|
Swingnose Crossing
A swingnose crossing or moveable point frog is a device used at a railway turnout to eliminate the gap at the common crossing (a.k.a. frog) which can cause damage and noise. Fixed crossing On a fixed railway crossing, the wheels need only drift by a small angle, say 1 in 20, before the vehicle may start to go in the wrong direction at the V of a V-crossing. This problem can limit the maximum speed of vehicles using the crossing. In addition, the open gap at a fixed V-crossing forms a weak point on the railway line where the heavily loaded wheel must bump across the resulting gap of about 10 cm, supported only by the portion of the wheel tread which is on the wing rail. This pounds the rail so much that the steel can deform and/or wear away. This damage may easily spread to other components including the wheels, and the noise can be a nuisance. Scheduling repair of damage can also be a problem in high traffic locations. Swingnose crossings virtually eliminate the gap ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Railroad Switch
A railroad switch (), turnout, or ''set ofpoints () is a mechanical installation enabling railway trains to be guided from one track to another, such as at a railway junction or where a spur or siding branches off. The most common type of switch consists of a pair of linked tapering rails, known as ''points'' (''switch rails'' or ''point blades''), lying between the diverging outer rails (the ''stock rails''). These points can be moved laterally into one of two positions to direct a train coming from the point blades toward the straight path or the diverging path. A train moving from the narrow end toward the point blades (i.e. it will be directed to one of the two paths, depending on the position of the points) is said to be executing a ''facing-point movement''. For many types of switch, a train coming from either of the converging directions will pass through the switch regardless of the position of the points, as the vehicle's wheels will force the points to move. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Swingnose Crossing Straight
A swingnose crossing or moveable point frog is a device used at a railway turnout to eliminate the gap at the common crossing (a.k.a. frog) which can cause damage and noise. Fixed crossing On a fixed railway crossing, the wheels need only drift by a small angle, say 1 in 20, before the vehicle may start to go in the wrong direction at the V of a V-crossing. This problem can limit the maximum speed of vehicles using the crossing. In addition, the open gap at a fixed V-crossing forms a weak point on the railway line where the heavily loaded wheel must bump across the resulting gap of about 10 cm, supported only by the portion of the wheel tread which is on the wing rail. This pounds the rail so much that the steel can deform and/or wear away. This damage may easily spread to other components including the wheels, and the noise can be a nuisance. Scheduling repair of damage can also be a problem in high traffic locations. Swingnose crossings virtually eliminate the gap ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Swingnose Crossing Curved
A swingnose crossing or moveable point frog is a device used at a railway turnout to eliminate the gap at the common crossing (a.k.a. frog) which can cause damage and noise. Fixed crossing On a fixed railway crossing, the wheels need only drift by a small angle, say 1 in 20, before the vehicle may start to go in the wrong direction at the V of a V-crossing. This problem can limit the maximum speed of vehicles using the crossing. In addition, the open gap at a fixed V-crossing forms a weak point on the railway line where the heavily loaded wheel must bump across the resulting gap of about 10 cm, supported only by the portion of the wheel tread which is on the wing rail. This pounds the rail so much that the steel can deform and/or wear away. This damage may easily spread to other components including the wheels, and the noise can be a nuisance. Scheduling repair of damage can also be a problem in high traffic locations. Swingnose crossings virtually eliminate the gap ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Heavy Rail
Various terms are used for passenger railway lines and equipment; the usage of these terms differs substantially between areas: Rapid transit A rapid transit system is an electric railway characterized by high speed (~) and rapid acceleration. It uses passenger railcars operating singly or in multiple unit trains on fixed rails. It operates on separate rights-of-way from which all other vehicular and foot traffic are excluded (i.e. is fully grade-separated from other traffic). It uses sophisticated signaling systems, and high platform loading. Originally, the term ''rapid transit'' was used in the 1800s to describe new forms of quick urban public transportation that had a right-of-way separated from street traffic. This set rapid transit apart from horsecars, trams, streetcars, omnibuses, and other forms of public transport. A variant of the term, ''mass rapid transit (MRT)'', is also used for metro systems in Southeast Asia and Taiwan. Though the term was almost alway ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
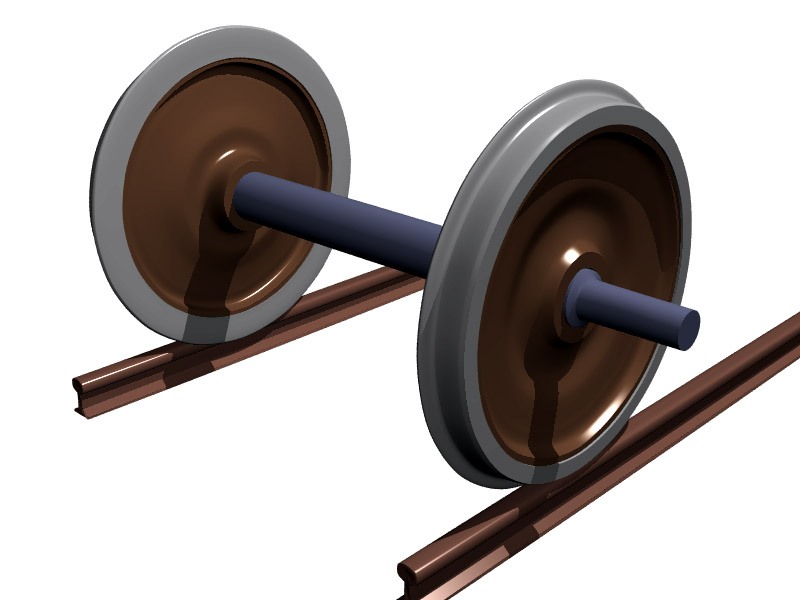
Axle Load
An axle or axletree is a central shaft for a rotating wheel or gear. On wheeled vehicles, the axle may be fixed to the wheels, rotating with them, or fixed to the vehicle, with the wheels rotating around the axle. In the former case, bearings or bushings are provided at the mounting points where the axle is supported. In the latter case, a bearing or bushing sits inside a central hole in the wheel to allow the wheel or gear to rotate around the axle. Sometimes, especially on bicycles, the latter type axle is referred to as a ''spindle''. Terminology On cars and trucks, several senses of the word ''axle'' occur in casual usage, referring to the shaft itself, its housing, or simply any transverse pair of wheels. Strictly speaking, a shaft which rotates with the wheel, being either bolted or splined in fixed relation to it, is called an ''axle'' or ''axle shaft''. However, in looser usage, an entire assembly including the surrounding axle housing (typically a casting) is als ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tonne
The tonne ( or ; symbol: t) is a unit of mass equal to 1000 kilograms. It is a non-SI unit accepted for use with SI. It is also referred to as a metric ton to distinguish it from the non-metric units of the short ton ( United States customary units), and the long ton ( British imperial units). It is equivalent to approximately 2204.6 pounds, 1.102 short tons, and 0.984 long tons. The official SI unit is the megagram (symbol: Mg), a less common way to express the same mass. Symbol and abbreviations The BIPM symbol for the tonne is t, adopted at the same time as the unit in 1879.Table 6 . BIPM. Retrieved on 2011-07-10. Its use is also official for the metric ton in the United States, having been adopted by the United States |
Point Motor
A point machine (also known as a point motor, switch machine or switch motor) is a device for operating railway turnouts especially at a distance. Overview In the earliest times, points were operated manually by levers. Gradually, these were centralized and came to be operated from a signal box, either by rods, or by double wire arrangements. Since the limitation of mechanical operation restricted the design of track layouts on the one hand, and tended to require more signal boxes, even lightly used ones, on the other hand, there has always been a desire of railway administrations to increase the distance that remote turnouts can be operated. This requires some kind of power operation of points and signals. The principal means of power operation include hydraulic, pneumatic and electric. More recently with the increase in weight of rail, and the introduction of high speed turnouts with finer angles requiring multiple drives, points have become stiffer and beyond the capabili ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Switched Diamond
A double junction is a railway junction where a double-track railway splits into two double track lines. Usually, one line is the main line and carries traffic through the junction at normal speed, while the other track is a branch line that carries traffic through the junction at reduced speed. A number of configurations are possible. At grade Diamond The simplest and oldest arrangement consists of two turnouts (points) and a fixed Diamond crossing. Because the diamond needs to be relatively coarse, say 1 in 8, the curve radius is necessarily small, leading to a speed of perhaps . This type of junction is common on street-running tramways, where speeds are quite low and junction must fit into the available road space. Because the points are close together, the entire junction can be controlled by the mechanical point rodding of a single signal box. Signal passed at danger (SPAD) protection — A train from R to P with 12 points reverse is protected from a train fr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |