|
Swing Producer
A swing producer or swing supplier is a supplier or a close oligopolistic group of suppliers of any commodity, controlling its global deposits and possessing large spare production capacity. A swing producer is able to increase or decrease commodity supply at minimal additional internal cost, and thus able to influence prices and balance the markets, providing downside protection in the short to middle term. Examples of swing producers include Saudi Arabia in oil, Russia in potash fertilizers, and, historically, the De Beers Company in diamonds. Modes By modeling the swing producer behavior, John Morecroft describes two modes: normal swing mode and punitive mode. Usually in the normal mode, the swing producer responds to market price fluctuations by marginally increasing or decreasing its output in order to maintain stable prices for all producers. However, independent participants can take unjust advantage of the reduced supply and increase their output in order to win a larger ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Oligopoly
An oligopoly () is a market in which pricing control lies in the hands of a few sellers. As a result of their significant market power, firms in oligopolistic markets can influence prices through manipulating the supply function. Firms in an oligopoly are mutually interdependent, as any action by one firm is expected to affect other firms in the market and evoke a reaction or consequential action. As a result, firms in oligopolistic markets often resort to collusion as means of maximising profits. Nonetheless, in the presence of fierce competition among market participants, oligopolies may develop without collusion. This is a situation similar to perfect competition, where oligopolists have their own market structure. In this situation, each company in the oligopoly has a large share in the industry and plays a pivotal, unique role. Many jurisdictions deem collusion to be illegal as it violates competition laws and is regarded as anti-competition behaviour. The EU com ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Commodity
In economics, a commodity is an economic goods, good, usually a resource, that specifically has full or substantial fungibility: that is, the Market (economics), market treats instances of the good as equivalent or nearly so with no regard to who Production (economics), produced them. The price of a commodity good is typically determined as a function of its market as a whole: well-established physical commodities have actively traded spot market, spot and derivative (finance), derivative markets. The wide availability of commodities typically leads to smaller profit margins and diminishes the importance of factors (such as brand, brand name) other than price. Most commodities are raw materials, basic resources, agriculture, agricultural, or mining products, such as iron ore, sugar, or grains like rice and wheat. Commodities can also be mass-produced unspecialized products such as chemical substance, chemicals and computer memory. Popular commodities include Petroleum, crude ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Saudi Arabia
Saudi Arabia, officially the Kingdom of Saudi Arabia (KSA), is a country in West Asia. Located in the centre of the Middle East, it covers the bulk of the Arabian Peninsula and has a land area of about , making it the List of Asian countries by area, fifth-largest country in Asia, the largest in the Middle East, and the List of countries and dependencies by area, 12th-largest in the world. It is bordered by the Red Sea to the west; Jordan, Iraq, and Kuwait to the north; the Persian Gulf, Bahrain, Qatar and the United Arab Emirates to the east; Oman to the southeast; and Yemen to Saudi Arabia–Yemen border, the south. The Gulf of Aqaba in the northwest separates Saudi Arabia from Egypt and Israel. Saudi Arabia is the only country with a coastline along both the Red Sea and the Persian Gulf, and most of Geography of Saudi Arabia, its terrain consists of Arabian Desert, arid desert, lowland, steppe, and List of mountains in Saudi Arabia, mountains. The capital and List of cities ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Russia
Russia, or the Russian Federation, is a country spanning Eastern Europe and North Asia. It is the list of countries and dependencies by area, largest country in the world, and extends across Time in Russia, eleven time zones, sharing Borders of Russia, land borders with fourteen countries. Russia is the List of European countries by population, most populous country in Europe and the List of countries and dependencies by population, ninth-most populous country in the world. It is a Urbanization by sovereign state, highly urbanised country, with sixteen of its urban areas having more than 1 million inhabitants. Moscow, the List of metropolitan areas in Europe, most populous metropolitan area in Europe, is the capital and List of cities and towns in Russia by population, largest city of Russia, while Saint Petersburg is its second-largest city and Society and culture in Saint Petersburg, cultural centre. Human settlement on the territory of modern Russia dates back to the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Potash
Potash ( ) includes various mined and manufactured salts that contain potassium in water- soluble form.Potash , USGS 2008 Minerals Yearbook The name derives from ''pot ash'', plant ashes or soaked in water in a pot, the primary means of manufacturing potash before the Industrial Era. The word '''' is derived from ''potash''. Potash is produced worldwide in amounts exceeding 71.9 million |
De Beers
The De Beers Group is a South African–British corporation that specializes in the diamond industry, including mining, exploitation, retail, inscription, grading, trading and industrial diamond manufacturing. The company is active in open-pit, underground, large-scale alluvial and coastal mining. It operates in 35 countries, with mining taking place in Botswana, Namibia, South Africa, and Canada. It also has an artisanal mining business, Gemfair, which operates in Sierra Leone. From its inception in 1888 until the start of the 21st century, De Beers controlled 80% to 85% of rough diamond distribution and was considered a monopoly. By 2000, the company's control of the world diamond supply decreased to 63%. The company was founded in 1888 by British businessman Cecil Rhodes, who was financed by the South African diamond magnate Alfred Beit and the London-based N M Rothschild & Sons bank. In 1926, Ernest Oppenheimer, a German immigrant to Britain and later South Africa who ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Diamond
Diamond is a Allotropes of carbon, solid form of the element carbon with its atoms arranged in a crystal structure called diamond cubic. Diamond is tasteless, odourless, strong, brittle solid, colourless in pure form, a poor conductor of electricity, and insoluble in water. Another solid form of carbon known as graphite is the Chemical stability, chemically stable form of carbon at Standard temperature and pressure, room temperature and pressure, but diamond is metastable and converts to it at a negligible rate under those conditions. Diamond has the highest Scratch hardness, hardness and thermal conductivity of any natural material, properties that are used in major industrial applications such as cutting and polishing tools. Because the arrangement of atoms in diamond is extremely rigid, few types of impurity can contaminate it (two exceptions are boron and nitrogen). Small numbers of lattice defect, defects or impurities (about one per million of lattice atoms) can color ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
System Dynamics Society
The System Dynamics Society is an international, nonprofit organization formed in 1983. History The society was formed in 1983 through resolution passed by 120 delegates naming Jay Forrester as the first president. The activity of the society has thereafter continued both to hold an international, annual conference and to sponsor publications of research in the area. Governance The society is structured intofficers and policy council members standing committees and Home office teams. List of presidents of the System Dynamics Society * 2023 - Shayne Gary – University of New South Wales - Australia * 2022 - J. Bradley Morrison – Brandeis University - United States of America * 2021 - Paulo Gonclaves - University of Lugano, Switzerland * 2020 - Birgit Kopainsky - University of Bergen, Norway * 2019 - Martin F. G. Schaffernicht – Universidad de Talca, Chile * 2018 - I. Martínez-Moyano – Argonne National Laboratory, United States of America * 2017 - Leonard Malczynski ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
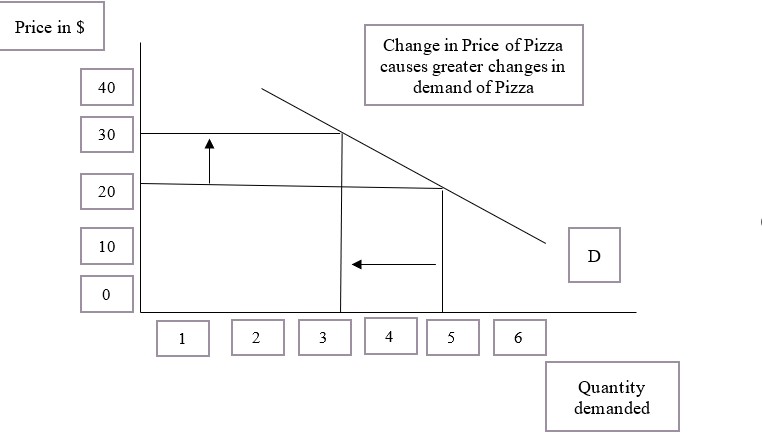
Elasticity (economics)
In economics, elasticity measures the responsiveness of one economic variable to a change in another. For example, if the price elasticity of the demand of a good is −2, then a 10% increase in price will cause the quantity demanded to fall by 20%. Elasticity in economics provides an understanding of changes in the behavior of the buyers and sellers with price changes. There are two types of elasticity for demand and supply, one is inelastic demand and supply and the other one is elastic demand and supply. Introduction The concept of price elasticity was first cited in an informal form in the book ''Principles of Economics (Marshall book), Principles of Economics'' published by the author Alfred Marshall in 1890. Subsequently, a major study of the price elasticity of supply and the price elasticity of demand for US products was undertaken by Joshua Levy and Trevor Pollock in the late 1960s. Elasticity is an important concept in neoclassical economic theory, and enables in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Peak Oil
Peak oil is the point when global oil production reaches its maximum rate, after which it will begin to decline irreversibly. The main concern is that global transportation relies heavily on gasoline and diesel. Adoption of electric vehicles, biofuels, or more efficient transport (like trains and waterways) could help reduce oil demand. Peak oil relates closely to oil depletion; while petroleum reserves are finite, the key issue is the economic viability of extraction at current prices. Initially, it was believed that oil production would decline due to reserve depletion, but a new theory suggests that reduced oil demand could lower prices, affecting extraction costs. Demand may also decline due to persistent high prices. Over the last century, many predictions of peak oil timing have been made, often later proven incorrect due to increased extraction rates. M. King Hubbert introduced the concept in a 1956 paper, predicting U.S. production would peak between 1965 and 1 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
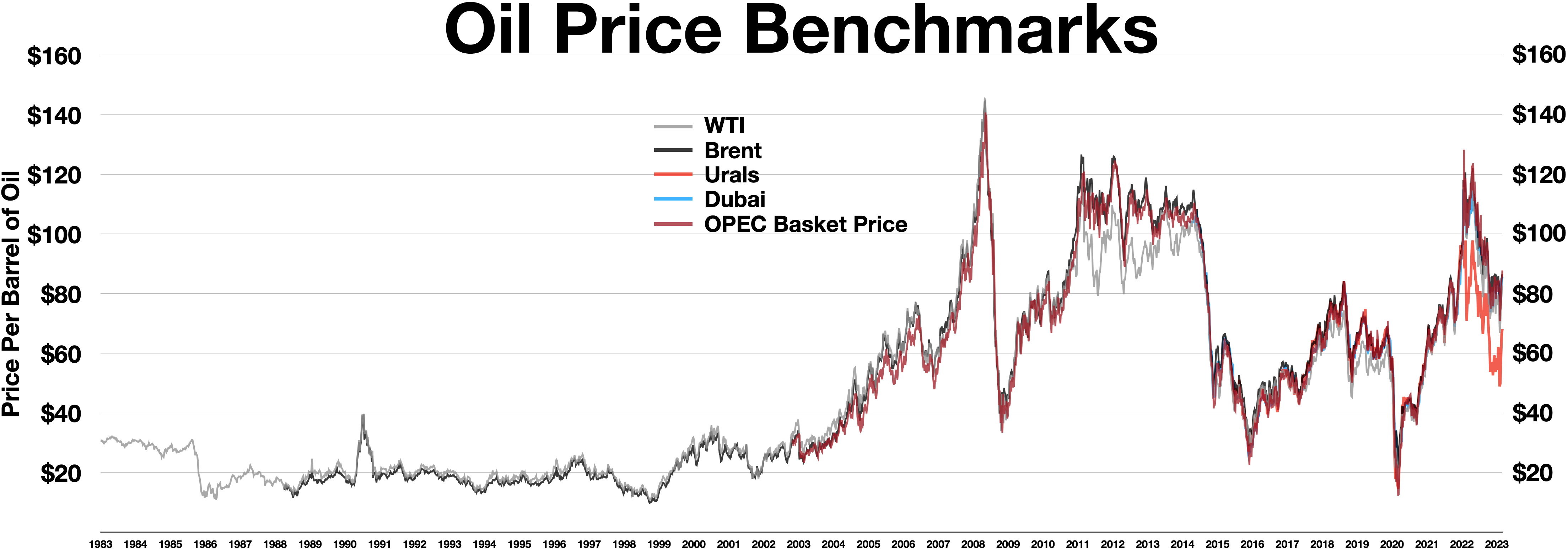
Price Of Petroleum
The price of oil, or the oil price, generally refers to the spot price of a barrel () of benchmark crude oil—a reference price for buyers and sellers of crude oil such as West Texas Intermediate (WTI), Brent Crude, Dubai Crude, OPEC Reference Basket, Tapis crude, Bonny Light, Urals oil, Isthmus, and Western Canadian Select (WCS). Oil prices are determined by global supply and demand, rather than any country's domestic production level. Through the years The global price of crude oil was relatively consistent in the nineteenth century and early twentieth century. This changed in the 1970s, with a significant increase in the price of oil globally. There have been a number of structural drivers of global oil prices historically, including oil supply, demand, and storage shocks, and shocks to global economic growth affecting oil prices. Notable events driving significant price fluctuations include the 1973 OPEC oil embargo targeting nations that had supported Israel d ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Commodity Markets
A commodity market is a market that trades in the primary economic sector rather than manufactured products. The primary sector includes agricultural products, energy products, and metals. Soft commodities may be perishable and harvested, while hard commodities are usually mined, such as gold and oil. Futures contracts are the oldest way of investing in commodities. Commodity markets can include physical trading and derivatives trading using spot prices, forwards, futures, and options on futures. Farmers have used a simple form of derivative trading in the commodities market for centuries for price risk management. A financial derivative is a financial instrument whose value is derived from a commodity termed an underlier. Derivatives are either exchange-traded or over-the-counter (OTC). An increasing number of derivatives are traded via clearing houses some with central counterparty clearing, which provide clearing and settlement services on a futures exchange, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |