Functions were originally the idealization of how a varying quantity depends on another quantity. For example, the position of a planet is a ''function'' of time. History of the function concept, Historically, the concept was elaborated with the infinitesimal calculus at the end of the 17th century, and, until the 19th century, the functions that were considered were differentiable function, differentiable (that is, they had a high degree of regularity). The concept of a function was formalized at the end of the 19th century in terms of set theory, and this greatly increased the possible applications of the concept. A f ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
ImageNet
The ImageNet project is a large visual database designed for use in Outline of object recognition, visual object recognition software research. More than 14 million images have been hand-annotated by the project to indicate what objects are pictured and in at least one million of the images, bounding boxes are also provided. ImageNet contains more than 20,000 categories, with a typical category, such as "balloon" or "strawberry", consisting of several hundred images. The database of annotations of third-party image URLs is freely available directly from ImageNet, though the actual images are not owned by ImageNet. Since 2010, the ImageNet project runs an annual software contest, the ImageNet Large Scale Visual Recognition Challenge (#History_of_the_ImageNet_challenge, ILSVRC), where software programs compete to correctly classify and detect objects and scenes. The challenge uses a "trimmed" list of one thousand non-overlapping classes. History AI researcher Fei-Fei Li began working ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Gating Mechanism
In neural networks, the gating mechanism is an architectural motif for controlling the flow of activation and gradient signals. They are most prominently used in recurrent neural networks (RNNs), but have also found applications in other architectures. RNNs Gating mechanisms are the centerpiece of long short-term memory (LSTM). They were proposed to mitigate the vanishing gradient problem often encountered by regular RNNs. An LSTM unit contains three gates: * An input gate, which controls the flow of new information into the memory cell * A forget gate, which controls how much information is retained from the previous time step * An output gate, which controls how much information is passed to the next layer. The equations for LSTM are: \begin \mathbf_t &= \sigma(\mathbf_t \mathbf_ + \mathbf_ \mathbf_ + \mathbf_i) \\ \mathbf_t &= \sigma(\mathbf_t \mathbf_ + \mathbf_ \mathbf_ + \mathbf_f) \\ \mathbf_t &= \sigma(\mathbf_t \mathbf_ + \mathbf_ \mathbf_ + \mathbf_o) \\ \tilde ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Activation Function
The activation function of a node in an artificial neural network is a function that calculates the output of the node based on its individual inputs and their weights. Nontrivial problems can be solved using only a few nodes if the activation function is ''nonlinear''. Modern activation functions include the logistic ( sigmoid) function used in the 2012 speech recognition model developed by Hinton et al; the ReLU used in the 2012 AlexNet computer vision model and in the 2015 ResNet model; and the smooth version of the ReLU, the GELU, which was used in the 2018 BERT model. Comparison of activation functions Aside from their empirical performance, activation functions also have different mathematical properties: ; Nonlinear: When the activation function is non-linear, then a two-layer neural network can be proven to be a universal function approximator. This is known as the Universal Approximation Theorem. The identity activation function does not satisfy this property. W ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Backpropagation
In machine learning, backpropagation is a gradient computation method commonly used for training a neural network to compute its parameter updates. It is an efficient application of the chain rule to neural networks. Backpropagation computes the gradient of a loss function with respect to the weights of the network for a single input–output example, and does so efficiently, computing the gradient one layer at a time, iterating backward from the last layer to avoid redundant calculations of intermediate terms in the chain rule; this can be derived through dynamic programming. Strictly speaking, the term ''backpropagation'' refers only to an algorithm for efficiently computing the gradient, not how the gradient is used; but the term is often used loosely to refer to the entire learning algorithm – including how the gradient is used, such as by stochastic gradient descent, or as an intermediate step in a more complicated optimizer, such as Adaptive Moment Estimation. The ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Vanishing Gradient Problem
In machine learning, the vanishing gradient problem is the problem of greatly diverging gradient magnitudes between earlier and later layers encountered when training neural networks with backpropagation. In such methods, neural network weights are updated proportional to their partial derivative of the loss function. As the number of forward propagation steps in a network increases, for instance due to greater network depth, the gradients of earlier weights are calculated with increasingly many multiplications. These multiplications shrink the gradient magnitude. Consequently, the gradients of earlier weights will be exponentially smaller than the gradients of later weights. This difference in gradient magnitude might introduce instability in the training process, slow it, or halt it entirely. For instance, consider the hyperbolic tangent activation function. The gradients of this function are in range . The product of repeated multiplication with such gradients decreases exponent ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
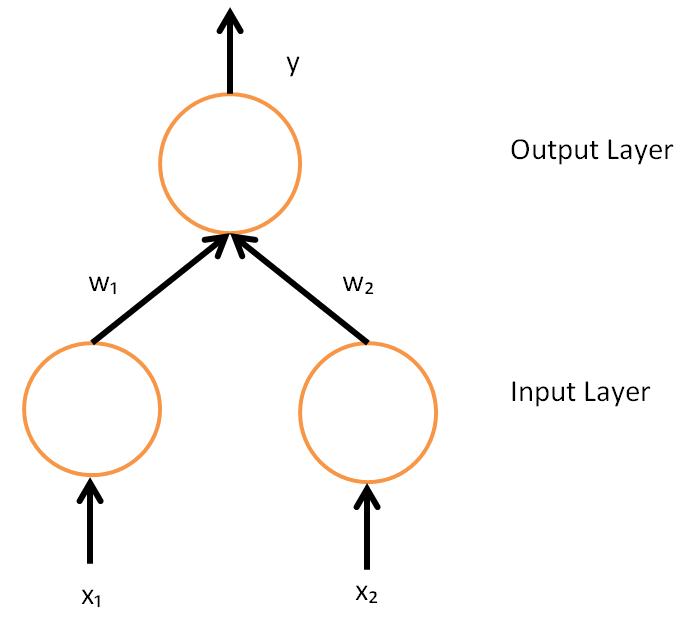
Artificial Neural Network
In machine learning, a neural network (also artificial neural network or neural net, abbreviated ANN or NN) is a computational model inspired by the structure and functions of biological neural networks. A neural network consists of connected units or nodes called '' artificial neurons'', which loosely model the neurons in the brain. Artificial neuron models that mimic biological neurons more closely have also been recently investigated and shown to significantly improve performance. These are connected by ''edges'', which model the synapses in the brain. Each artificial neuron receives signals from connected neurons, then processes them and sends a signal to other connected neurons. The "signal" is a real number, and the output of each neuron is computed by some non-linear function of the sum of its inputs, called the '' activation function''. The strength of the signal at each connection is determined by a ''weight'', which adjusts during the learning process. Typically, ne ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Activation Function
The activation function of a node in an artificial neural network is a function that calculates the output of the node based on its individual inputs and their weights. Nontrivial problems can be solved using only a few nodes if the activation function is ''nonlinear''. Modern activation functions include the logistic ( sigmoid) function used in the 2012 speech recognition model developed by Hinton et al; the ReLU used in the 2012 AlexNet computer vision model and in the 2015 ResNet model; and the smooth version of the ReLU, the GELU, which was used in the 2018 BERT model. Comparison of activation functions Aside from their empirical performance, activation functions also have different mathematical properties: ; Nonlinear: When the activation function is non-linear, then a two-layer neural network can be proven to be a universal function approximator. This is known as the Universal Approximation Theorem. The identity activation function does not satisfy this property. W ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Google
Google LLC (, ) is an American multinational corporation and technology company focusing on online advertising, search engine technology, cloud computing, computer software, quantum computing, e-commerce, consumer electronics, and artificial intelligence (AI). It has been referred to as "the most powerful company in the world" by the BBC and is one of the world's List of most valuable brands, most valuable brands. Google's parent company, Alphabet Inc., is one of the five Big Tech companies alongside Amazon (company), Amazon, Apple Inc., Apple, Meta Platforms, Meta, and Microsoft. Google was founded on September 4, 1998, by American computer scientists Larry Page and Sergey Brin. Together, they own about 14% of its publicly listed shares and control 56% of its stockholder voting power through super-voting stock. The company went public company, public via an initial public offering (IPO) in 2004. In 2015, Google was reorganized as a wholly owned subsidiary of Alphabet Inc. Go ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Reinforcement Learning
Reinforcement learning (RL) is an interdisciplinary area of machine learning and optimal control concerned with how an intelligent agent should take actions in a dynamic environment in order to maximize a reward signal. Reinforcement learning is one of the three basic machine learning paradigms, alongside supervised learning and unsupervised learning. Reinforcement learning differs from supervised learning in not needing labelled input-output pairs to be presented, and in not needing sub-optimal actions to be explicitly corrected. Instead, the focus is on finding a balance between exploration (of uncharted territory) and exploitation (of current knowledge) with the goal of maximizing the cumulative reward (the feedback of which might be incomplete or delayed). The search for this balance is known as the exploration–exploitation dilemma. The environment is typically stated in the form of a Markov decision process (MDP), as many reinforcement learning algorithms use dyn ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Swish
Swish may refer to: Games * Swish, a basketball shot that goes through the basket without touching the rim or backboard *Swish, a form of table tennis that can be played both by people who are blind or vision impaired and by people who are sighted Music * Swish (band), an indie rock band established in 1996 *Swish (hip hop producer), an American hip hop producer/rapper * ''Swish'' (album), an album by Joywave *''SWISH'', the former name of the Christian rock band Hawk Nelson *''Swish'', the second title for ''The Life of Pablo'', a 2016 album by Kanye West *"Swish", a song by Kid Ink from the EP '' 7 Series'' * "Swish" (song), a 2018 song by Tyga Software *Swish (payment), a mobile phone payment system in Sweden *SWiSH Max, software used to create cross-platform presentations *SWISH-E, software to index collections of documents People *Bill Nicholson (baseball) of the Chicago Cubs (1914–1996) *Nick Swisher of the New York Yankees (born 1980) Others *Swish cymbal, a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Rectifier (neural Networks)
In the context of Neural network (machine learning), artificial neural networks, the rectifier or ReLU (rectified linear unit) activation function is an activation function defined as the non-negative part of its argument, i.e., the ramp function: :\operatorname(x) = x^+ = \max(0, x) = \frac = \begin x & \text x > 0, \\ 0 & x \le 0 \end where x is the input to a Artificial neuron, neuron. This is analogous to half-wave rectification in electrical engineering. ReLU is one of the most popular activation functions for artificial neural networks, and finds application in computer vision and speech recognitionAndrew L. Maas, Awni Y. Hannun, Andrew Y. Ng (2014)Rectifier Nonlinearities Improve Neural Network Acoustic Models using Deep learning, deep neural nets and computational neuroscience. History The ReLU was first used by Alston Scott Householder, Alston Householder in 1941 as a mathematical abstraction of biological neural networks. Kunihiko Fukushima in 1969 used R ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |